- Sodium-hydrogen antiporter 3 regulator 1
-
Sodium-hydrogen antiporter 3 regulator 1 is a regulator of Sodium-hydrogen antiporter 3. It is encoded by the gene SLC9A3R1. It is also known as ERM Binding Protein 50 (EBP50) or Na+/H+ Exchanger Regulatory Factor (NHERF1). It is believed[1] to interact via long-range allostery, involving significant protein dynamics.
Contents
Mechanism
Members of the ezrin (VIL2; MIM 123900)-radixin (RDX; MIM 179410)-moesin (MSN; MIM 309845) (ERM) protein family are highly concentrated in the apical aspect of polarized epithelial cells. These cells are studded with microvilli containing bundles of actin filaments, which must attach to the membrane to assemble and maintain the microvilli. The ERM proteins, together with merlin, the NF2 (MIM 607379) gene product, are thought to be linkers between integral membrane and cytoskeletal proteins, and they bind directly to actin in vitro. Actin cytoskeleton reorganization requires the activation of a sodium/hydrogen exchanger (SLC9A3; MIM 182307). SLC9A3R1 is an ERM-binding protein.[supplied by OMIM][2]
Interactions
Sodium-hydrogen antiporter 3 regulator 1 has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin,[3] GNAQ,[4] Kappa Opioid receptor,[5][6] SLC4A8,[7][8] Beta-2 adrenergic receptor,[9][10][11] PDZK1,[12] YAP1,[13] Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator,[8][10][14][15][16][17][18] PAG1,[19] PDGFRB,[20] Parathyroid hormone receptor 1,[21] EZR[19][22] and PDGFRA.[20]
See also
References
- ^ B. Farago, Li J, Cornilescu G, Callaway DJE, Bu Z (November 2010). "Activation of Nanoscale Allosteric Protein Domain Motion Revealed by Neutron Spin Echo Spectroscopy". Biophysical Journal 99 (10): 3473–3482. Bibcode 2010BpJ....99.3473F. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2010.09.058. PMC 2980739. PMID 21081097. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0006-3495(10)01208-7.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: SLC9A3R1 solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 3 regulator 1". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=9368.
- ^ Shibata, Tatsuhiro; Chuma Makoto, Kokubu Akiko, Sakamoto Michiie, Hirohashi Setsuo (Jul. 2003). "EBP50, a beta-catenin-associating protein, enhances Wnt signaling and is over-expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma". Hepatology (United States) 38 (1): 178–86. doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50270. ISSN 0270-9139. PMID 12830000.
- ^ Rochdi, Moulay Driss; Watier Valérie, La Madeleine Carole, Nakata Hiroko, Kozasa Tohru, Parent Jean-Luc (Oct. 2002). "Regulation of GTP-binding protein alpha q (Galpha q) signaling by the ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein-50 (EBP50)". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (43): 40751–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207910200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12193606.
- ^ Huang, Peng; Steplock Deborah, Weinman Edward J, Hall Randy A, Ding Zhe, Li Jianguo, Wang Yulin, Liu-Chen Lee-Yuan (Jun. 2004). "kappa Opioid receptor interacts with Na(+)/H(+)-exchanger regulatory factor-1/Ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein-50 (NHERF-1/EBP50) to stimulate Na(+)/H(+) exchange independent of G(i)/G(o) proteins". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 279 (24): 25002–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313366200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 15070904.
- ^ Li, Jian-Guo; Chen Chongguang, Liu-Chen Lee-Yuan (Jul. 2002). "Ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein-50/Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor (EBP50/NHERF) blocks U50,488H-induced down-regulation of the human kappa opioid receptor by enhancing its recycling rate". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (30): 27545–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.M200058200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12004055.
- ^ Pushkin, Alexander; Abuladze Natalia, Newman Debra, Muronets Vladimir, Sassani Pejvak, Tatishchev Sergei, Kurtz Ira (Mar. 2003). "The COOH termini of NBC3 and the 56-kDa H+-ATPase subunit are PDZ motifs involved in their interaction". Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. (United States) 284 (3): C667–73. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00225.2002. ISSN 0363-6143. PMID 12444018.
- ^ a b Park, Meeyoung; Ko Shigeru B H, Choi Joo Young, Muallem Gaia, Thomas Philip J, Pushkin Alexander, Lee Myeong-Sok, Kim Joo Young, Lee Min Goo, Muallem Shmuel, Kurtz Ira (Dec. 2002). "The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator interacts with and regulates the activity of the HCO3- salvage transporter human Na+-HCO3- cotransport isoform 3". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (52): 50503–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201862200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12403779.
- ^ Karthikeyan, Subramanian; Leung Teli, Ladias John A A (May. 2002). "Structural determinants of the Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor interaction with the beta 2 adrenergic and platelet-derived growth factor receptors". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (21): 18973–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201507200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11882663.
- ^ a b Hall, R A; Ostedgaard L S, Premont R T, Blitzer J T, Rahman N, Welsh M J, Lefkowitz R J (Jul. 1998). "A C-terminal motif found in the β2-adrenergic receptor, P2Y1 receptor and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator determines binding to the Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor family of PDZ proteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (UNITED STATES) 95 (15): 8496–501. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.15.8496. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 21104. PMID 9671706. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=21104.
- ^ Hall, R A; Premont R T, Chow C W, Blitzer J T, Pitcher J A, Claing A, Stoffel R H, Barak L S, Shenolikar S, Weinman E J, Grinstein S, Lefkowitz R J (Apr. 1998). "The beta2-adrenergic receptor interacts with the Na+/H+-exchanger regulatory factor to control Na+/H+ exchange". Nature (ENGLAND) 392 (6676): 626–30. doi:10.1038/33458. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 9560162.
- ^ Gisler, Serge M; Pribanic Sandra, Bacic Desa, Forrer Patrik, Gantenbein Andrea, Sabourin Luc A, Tsuji Akira, Zhao Zhuo-Shen, Manser Edward, Biber Jürg, Murer Heini (Nov. 2003). "PDZK1: I. a major scaffolder in brush borders of proximal tubular cells". Kidney Int. (United States) 64 (5): 1733–45. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00266.x. ISSN 0085-2538. PMID 14531806.
- ^ Mohler, P J; Kreda S M, Boucher R C, Sudol M, Stutts M J, Milgram S L (Nov. 1999). "Yes-Associated Protein 65 Localizes P62c-Yes to the Apical Compartment of Airway Epithelia by Association with Ebp50". J. Cell Biol. (UNITED STATES) 147 (4): 879–90. doi:10.1083/jcb.147.4.879. ISSN 0021-9525. PMC 2156157. PMID 10562288. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2156157.
- ^ Hegedüs, Tamás; Sessler Tamás, Scott Robert, Thelin William, Bakos Eva, Váradi András, Szabó Katalin, Homolya László, Milgram Sharon L, Sarkadi Balázs (Mar. 2003). "C-terminal phosphorylation of MRP2 modulates its interaction with PDZ proteins". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. (United States) 302 (3): 454–61. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00196-7. ISSN 0006-291X. PMID 12615054.
- ^ Wang, S; Raab R W, Schatz P J, Guggino W B, Li M (May. 1998). "Peptide binding consensus of the NHE-RF-PDZ1 domain matches the C-terminal sequence of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)". FEBS Lett. (NETHERLANDS) 427 (1): 103–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00402-5. ISSN 0014-5793. PMID 9613608.
- ^ Moyer, B D; Duhaime M, Shaw C, Denton J, Reynolds D, Karlson K H, Pfeiffer J, Wang S, Mickle J E, Milewski M, Cutting G R, Guggino W B, Li M, Stanton B A (Sep. 2000). "The PDZ-interacting domain of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator is required for functional expression in the apical plasma membrane". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 275 (35): 27069–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004951200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10852925.
- ^ Gentzsch, Martina; Cui Liying, Mengos April, Chang Xiu-Bao, Chen Jey-Hsin, Riordan John R (Feb. 2003). "The PDZ-binding chloride channel ClC-3B localizes to the Golgi and associates with cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-interacting PDZ proteins". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 278 (8): 6440–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211050200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12471024.
- ^ Short, D B; Trotter K W, Reczek D, Kreda S M, Bretscher A, Boucher R C, Stutts M J, Milgram S L (Jul. 1998). "An apical PDZ protein anchors the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator to the cytoskeleton". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 273 (31): 19797–801. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.31.19797. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9677412.
- ^ a b Brdicková, N; Brdicka T, Andera L, Spicka J, Angelisová P, Milgram S L, Horejsí V (Oct. 2001). "Interaction between two adapter proteins, PAG and EBP50: a possible link between membrane rafts and actin cytoskeleton". FEBS Lett. (Netherlands) 507 (2): 133–6. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02955-6. ISSN 0014-5793. PMID 11684085.
- ^ a b Maudsley, S; Zamah A M, Rahman N, Blitzer J T, Luttrell L M, Lefkowitz R J, Hall R A (Nov. 2000). "Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Association with Na+/H+ Exchanger Regulatory Factor Potentiates Receptor Activity". Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES) 20 (22): 8352–63. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.22.8352-8363.2000. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 102142. PMID 11046132. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=102142.
- ^ Mahon, Matthew J; Donowitz Mark, Yun C Chris, Segre Gino V (Jun. 2002). "Na(+)/H(+ ) exchanger regulatory factor 2 directs parathyroid hormone 1 receptor signalling". Nature (England) 417 (6891): 858–61. doi:10.1038/nature00816. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 12075354.
- ^ Reczek, D; Berryman M, Bretscher A (Oct. 1997). "Identification of EBP50: A PDZ-containing Phosphoprotein that Associates with Members of the Ezrin-Radixin-Moesin Family". J. Cell Biol. (UNITED STATES) 139 (1): 169–79. doi:10.1083/jcb.139.1.169. ISSN 0021-9525. PMC 2139813. PMID 9314537. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2139813.
Further reading
- Weinman EJ, Steplock D, Wang Y, Shenolikar S (1995). "Characterization of a protein cofactor that mediates protein kinase A regulation of the renal brush border membrane Na(+)-H+ exchanger". J. Clin. Invest. 95 (5): 2143–9. doi:10.1172/JCI117903. PMC 295815. PMID 7738182. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=295815.
- Yun CH, Oh S, Zizak M, et al. (1997). "cAMP-mediated inhibition of the epithelial brush border Na+/H+ exchanger, NHE3, requires an associated regulatory protein". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (7): 3010–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.7.3010. PMC 20313. PMID 9096337. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=20313.
- Reczek D, Berryman M, Bretscher A (1998). "Identification of EBP50: A PDZ-containing Phosphoprotein that Associates with Members of the Ezrin-Radixin-Moesin Family". J. Cell Biol. 139 (1): 169–79. doi:10.1083/jcb.139.1.169. PMC 2139813. PMID 9314537. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2139813.
- Murthy A, Gonzalez-Agosti C, Cordero E, et al. (1998). "NHE-RF, a regulatory cofactor for Na(+)-H+ exchange, is a common interactor for merlin and ERM (MERM) proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (3): 1273–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.3.1273. PMID 9430655.
- Hall RA, Premont RT, Chow CW, et al. (1998). "The beta2-adrenergic receptor interacts with the Na+/H+-exchanger regulatory factor to control Na+/H+ exchange". Nature 392 (6676): 626–30. doi:10.1038/33458. PMID 9560162.
- Wang S, Raab RW, Schatz PJ, et al. (1998). "Peptide binding consensus of the NHE-RF-PDZ1 domain matches the C-terminal sequence of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)". FEBS Lett. 427 (1): 103–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00402-5. PMID 9613608.
- Hall RA, Ostedgaard LS, Premont RT, et al. (1998). "A C-terminal motif found in the β2-adrenergic receptor, P2Y1 receptor and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator determines binding to the Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor family of PDZ proteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (15): 8496–501. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.15.8496. PMC 21104. PMID 9671706. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=21104.
- Short DB, Trotter KW, Reczek D, et al. (1998). "An apical PDZ protein anchors the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator to the cytoskeleton". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (31): 19797–801. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.31.19797. PMID 9677412.
- Hall RA, Spurney RF, Premont RT, et al. (1999). "G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6A phosphorylates the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor via a PDZ domain-mediated interaction". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (34): 24328–34. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.34.24328. PMID 10446210.
- Cao TT, Deacon HW, Reczek D, et al. (1999). "A kinase-regulated PDZ-domain interaction controls endocytic sorting of the beta2-adrenergic receptor". Nature 401 (6750): 286–90. doi:10.1038/45816. PMID 10499588.
- Mohler PJ, Kreda SM, Boucher RC, et al. (1999). "Yes-Associated Protein 65 Localizes P62c-Yes to the Apical Compartment of Airway Epithelia by Association with Ebp50". J. Cell Biol. 147 (4): 879–90. doi:10.1083/jcb.147.4.879. PMC 2156157. PMID 10562288. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2156157.
- Breton S, Wiederhold T, Marshansky V, et al. (2000). "The B1 subunit of the H+ATPase is a PDZ domain-binding protein. Colocalization with NHE-RF in renal B-intercalated cells". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (24): 18219–24. doi:10.1074/jbc.M909857199. PMID 10748165.
- Moyer BD, Duhaime M, Shaw C, et al. (2000). "The PDZ-interacting domain of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator is required for functional expression in the apical plasma membrane". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (35): 27069–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004951200. PMID 10852925.
- Tang Y, Tang J, Chen Z, et al. (2001). "Association of mammalian trp4 and phospholipase C isozymes with a PDZ domain-containing protein, NHERF". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (48): 37559–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006635200. PMID 10980202.
- Maudsley S, Zamah AM, Rahman N, et al. (2000). "Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Association with Na+/H+ Exchanger Regulatory Factor Potentiates Receptor Activity". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (22): 8352–63. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.22.8352-8363.2000. PMC 102142. PMID 11046132. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=102142.
- Gisler SM, Stagljar I, Traebert M, et al. (2001). "Interaction of the type IIa Na/Pi cotransporter with PDZ proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (12): 9206–13. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008745200. PMID 11099500.
- Reczek D, Bretscher A (2001). "Identification of Epi64, a Tbc/Rabgap Domain–Containing Microvillar Protein That Binds to the First PDZ Domain of Ebp50 and E3karp". J. Cell Biol. 153 (1): 191–206. doi:10.1083/jcb.153.1.191. PMC 2185518. PMID 11285285. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2185518.
- Karthikeyan S, Leung T, Ladias JA (2001). "Structural basis of the Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor PDZ1 interaction with the carboxyl-terminal region of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (23): 19683–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.C100154200. PMID 11304524.
- Karthikeyan S, Leung T, Birrane G, et al. (2001). "Crystal structure of the PDZ1 domain of human Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor provides insights into the mechanism of carboxyl-terminal leucine recognition by class I PDZ domains". J. Mol. Biol. 308 (5): 963–73. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4634. PMID 11352585.
- Brdicková N, Brdicka T, Andera L, et al. (2001). "Interaction between two adapter proteins, PAG and EBP50: a possible link between membrane rafts and actin cytoskeleton". FEBS Lett. 507 (2): 133–6. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02955-6. PMID 11684085.
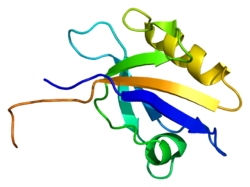
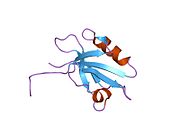
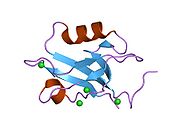
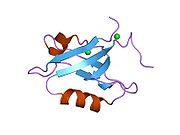
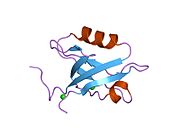
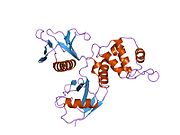
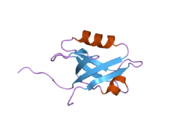
PDB gallery 1g9o: FIRST PDZ DOMAIN OF THE HUMAN NA+/H+ EXCHANGER REGULATORY FACTOR1gq4: STRUCTURAL DETERMINANTS OF THE NHERF INTERACTION WITH BETA2AR AND PDGFR1gq5: STRUCTURAL DETERMINANTS OF THE NHERF INTERACTION WITH BETA2-AR AND PDGFR1i92: STRUCTURAL BASIS OF THE NHERF PDZ1-CFTR INTERACTION1sgh: Moesin FERM domain bound to EBP50 C-terminal peptide2ozf: The crystal structure of the 2nd PDZ domain of the human NHERF-1 (SLC9A3R1)This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
By group SLC1–10 - (6) sodium- and chloride- dependent sodium:neurotransmitter symporters (SLC6A1, SLC6A2, SLC6A3, SLC6A4, SLC6A5, SLC6A6, SLC6A7, SLC6A8, SLC6A9, SLC6A10, SLC6A11, SLC6A12, SLC6A13, SLC6A14, SLC6A15, SLC6A16, SLC6A17, SLC6A18, SLC6A19, SLC6A20)
- (7) cationic amino-acid transporter/glycoprotein-associated (SLC7A1, SLC7A2, SLC7A3, SLC7A4) glycoprotein-associated/light or catalytic subunits of heterodimeric amino-acid transporters (SLC7A5, SLC7A6, SLC7A7, SLC7A8, SLC7A9, SLC7A10, SLC7A11, SLC7A13, SLC7A14)
- (8) Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (SLC8A1, SLC8A2, SLC8A3)
SLC11–20 - (12) electroneutral cation-Cl cotransporter (SLC12A1, SLC12A1, SLC12A2, SLC12A3, SLC12A4, SLC12A5, SLC12A6, SLC12A7, SLC12A8, SLC12A9)
- (14) urea transporter (SLC14A1, SLC14A2)
- (15) proton oligopeptide cotransporter (SLC15A1, SLC15A2, SLC15A3, SLC15A4)
- (16) monocarboxylate transporter (SLC16A1, SLC16A2, SLC16A3, SLC16A4, SLC16A5, SLC16A6, SLC16A7, SLC16A8, SLC16A9, SLC16A10, SLC16A11, SLC16A12, SLC16A13, SLC16A14)
SLC21–30 - (21) organic anion transporting (SLCO1A2, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3, SLCO1B4, SLCO1C1) (SLCO2A1, SLCO2B1) (SLCO3A1) (SLCO4A1, SLCO4C1) (SLCO5A1) (SLCO6A1)
- (22) organic cation/anion/zwitterion transporter (SLC22A1, SLC22A2, SLC22A3, SLC22A4, SLC22A5, SLC22A6, SLC22A7, SLC22A8, SLC22A9, SLC22A10, SLC22A11, SLC22A12, SLC22A13, SLC22A14, SLC22A15, SLC22A16, SLC22A17, SLC22A18, SLC22A19, SLC22A20)
- (24) Na+/(Ca2+-K+) exchanger (SLC24A1, SLC24A2, SLC24A3, SLC24A4, SLC24A5, SLC24A6)
- (25) mitochondrial carrier (SLC25A1, SLC25A2, SLC25A3, SLC25A4, SLC25A5, SLC25A6, SLC25A7, SLC25A8, SLC25A9, SLC25A10, SLC25A11, SLC25A12, SLC25A13, SLC25A14, SLC25A15, SLC25A16, SLC25A17, SLC25A18, SLC25A19, SLC25A20, SLC25A21, SLC25A22, SLC25A23, SLC25A24, SLC25A25, SLC25A26, SLC25A27, SLC25A28, SLC25A29, SLC25A30, SLC25A31, SLC25A32, SLC25A33, SLC25A34, SLC25A35, SLC25A36, SLC25A37, SLC25A38, SLC25A39, SLC25A40, SLC25A41, SLC25A42, SLC25A43, SLC25A44, SLC25A45, SLC25A46)
SLC31–40 - (32) vesicular inhibitory amino-acid transporter (SLC32A1)
- (33) Acetyl-CoA transporter (SLC33A1)
- (35) nucleoside-sugar transporter (SLC35A1, SLC35A2, SLC35A3, SLC35A4, SLC35A5) (SLC35B1, SLC35B2, SLC35B3, SLC35B4) (SLC35C1, SLC35C2) (SLC35D1, SLC35D2, SLC35D3) (SLC35E1, SLC35E2, SLC35E3, SLC35E4)
- (36) proton-coupled amino-acid transporter (SLC36A1, SLC36A2, SLC36A3, SLC36A4)36A2 ·
- (37) sugar-phosphate/phosphate exchanger (SLC37A1, SLC37A2, SLC37A3, SLC37A4)
- (38) System A & N, sodium-coupled neutral amino-acid transporter (SLC38A1, SLC38A2, SLC38A3, SLC38A4, SLC38A5, SLC38A6, SLC38A10)
- (39) metal ion transporter (SLC39A1, SLC39A2, SLC39A3, SLC39A4, SLC39A5, SLC39A6, SLC39A7, SLC39A8, SLC39A9, SLC39A10, SLC39A11, SLC39A12, SLC39A13, SLC39A14)
- (40) basolateral iron transporter (SLC40A1)
SLC41–48 SLCO1–4 Ion pumps see also solute carrier disorders
B memb: cead, trns (1A, 1C, 1F, 2A, 3A1, 3A2-3, 3D), othrCategories:- Human proteins
- Solute carrier family
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.