- Symmetric multiprocessing
-
In computing, symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) involves a multiprocessor computer hardware architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a single shared main memory and are controlled by a single OS instance. Most common multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture. In the case of multi-core processors, the SMP architecture applies to the cores, treating them as separate processors. Processors may be interconnected using buses, crossbar switches or on-chip mesh networks. The bottleneck in the scalability of SMP using buses or crossbar switches is the bandwidth and power consumption of the interconnect among the various processors, the memory, and the disk arrays. Mesh architectures avoid these bottlenecks, and provide nearly linear scalability to much higher processor counts at the sacrifice of programmability:
Serious programming challenges remain with this kind of architecture because it requires two distinct modes of programming, one for the CPUs themselves and one for the interconnect between the CPUs. A single programming language would have to be able to not only partition the workload, but also comprehend the memory locality, which is severe in a mesh-based architecture.[1]
A computer system that uses symmetric multiprocessing is called a symmetric multiprocessor or symmetric multiprocessor system (SMP system).[2][3] SMP systems allow any processor to work on any task no matter where the data for that task are located in memory, provided that each task in the system is not in execution on two or more processors at the same time; with proper operating system support, SMP systems can easily move tasks between processors to balance the workload efficiently.
Contents
Alternatives
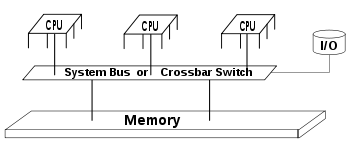 Diagram of a typical SMP system. Three processors are connected to the same memory module through a system bus or crossbar switch
Diagram of a typical SMP system. Three processors are connected to the same memory module through a system bus or crossbar switch
SMP using a single shared system bus represents one of the earliest styles of multiprocessor machine architectures, typically used for building smaller computers with up to 8 processors.
Larger computer systems might use newer architectures such as NUMA (Non-Uniform Memory Access), which dedicates different memory banks to different processors. In a NUMA architecture, processors may access local memory quickly and remote memory more slowly. This can dramatically improve memory throughput as long as the data are localized to specific processes (and thus processors). On the downside, NUMA makes the cost of moving data from one processor to another, as in workload balancing, more expensive. The benefits of NUMA are limited to particular workloads, notably on servers where the data are often associated strongly with certain tasks or users.
Finally, there is computer clustered multiprocessing (such as Beowulf), in which not all memory is available to all processors. Clustering techniques are used fairly extensively to build very large supercomputers.
In this discussion, a single processor is denoted as a uni processor (UP).
Advantages and disadvantages
SMP has many uses in science, industry, and business which often use custom-programmed software for multithreaded (multitasked) processing. However, most consumer products such as word processors and computer games are written in such a manner that they cannot gain large benefits from concurrent systems. For games this is usually because writing a program to increase performance on SMP systems can produce a performance loss on uniprocessor systems. Recently[update], however, multi-core chips are becoming more common in new computers, and the balance between installed uni- and multi-core computers may change in the coming years.
Uniprocessor and SMP systems require different programming methods to achieve maximum performance. Therefore two separate versions of the same program may have to be maintained, one for each. Programs running on SMP systems may experience a performance increase even when they have been written for uniprocessor systems. This is because hardware interrupts that usually suspend program execution while the kernel handles them can execute on an idle processor instead. The effect in most applications (e.g. games) is not so much a performance increase as the appearance that the program is running much more smoothly. In some applications, particularly compilers and some distributed computing projects, one will see an improvement by a factor of (nearly) the number of additional processors.
In situations where more than one program executes at the same time, an SMP system will have considerably better performance than a uni-processor because different programs can run on different CPUs simultaneously.
Systems programmers must build support for SMP into the operating system: otherwise, the additional processors remain idle and the system functions as a uniprocessor system.
In cases where an SMP environment processes many jobs, administrators often experience a loss of hardware efficiency. Software programs have been developed to schedule jobs so that the processor utilization reaches its maximum potential. Good software packages can achieve this maximum potential by scheduling each CPU separately, as well as being able to integrate multiple SMP machines and clusters.
Access to RAM is serialized; this and cache coherency issues causes performance to lag slightly behind the number of additional processors in the system (aga).
Entry-level systems
Before about 2006, entry-level servers and workstations with two processors dominated the SMP market. With the introduction of dual-core devices, SMP is found in most new desktop machines and in many laptop machines. The most popular entry-level SMP systems use the x86 instruction set architecture and are based on Intel’s Xeon, Pentium D, Core Duo, and Core 2 Duo based processors or AMD’s Athlon64 X2, Quad FX or Opteron 200 and 2000 series processors. Servers use those processors and other readily available non-x86 processor choices, including the Sun Microsystems UltraSPARC, Fujitsu SPARC64 III and later, SGI MIPS, Intel Itanium, Hewlett Packard PA-RISC, Hewlett-Packard (merged with Compaq which acquired first Digital Equipment Corporation) DEC Alpha, IBM POWER and Apple Computer PowerPC (specifically G4 and G5 series, as well as earlier PowerPC 604 and 604e series) processors. In all cases, these systems are available in uniprocessor versions as well.
Earlier SMP systems used motherboards that have two or more CPU sockets. More recently[update], microprocessor manufacturers introduced CPU devices with two or more processors in one device, for example, the Itanium, POWER, UltraSPARC, Opteron, Athlon, Core 2, and Xeon all have multi-core variants. Athlon and Core 2 Duo multiprocessors are socket-compatible with uniprocessor variants, so an expensive dual socket motherboard is no longer needed to implement an entry-level SMP machine. It should also be noted that dual socket Opteron designs are technically ccNUMA designs, though they can be programmed as SMP for a slight loss in performance.
Mid-level systems
The Burroughs D825 first implemented SMP in 1962.[4][5] It was implemented later on other mainframes. Mid-level servers, using between four and eight processors, can be found using the Intel Xeon MP, AMD Opteron 800 and 8000 series and the above-mentioned UltraSPARC, SPARC64, MIPS, Itanium, PA-RISC, Alpha and POWER processors. High-end systems, with sixteen or more processors, are also available with all of the above processors.
Sequent Computer Systems built large SMP machines using Intel 80386 (and later 80486) processors. Some smaller 80486 systems existed, but the major x86 SMP market began with the Intel Pentium technology supporting up to two processors. The Intel Pentium Pro expanded SMP support with up to four processors natively. Later, the Intel Pentium II, and Intel Pentium III processors allowed dual CPU systems, except for the respective Celerons. This was followed by the Intel Pentium II Xeon and Intel Pentium III Xeon processors which could be used with up to four processors in a system natively. In 2001 AMD released their Athlon MP, or MultiProcessor CPU, together with the 760MP motherboard chipset as their first offering in the dual processor marketplace. Although several much larger systems were built, they were all limited by the physical memory addressing limitation of 64 GiB. With the introduction of 64-bit memory addressing on the AMD64 Opteron in 2003 and Intel 64 (EM64T) Xeon in 2005, systems are able to address much larger amounts of memory; their addressable limitation of 16 EiB is not expected to be reached in the foreseeable future.
Operating systems running on SMP computers
- BeOS and derivatives
- BSD descendants:
- Burroughs (Unisys) MCP (1961–present)
- HP-UX
- IBM AIX
- IBM i (formerly known as i5/OS or OS/400)
- INTEGRITY
- IRIX
- LynxOS [6]
- LabVIEW Real-Time Module (version 8.5 or later)[7]
- Linux-based systems
- Mac OS (7.5.5 to 9.2.2) and Mac OS X
- The Microsoft Windows NT family (this includes Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, etc.)
- Microsoft Windows Embedded Compact (formerly known as Windows Embedded CE / Windows CE.NET / Windows CE) has added SMP support at version 7 [8]
- Nucleus RTOS
- OpenVMS (since VMS 5.0)
- OS/2 (since 2.11[9])
- OSE real-time operating system (OSE5)
- PikeOS real-time operating system for embedded systems
- Plan 9
- QNX real-time operating system (2000–present)
- Sequent DYNIX and DYNIX/ptx
- SkyOS
- Sun Solaris
- Syllable
- Tandem/HP NonStop kernel
- TOPS-10 Operating System for PDP-10 36-bit architecture (True SMP since version 7.01[10])
- UNIVAC EXEC 8 (1964–present)
- VxWorks
- z/OS
- z/TPF
- z/VM
- z/VSE
SMP-capable processors
- ARM
- ARM11 MPCore
- ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore
- ARM Cortex-A5 MPCore
- ARM Cortex-A15 MPCore
- Advanced Micro Devices (AMD)
- Athlon MP
- Athlon 64 X2
- Turion 64 X2
- AMD Opteron
- Phenom
- Phenom II
- Athlon II
- Azul Systems
- Vega 1
- Vega 2
- DEC Alpha
- Hewlett-Packard
- HP PA-RISC
- International Business Machines (IBM)
- Inmos
- INMOS transputers: T400, T800 and T9000
- Intel
- Intel 486/DX
- Intel OverDrive Processor, Socket 7; Intel OverDrive Processor, Socket 8
- Intel Pentium Pro; Intel Pentium II; Intel Pentium III
- Intel Pentium D
- Intel Core; Intel Pentium Dual-Core; Intel Core 2
- Intel Core i7
- Intel Core i5
- Intel Xeon
- Intel Itanium; Intel Itanium 2
- glueless up to four processors (max. 16 in IA-32 compatibility mode)
- Motorola/Freescale/Apple
- Sun Microsystems
- UltraSPARC The Sparkle SPARC Derivative was multi-processor capable in 1991
- SGI/MIPS
- Razamicroelectronic
- XLR
- Tilera
- Cavium Networks
- Octeon-I, II Up to 32 MIPS64 cores Soc [13]
See also
- Asymmetric Multi-Processing
- Massively Parallel Processing
- Non-Uniform Memory Access
- Simultaneous multithreading
- Sequent Computer Systems
- Software lockout
References
- ^ Lina J. Karam, Ismail AlKamal, Alan Gatherer, Gene A. Frantz, David V. Anderson, Brian L. Evans (2009). "Trends in Multi-core DSP Platforms". IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, Special Issue on Signal Processing on Platforms with Multiple Cores. http://users.ece.utexas.edu/~bevans/papers/2009/multicore/MulticoreDSPsForIEEESPMFinal.pdf.
- ^ http://publib.boulder.ibm.com/infocenter/pseries/v5r3/index.jsp?topic=/com.ibm.aix.prftungd/doc/prftungd/smp_concepts_arch.htm
- ^ http://publib.boulder.ibm.com/infocenter/idshelp/v115/index.jsp?topic=/com.ibm.glos.doc/glossaryS.htm
- ^ http://ei.cs.vt.edu/~history/Parallel.html 1962
- ^ 1964 BRL Report
- ^ [1]
- ^ Real-Time Measurement and Control
- ^ [2]
- ^ OS/2's Symmetrical Multiprocessing Demystified
- ^ http://www.inwap.com/pdp10/paper-smp.txt
- ^ "Network processors double performance, run Linux". http://linuxdevices.com/news/NS6961076616.html.
- ^ "Indepth chip review". http://linuxdevices.com/news/NS8981295285.html.
- ^ Eric Brown. "Linux-ready MIPS64 SoCs jump to 32 cores". http://www.linuxdevices.com/news/NS2164244578.html.
External links
- History of Multi-Processing
- Practical Parallel Programming in Pascal
- Enea OSE
- Linux and Multiprocessing
- Intel
- AMD
- OpenMP - Tutorial for parallel programming
- BMDFM: Binary Modular Dataflow Machine - SMP Runtime Environment (BMDFM)
Parallel computing General 
Levels Threads Theory Elements Coordination Multiprocessing · Multithreading (computer architecture) · Memory coherency · Cache coherency · Cache invalidation · Barrier · Synchronization · Application checkpointingProgramming Hardware Multiprocessor (Symmetric · Asymmetric) · Memory (NUMA · COMA · distributed · shared · distributed shared) · SMT
MPP · Superscalar · Vector processor · Supercomputer · BeowulfAPIs Ateji PX · POSIX Threads · OpenMP · OpenHMPP · PVM · MPI · UPC · Intel Threading Building Blocks · Boost.Thread · Global Arrays · Charm++ · Cilk · Co-array Fortran · OpenCL · CUDA · Dryad · DryadLINQProblems Embarrassingly parallel · Grand Challenge · Software lockout · Scalability · Race conditions · Deadlock · Livelock · Deterministic algorithm · Parallel slowdown
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
