- Cloud computing
-
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing as a service rather than a product, whereby shared resources, software, and information are provided to computers and other devices as a utility (like the electricity grid) over a network (typically the Internet).
Contents
Overview
Cloud computing is a marketing term for technologies that provide computation, software, data access, and storage services that do not require end-user knowledge of the physical location and configuration of the system that delivers the services. A parallel to this concept can be drawn with the electricity grid, wherein end-users consume power without needing to understand the component devices or infrastructure required to provide the service.
Cloud computing describes a new supplement, consumption, and delivery model for IT services based on Internet protocols, and it typically involves provisioning of dynamically scalable and often virtualised resources.[1][2] It is a byproduct and consequence of the ease-of-access to remote computing sites provided by the Internet.[3] This may take the form of web-based tools or applications that users can access and use through a web browser as if the programs were installed locally on their own computers.[4]
Cloud computing providers deliver applications via the internet, which are accessed from web browsers and desktop and mobile apps, while the business software and data are stored on servers at a remote location. In some cases, legacy applications (line of business applications that until now have been prevalent in thin client Windows computing) are delivered via a screen-sharing technology, while the computing resources are consolidated at a remote data center location; in other cases, entire business applications have been coded using web-based technologies such as AJAX.
At the foundation of cloud computing is the broader concept of infrastructure convergence (or Converged Infrastructure) and shared services.[5] This type of data center environment allows enterprises to get their applications up and running faster, with easier manageability and less maintenance, and enables IT to more rapidly adjust IT resources (such as servers, storage, and networking) to meet fluctuating and unpredictable business demand.[6] [7]
Most cloud computing infrastructures consist of services delivered through shared data-centers and appearing as a single point of access for consumers' computing needs. Commercial offerings may be required to meet service-level agreements (SLAs), but specific terms are less often negotiated by smaller companies.[8][9]
The tremendous impact of cloud computing on business has prompted the federal United States government to look to the cloud as a means to reorganize their IT infrastructure and decrease their spending budgets. With the advent of the top government official mandating cloud adoption, many agencies already have at least one or more cloud systems online. [10]
Comparison
Cloud computing shares characteristics with:
- Autonomic computing — Computer systems capable of self-management.[11]
- Client–server model — Client–server computing refers broadly to any distributed application that distinguishes between service providers (servers) and service requesters (clients).[12]
- Grid computing — "A form of distributed and parallel computing, whereby a 'super and virtual computer' is composed of a cluster of networked, loosely coupled computers acting in concert to perform very large tasks."
- Mainframe computer — Powerful computers used mainly by large organisations for critical applications, typically bulk data processing such as census, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning, and financial transaction processing.[13]
- Utility computing — The "packaging of computing resources, such as computation and storage, as a metered service similar to a traditional public utility, such as electricity."[14]
- Peer-to-peer — Distributed architecture without the need for central coordination, with participants being at the same time both suppliers and consumers of resources (in contrast to the traditional client–server model).
Characteristics
Cloud computing exhibits the following key characteristics:
- Empowerment of end-users of computing resources by putting the provisioning of those resources in their own control, as opposed to the control of a centralized IT service (for example)
- Agility improves with users' ability to re-provision technological infrastructure resources.
- Application programming interface (API) accessibility to software that enables machines to interact with cloud software in the same way the user interface facilitates interaction between humans and computers. Cloud computing systems typically use REST-based APIs.
- Cost is claimed to be reduced and in a public cloud delivery model capital expenditure is converted to operational expenditure.[15] This is purported to lower barriers to entry, as infrastructure is typically provided by a third-party and does not need to be purchased for one-time or infrequent intensive computing tasks. Pricing on a utility computing basis is fine-grained with usage-based options and fewer IT skills are required for implementation (in-house).[16]
- Device and location independence[17] enable users to access systems using a web browser regardless of their location or what device they are using (e.g., PC, mobile phone). As infrastructure is off-site (typically provided by a third-party) and accessed via the Internet, users can connect from anywhere.[16]
- Multi-tenancy enables sharing of resources and costs across a large pool of users thus allowing for:
- Centralisation of infrastructure in locations with lower costs (such as real estate, electricity, etc.)
- Peak-load capacity increases (users need not engineer for highest possible load-levels)
- Utilisation and efficiency improvements for systems that are often only 10–20% utilised.[18]
- Reliability is improved if multiple redundant sites are used, which makes well-designed cloud computing suitable for business continuity and disaster recovery.[19]
- Scalability and Elasticity via dynamic ("on-demand") provisioning of resources on a fine-grained, self-service basis near real-time, without users having to engineer for peak loads.[20][21]
- Performance is monitored, and consistent and loosely coupled architectures are constructed using web services as the system interface.[16]
- Security could improve due to centralisation of data, increased security-focused resources, etc., but concerns can persist about loss of control over certain sensitive data, and the lack of security for stored kernels.[22] Security is often as good as or better than other traditional systems, in part because providers are able to devote resources to solving security issues that many customers cannot afford.[23] However, the complexity of security is greatly increased when data is distributed over a wider area or greater number of devices and in multi-tenant systems that are being shared by unrelated users. In addition, user access to security audit logs may be difficult or impossible. Private cloud installations are in part motivated by users' desire to retain control over the infrastructure and avoid losing control of information security.
- Maintenance of cloud computing applications is easier, because they do not need to be installed on each user's computer.
History
The term "cloud" is used as a metaphor for the Internet, based on the cloud drawing used in the past to represent the telephone network,[24] and later to depict the Internet in computer network diagrams as an abstraction of the underlying infrastructure it represents.[25]
Cloud computing is a natural evolution of the widespread adoption of virtualisation, service-oriented architecture, autonomic, and utility computing. Details are abstracted from end-users, who no longer have need for expertise in, or control over, the technology infrastructure "in the cloud" that supports them.[26]
The underlying concept of cloud computing dates back to the 1960s, when John McCarthy opined that "computation may someday be organised as a public utility." Almost all the modern-day characteristics of cloud computing (elastic provision, provided as a utility, online, illusion of infinite supply), the comparison to the electricity industry and the use of public, private, government, and community forms, were thoroughly explored in Douglas Parkhill's 1966 book, The Challenge of the Computer Utility. Other scholars have shown that cloud computing's roots go all the way back to the 1950s when scientist Herb Grosch (the author of Grosch's law) postulated that the entire world would operate on dumb terminals powered by about 15 large data centers. [27]
The actual term "cloud" borrows from telephony in that telecommunications companies, who until the 1990s offered primarily dedicated point-to-point data circuits, began offering Virtual Private Network (VPN) services with comparable quality of service but at a much lower cost. By switching traffic to balance utilisation as they saw fit, they were able to utilise their overall network bandwidth more effectively. The cloud symbol was used to denote the demarcation point between that which was the responsibility of the provider and that which was the responsibility of the user. Cloud computing extends this boundary to cover servers as well as the network infrastructure.[28]
After the dot-com bubble, Amazon played a key role in the development of cloud computing by modernising their data centers, which, like most computer networks, were using as little as 10% of their capacity at any one time, just to leave room for occasional spikes. Having found that the new cloud architecture resulted in significant internal efficiency improvements whereby small, fast-moving "two-pizza teams" could add new features faster and more easily, Amazon initiated a new product development effort to provide cloud computing to external customers, and launched Amazon Web Service (AWS) on a utility computing basis in 2006.[18][29]
In early 2008, Eucalyptus became the first open-source, AWS API-compatible platform for deploying private clouds. In early 2008, OpenNebula, enhanced in the RESERVOIR European Commission-funded project, became the first open-source software for deploying private and hybrid clouds, and for the federation of clouds.[30] In the same year, efforts were focused on providing QoS guarantees (as required by real-time interactive applications) to cloud-based infrastructures, in the framework of the IRMOS European Commission-funded project, resulting to a real-time cloud environment.[31] By mid-2008, Gartner saw an opportunity for cloud computing "to shape the relationship among consumers of IT services, those who use IT services and those who sell them"[32] and observed that "[o]rganisations are switching from company-owned hardware and software assets to per-use service-based models" so that the "projected shift to cloud computing ... will result in dramatic growth in IT products in some areas and significant reductions in other areas."[33]
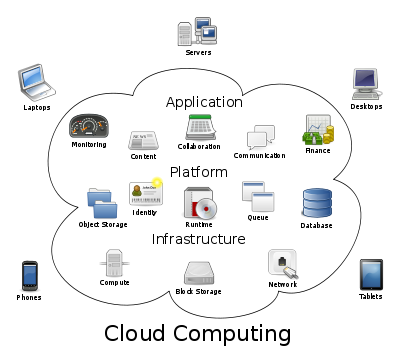
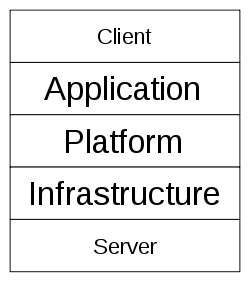
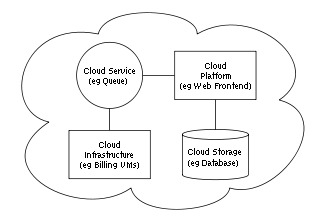
Layers
Once an internet protocol connection is established among several computers, it is possible to share services within any one of the following layers.
Client
See also: Category:Cloud clientsA cloud client consists of computer hardware and/or computer software that relies on cloud computing for application delivery and that is in essence useless without it. Examples include some computers, phones and other devices, operating systems, and browsers.[34][35][36]
Application
See also: Category:Cloud applicationsCloud application services or "Software as a Service (SaaS)" deliver software as a service over the Internet, eliminating the need to install and run the application on the customer's own computers and simplifying maintenance and support.
Platform
See also: Category:Cloud platformsCloud platform services, also known as platform as a service (PaaS), deliver a computing platform and/or solution stack as a service, often consuming cloud infrastructure and sustaining cloud applications.[37] It facilitates deployment of applications without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers.[38][39] Cloud computing is becoming a major change in our industry, and one of the most important parts of this change is the shift of cloud platforms. Platforms let developers write certain applications that can run in the cloud, or even use services provided by the cloud. There are different names being used for platforms which can include the on-demand platform, or Cloud 9. It your choice on what you would like to call the platform, but they all have great potential in developing. When development teams create applications for the cloud, they must must build it's own cloud platform.
Infrastructure
See also: Category:Cloud infrastructureCloud infrastructure services, also known as "infrastructure as a service" (IaaS), deliver computer infrastructure – typically a platform virtualisation environment – as a service, along with raw (block) storage and networking. Rather than purchasing servers, software, data-center space or network equipment, clients instead buy those resources as a fully outsourced service. Suppliers typically bill such services on a utility computing basis; the amount of resources consumed (and therefore the cost) will typically reflect the level of activity.[40]
Server
The servers layer consists of computer hardware and/or computer software products that are specifically designed for the delivery of cloud services, including multi-core processors, cloud-specific operating systems and combined offerings.[41][42][43][44]
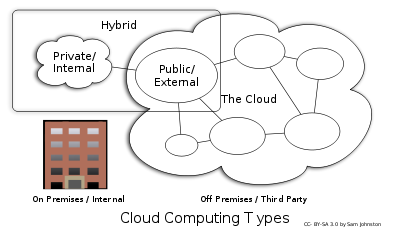
Deployment models
Public cloud
Public cloud describes cloud computing in the traditional mainstream sense, whereby resources are dynamically provisioned to the general public on a fine-grained, self-service basis over the Internet, via web applications/web services, from an off-site third-party provider who bills on a fine-grained utility computing basis.[16]
Community cloud
Community cloud shares infrastructure between several organizations from a specific community with common concerns (security, compliance, jurisdiction, etc.), whether managed internally or by a third-party and hosted internally or externally. The costs are spread over fewer users than a public cloud (but more than a private cloud), so only some of the benefits of cloud computing are realized.[45]
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid cloud is a composition of two or more clouds (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities but are bound together, offering the benefits of multiple deployment models. It can also be defined as multiple cloud systems that are connected in a way that allows programs and data to be moved easily from one deployment system to another.[45]
Private cloud
Private cloud is infrastructure operated solely for a single organization, whether managed internally or by a third-party and hosted internally or externally.[45]
They have attracted criticism because users "still have to buy, build, and manage them" and thus do not benefit from lower up-front capital costs and less hands-on management,[46] essentially "[lacking] the economic model that makes cloud computing such an intriguing concept".[47][48]
Vertical Markets for Clouds
Healthcare IT Spending on Cloud to Surpass $1 Billion said the Business Technology Roundtable in their August 2011 issue.
One of the most invaluable applications is the sharing of medical imaging through the computing cloud that actually saves lives and reduces costs in an industry that is beset with cost overruns.
Government Cloud Computing is another vertical sector that is growing quickly as governments need to make do with less revenue. Cities such as New York City have adopted cloud technology effectively for their citizens.Architecture
Cloud architecture,[49] the systems architecture of the software systems involved in the delivery of cloud computing, typically involves multiple cloud components communicating with each other over a loose coupling mechanism such as a messaging queue.
The Intercloud
Main article: IntercloudThe Intercloud[50] is an interconnected global "cloud of clouds"[51][52] and an extension of the Internet "network of networks" on which it is based.[53][54][55]
Cloud engineering
Cloud engineering is the application of engineering disciplines to cloud computing. It brings a systematic approach to the high level concerns of commercialisation, standardisation, and governance in conceiving, developing, operating and maintaining cloud computing systems. It is a multidisciplinary method encompassing contributions from diverse areas such as systems, software, web, performance, information, security, platform, risk, and quality engineering.
Issues
Privacy
The cloud model has been criticised by privacy advocates for the greater ease in which the companies hosting the cloud services control, thus, can monitor at will, lawfully or unlawfully, the communication and data stored between the user and the host company. Instances such as the secret NSA program, working with AT&T, and Verizon, which recorded over 10 million phone calls between American citizens, causes uncertainty among privacy advocates, and the greater powers it gives to telecommunication companies to monitor user activity.[56] While there have been efforts (such as US-EU Safe Harbor) to "harmonise" the legal environment, providers such as Amazon still cater to major markets (typically the United States and the European Union) by deploying local infrastructure and allowing customers to select "availability zones."[57] Cloud computing poses privacy concerns basically, because the service provider at any point in time, may access the data that is on the cloud. They could accidentally or deliberately alter or even delete some info. [58]
Compliance
In order to obtain compliance with regulations including FISMA, HIPAA, and SOX in the United States, the Data Protection Directive in the EU and the credit card industry's PCI DSS, users may have to adopt community or hybrid deployment modes that are typically more expensive and may offer restricted benefits. This is how Google is able to "manage and meet additional government policy requirements beyond FISMA"[59][60] and Rackspace Cloud or QubeSpace are able to claim PCI compliance.[61]
Many providers also obtain SAS 70 Type II certification, but this has been criticised on the grounds that the hand-picked set of goals and standards determined by the auditor and the auditee are often not disclosed and can vary widely.[62] Providers typically make this information available on request, under non-disclosure agreement.[63] [64]
Customers in the EU contracting with cloud providers established outside the EU/EEA have to adhere to the EU regulations on export of personal data.[65]
Legal
As can be expected with any revolutionary change in the landscape of global computing, certain legal issues arise; everything from trademark infringement, security concerns to the sharing of propriety data resources.
Open source
See also: Category:Open source cloud computingOpen-source software has provided the foundation for many cloud computing implementations, one prominent example being the Hadoop framework.[66] In November 2007, the Free Software Foundation released the Affero General Public License, a version of GPLv3 intended to close a perceived legal loophole associated with free software designed to be run over a network.[67]
Open standards
See also: Category:Cloud standardsMost cloud providers expose APIs that are typically well-documented (often under a Creative Commons license[68]) but also unique to their implementation and thus not interoperable. Some vendors have adopted others' APIs and there are a number of open standards under development, with a view to delivering interoperability and portability.[69]
Security
Main article: Cloud computing securityAs cloud computing is achieving increased popularity, concerns are being voiced about the security issues introduced through adoption of this new model. The effectiveness and efficiency of traditional protection mechanisms are being reconsidered as the characteristics of this innovative deployment model differ widely from those of traditional architectures.[70]
The relative security of cloud computing services is a contentious issue that may be delaying its adoption.[71] Issues barring the adoption of cloud computing are due in large part to the private and public sectors unease surrounding the external management of security-based services. It is the very nature of cloud computing-based services, private or public, that promote external management of provided services. This delivers great incentive to cloud computing service providers to prioritize building and maintaining strong management of secure services.[72] Security issues have been categorised into sensitive data access, data segregation, privacy, bug exploitation, recovery, accountability, malicious insiders, management console security, account control, and multi-tenancy issues. Solutions to various cloud security issues vary, from cryptography, particularly public key infrastructure (PKI), to use of multiple cloud providers, standardisation of APIs, and improving virtual machine support and legal support.[70][73][74]
Sustainability
Although cloud computing is often assumed to be a form of "green computing", there is as of yet no published study to substantiate this assumption.[75] Siting the servers affects the environmental effects of cloud computing. In areas where climate favors natural cooling and renewable electricity is readily available, the environmental effects will be more moderate. (The same holds true for "traditional" data centers.) Thus countries with favorable conditions, such as Finland,[76] Sweden and Switzerland,[77] are trying to attract cloud computing data centers. Energy efficiency in cloud computing can result from energy-aware scheduling and server consolidation [78]. However, in the case of distributed clouds over data centers with different source of energies including renewable source of energies, a small compromise on energy consumption reduction could result in high carbon footprint reduction [79].
Abuse
As with privately purchased hardware, crackers posing as legitimate customers can purchase the services of cloud computing for nefarious purposes. This includes password cracking and launching attacks using the purchased services.[80] In 2009, a banking trojan illegally used the popular Amazon service as a command and control channel that issued software updates and malicious instructions to PCs that were infected by the malware.[81]
Research
Many universities, vendors and government organisations are investing in research around the topic of cloud computing:[82][83]
- In October 2007 the Academic Cloud Computing Initiative (ACCI) was announced as a multi-university project designed to enhance students' technical knowledge to address the challenges of cloud computing.[84]
- In July 2011 the High Performance Computing Cloud (HPCCLoud) project was kicked-off aiming at finding out the possibilities of enhancing performance on cloud environments while running the scientific applications - development of HPCCLoud Performance Analysis Toolkit which was funded by CIM-Returning Experts Programme - under the coordination of Prof. Dr. Shajulin Benedict.
- In June 2011 the Telecommunications Industry Association developed a Cloud Computing White Paper, to analyze the integration challenges and opportunities between cloud services and traditional U.S. telecommunications standards[85].
See also
External links
References
- ^ "Gartner Says Cloud Computing Will Be As Influential As E-business". Gartner.com. http://www.gartner.com/it/page.jsp?id=707508. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Gruman, Galen (2008-04-07). "What cloud computing really means". InfoWorld. http://www.infoworld.com/d/cloud-computing/what-cloud-computing-really-means-031. Retrieved 2009-06-02.
- ^ "Cloud Computing: Clash of the clouds". The Economist. 2009-10-15. http://www.economist.com/displaystory.cfm?story_id=14637206. Retrieved 2009-11-03.
- ^ Cloud Computing Defined 17 July 2010. Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- ^ Kerravala, Zeus, Yankee Group, "Migrating to the cloud is dependent on a converged infrastructure," Tech Target.
- ^ Baburajan, Rajani, “The Rising Cloud Storage Market Opportunity Strengthens Vendors,” infoTECH, August 24, 2011.
- ^ Oestreich, Ken, "Converged Infrastructure," CTO Forum, November 15, 2010.
- ^ Buyya, Rajkumar; Chee Shin Yeo, Srikumar Venugopal (PDF). Market-Oriented Cloud Computing: Vision, Hype, and Reality for Delivering IT Services as Computing Utilities. Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering, University of Melbourne, Australia. p. 9. http://www.gridBus.org/~raj/papers/hpcc2008_keynote_cloudcomputing.pdf. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
- ^ "Getting clear about cloud computing". The Irish Times. http://www.irishtimes.com/business-services/cloud-computing-ireland/getting-clear-about-cloud-computing/.
- ^ Thomas J. Kwasniewski, EJ Puig, "Cloud Computing in the Government", Data & Analysis Center for Software, July 2011
- ^ "What's In A Name? Utility vs. Cloud vs Grid". Datacenterknowledge.com. http://www.datacenterknowledge.com/archives/2008/Mar/25/whats_in_a_name_utility_vs_cloud_vs_grid.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Distributed Application Architecture". Sun Microsystem. http://java.sun.com/developer/Books/jdbc/ch07.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-16.
- ^ "Sun CTO: Cloud computing is like the mainframe". Itknowledgeexchange.techtarget.com. 2009-03-11. http://itknowledgeexchange.techtarget.com/mainframe-blog/sun-cto-cloud-computing-is-like-the-mainframe/. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "It's probable that you've misunderstood 'Cloud Computing' until now". TechPluto. http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1496091.1496100&coll=&dl=ACM&CFID=21518680&CFTOKEN=18800807. Retrieved 2010-09-14.
- ^ "Recession Is Good For Cloud Computing – Microsoft Agrees". CloudAve. http://www.cloudave.com/link/recession-is-good-for-cloud-computing-microsoft-agrees. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ a b c d "Defining "Cloud Services" and "Cloud Computing"". IDC. 2008-09-23. http://blogs.idc.com/ie/?p=190. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Farber, Dan (2008-06-25). "The new geek chic: Data centers". CNET News. http://news.cnet.com/8301-13953_3-9977049-80.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ a b Jeff Bezos' Risky Bet.
- ^ King, Rachael (2008-08-04). "Cloud Computing: Small Companies Take Flight". Businessweek. http://www.businessweek.com/technology/content/aug2008/tc2008083_619516.htm. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Defining and Measuring Cloud Elasticity". KIT Software Quality Departement. http://digbib.ubka.uni-karlsruhe.de/volltexte/1000023476. Retrieved 13 August 2011.
- ^ "Economies of Cloud Scale Infrastructure". Cloud Slam 2011. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nfDsY3f4nVI. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ "Encrypted Storage and Key Management for the cloud". Cryptoclarity.com. 2009-07-30. http://www.cryptoclarity.com/CryptoClarityLLC/Welcome/Entries/2009/7/23_Encrypted_Storage_and_Key_Management_for_the_cloud.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Mills, Elinor (2009-01-27). "Cloud computing security forecast: Clear skies". CNET News. http://news.cnet.com/8301-1009_3-10150569-83.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Writing & Speaking". Sellsbrothers.com. http://www.sellsbrothers.com/writing/intro2tapi/default.aspx?content=pstn.htm. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "The Internet Cloud". Thestandard.com. http://www.thestandard.com/article/0,1902,5466,00.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Danielson, Krissi (2008-03-26). "Distinguishing Cloud Computing from Utility Computing". Ebizq.net. http://www.ebizq.net/blogs/saasweek/2008/03/distinguishing_cloud_computing/. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Regulation of the Cloud in India, Ryan, Falvey & Merchant, Journal of Internet Law, Vol 15, No. 4 (October 2011).
- ^ "July, 1993 meeting report from the IP over ATM working group of the IETF". http://mirror.switch.ch/ftp/doc/ietf/ipatm/atm-minutes-93jul.txt. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ [1].
- ^ B. Rochwerger, J. Caceres, R.S. Montero, D. Breitgand, E. Elmroth, A. Galis, E. Levy, I.M. Llorente, K. Nagin, Y. Wolfsthal, E. Elmroth, J. Caceres, M. Ben-Yehuda, W. Emmerich, F. Galan. "The RESERVOIR Model and Architecture for Open Federated Cloud Computing", IBM Journal of Research and Development, Vol. 53, No. 4. (2009)
- ^ D. Kyriazis, A. Menychtas, G. Kousiouris, K. Oberle, T. Voith, M. Boniface, E. Oliveros, T. Cucinotta, S. Berger, “A Real-time Service Oriented Infrastructure”, International Conference on Real-Time and Embedded Systems (RTES 2010), Singapore, November 2010
- ^ Keep an eye on cloud computing, Amy Schurr, Network World, 2008-07-08, citing the Gartner report, "Cloud Computing Confusion Leads to Opportunity". Retrieved 2009-09-11.
- ^ Gartner Says Worldwide IT Spending On Pace to Surpass Trillion in 2008, Gartner, 2008-08-18. Retrieved 2009-09-11.
- ^ Claburn, Thomas. "Google Reveals Nexus One 'Super Phone'". InformationWeek. http://www.informationweek.com/news/software/web_services/showArticle.jhtml?articleID=222200331. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "What Makes a Cloud Computer?". Gigaom.com. 2008-06-22. http://gigaom.com/2008/06/22/what-makes-a-good-cloud-computer/. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ by Brian BraikerSeptember 02, 2008 (2008-09-02). "The Cloud's Chrome Lining". Newsweek.com. http://www.newsweek.com/id/156911. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "An example of a 'Cloud Platform' for building applications". Eccentex.com. http://www.eccentex.com/platform/workflow.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Jack Schofield (2008-04-17). "Google angles for business users with 'platform as a service'". London: Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/technology/2008/apr/17/google.software. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "The Emerging Cloud Service Architecture". Aws.typepad.com. 2008-06-03. http://aws.typepad.com/aws/2008/06/the-forthcoming.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "EMC buys Pi and forms a cloud computing group". Searchstorage.techtarget.com. 2008-02-21. http://searchstorage.techtarget.com/news/article/0,289142,sid5_gci1301852,00.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Nimbus Cloud Guide[dead link]
- ^ Myslewski, Rik (2009-12-02). "Intel puts cloud on single megachip". Theregister.co.uk. http://www.theregister.co.uk/2009/12/02/intel_scc/. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Duffy, Jim (2009-05-12). "Cisco unveils cloud computing platform for service providers". Infoworld.com. http://www.infoworld.com/d/cloud-computing/cisco-unveils-cloud-computing-platform-service-providers-113. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Markoff, John (2008-10-27). "Microsoft Plans 'Cloud' Operating System". Nytimes.com. http://www.nytimes.com/2008/10/28/technology/28soft.html. Retrieved 2011-08-20.
- ^ a b c "The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing". National Institute of Science and Technology. http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-145/SP800-145.pdf. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ^ Foley, John. "Private Clouds Take Shape". InformationWeek. http://www.informationweek.com/news/services/business/showArticle.jhtml?articleID=209904474. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Haff, Gordon (2009-01-27). "Just don't call them private clouds". CNET News. http://news.cnet.com/8301-13556_3-10150841-61.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "There's No Such Thing As A Private Cloud". InformationWeek. 2010-06-30. http://www.informationweek.com/cloud-computing/blog/archives/2009/01/theres_no_such.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Building GrepTheWeb in the Cloud, Part 1: Cloud Architectures". Developer.amazonwebservices.com. http://developer.amazonwebservices.com/connect/entry.jspa?externalID=1632&categoryID=100. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Bernstein, David; Ludvigson, Erik; Sankar, Krishna; Diamond, Steve; Morrow, Monique (2009-05-24). Blueprint for the Intercloud – Protocols and Formats for Cloud Computing Interoperability. IEEE Computer Society. pp. 328–336. doi:10.1109/ICIW.2009.55. http://www2.computer.org/portal/web/csdl/doi/10.1109/ICIW.2009.55.
- ^ "Kevin Kelly: A Cloudbook for the Cloud". Kk.org. http://www.kk.org/thetechnium/archives/2007/11/a_cloudbook_for.php. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Intercloud is a global cloud of clouds". Samj.net. 2009-06-22. http://samj.net/2009/06/intercloud-is-global-cloud-of-clouds.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Vint Cerf: Despite Its Age, The Internet is Still Filled with Problems". Readwriteweb.com. http://www.readwriteweb.com/archives/vint_cerf_despite_its_age_the.php?mtcCampaign=2765. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "SP360: Service Provider: From India to Intercloud". Blogs.cisco.com. http://blogs.cisco.com/sp/comments/from_india_to_intercloud/. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Canada (2007-11-29). "Head in the clouds? Welcome to the future". Toronto: Theglobeandmail.com. http://www.theglobeandmail.com/servlet/story/LAC.20071129.TWLINKS29/TPStory/Business. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Cauley, Leslie (2006-05-11). "NSA has massive database of Americans' phone calls". USATODAY.com. http://www.usatoday.com/news/washington/2006-05-10-nsa_x.htm. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Feature Guide: Amazon EC2 Availability Zones". Amazon Web Services. http://developer.amazonwebservices.com/connect/entry.jspa?externalID=1347&categoryID=112. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ {{cite web|url=http://cacm.acm.org/magazines/2011/1/103200-cloud-computing-privacy-concerns-on-our-doorstep/fulltext |title=Cloud Computing Privacy Concerns on Our Doorstep}}
- ^ "FISMA compliance for federal cloud computing on the horizon in 2010". SearchCompliance.com. http://searchcompliance.techtarget.com/news/article/0,289142,sid195_gci1377298,00.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Google Apps and Government". Official Google Enterprise Blog. 2009-09-15. http://googleenterprise.blogspot.com/2009/09/google-apps-and-government.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Cloud Hosting is Secure for Take-off: Mosso Enables The Spreadsheet Store, an Online Merchant, to become PCI Compliant". Rackspace. 2009-03-14. http://www.rackspace.com/cloud/blog/2009/03/05/cloud-hosting-is-secure-for-take-off-mosso-enables-the-spreadsheet-store-an-online-merchant-to-become-pci-compliant/. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Amazon gets SAS 70 Type II audit stamp, but analysts not satisfied". SearchCloudComputing.com. 2009-11-17. http://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/news/article/0,289142,sid201_gci1374629,00.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Assessing Cloud Computing Agreements and Controls". WTN News. http://wistechnology.com/articles/6954/. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Cloud Certification From Compliance Mandate to Competitive Differentiator". Cloudcor. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wYiFdnZAlNQ. Retrieved 2011-09-20.
- ^ "How the New EU Rules on Data Export Affect Companies in and Outside the EU | Dr. Thomas Helbing – Kanzlei für Datenschutz-, Online- und IT-Recht". Dr. Thomas Helbing. http://www.thomashelbing.com/en/how-new-eu-rules-data-export-affect-companies-and-outside-eu. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Open source fuels growth of cloud computing, software-as-a-service". Network World. http://www.networkworld.com/news/2008/072808-open-source-cloud-computing.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "AGPL: Open Source Licensing in a Networked Age". Redmonk.com. 2009-04-15. http://redmonk.com/sogrady/2009/04/15/open-source-licensing-in-a-networked-age/. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ GoGrid Moves API Specification to Creative Commons[dead link]
- ^ "Eucalyptus Completes Amazon Web Services Specs with Latest Release". Ostatic.com. http://ostatic.com/blog/eucalyptus-completes-amazon-web-services-specs-with-latest-release. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ a b Zissis, Dimitrios; Lekkas (2010). "Addressing cloud computing security issues". Future Generation Computer Systems. doi:10.1016/j.future.2010.12.006. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167739X10002554.
- ^ "Are security issues delaying adoption of cloud computing?". Network World. http://www.networkworld.com/news/2009/042709-burning-security-cloud-computing.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "Security of virtualization, cloud computing divides IT and security pros". Network World. 2010-02-22. http://www.networkworld.com/news/2010/022210-virtualization-cloud-security-debate.html. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Armbrust, M; Fox, A., Griffith, R., Joseph, A., Katz, R., Konwinski, A., Lee, G., Patterson, D., Rabkin, A., Zaharia, (2010). "A view of cloud computing.". Communication of the ACM 53 (4): 50–58. doi:10.1145/1721654.1721672.
- ^ Anthens, G. "Security in the cloud". Communications of the ACM 53 (11). doi:10.1145/1839676.1839683.
- ^ James Urquhart (January 7, 2010). "Cloud computing's green paradox". CNET News. http://news.cnet.com/8301-19413_3-10428065-240.html. Retrieved March 12, 2010. "...there is some significant evidence that the cloud is encouraging more compute consumption"
- ^ Finland – First Choice for Siting Your Cloud Computing Data Center.. Retrieved 4 August 2010.
- ^ Swiss Carbon-Neutral Servers Hit the Cloud.. Retrieved 4 August 2010.
- ^ Berl, Andreas, et al., Energy-Efficient Cloud Computing, The Computer Journal, 2010.
- ^ Farrahi Moghaddam, Fereydoun, et al., Low Carbon Virtual Private Clouds, IEEE Cloud 2011.
- ^ Alpeyev, Pavel (2011-05-14). "Amazon.com Server Said to Have Been Used in Sony Attack". Bloomberg. http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2011-05-13/sony-network-said-to-have-been-invaded-by-hackers-using-amazon-com-server.html. Retrieved 2011-08-20.
- ^ http://www.theregister.co.uk/2011/05/14/playstation_network_attack_from_amazon/
- ^ "Cloud Net Directory. Retrieved 2010-03-01". Cloudbook.net. http://www.cloudbook.net/directories/research-clouds. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ "– National Science Foundation (NSF) News – National Science Foundation Awards Millions to Fourteen Universities for Cloud Computing Research – US National Science Foun". Nsf.gov. http://www.nsf.gov/news/news_summ.jsp?cntn_id=114686. Retrieved 2011-08-20.
- ^ ""IBM, Google Team on an Enterprise Cloud." May 2008. Rich Miller Retrieved 2010-04-01". DataCenterKnowledge.com. 2008-05-02. http://www.datacenterknowledge.com/archives/2008/05/02/ibm-google-team-on-an-enterprise-cloud/. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ http://www.tiaonline.org/market_intelligence/publication_download.cfm?file=TIA_Cloud_Computing_White_Paper
Cloud computing Clients - Browsers
- Devices
- Netbooks
- Tablets
- Smart phones
- Operating Systems
- Android
- iOS
- Windows Phone 7
Applications Platforms - Amazon
- App Engine
- Azure
- Engine Yard
- Force.com
- Heroku
- RightScale
Infrastructure Technologies - Networking
- Security
- Datacenters
- Internet
- Structured storage
- Virtualization
- Web Services
- Virtual Appliance
Categories:- Cloud computing
- Cloud platforms
- Open source cloud computing
- Computing stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.