- Surčin
-
Surčin
Сурчин— Municipality and Town — 
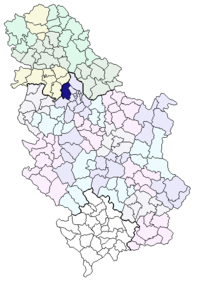
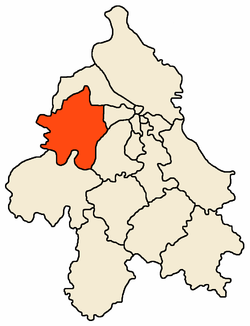
Coat of armsLocation of the municipality of Surčin within Serbia Coordinates: 44°48′N 20°17′E / 44.8°N 20.283°E Country Serbia District Belgrade Settlements 7 Government – Mayor Vojislav Janošević (DS) Area[1] – Municipality 285 km2 (110 sq mi) Population (2011 census)[2] – Town 14,292 – Municipality 38,695 Time zone CET (UTC+1) – Summer (DST) CEST (UTC+2) Postal code 11271 Area code +381 11 Car plates BG Website www.surcin.rs Surčin (Serbian Cyrillic: Сурчин, pronounced [sǔrt͡ʃiːn]) is a neighborhood of Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. It is the youngest of Belgrade's 17 municipalities, as it split from the municipality of Zemun in 2003. Surčin municipality has 38,695 residents while Surčin town itself has 14,292. The most important feature is the Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport, located just a few kilometers west of the town.
Contents
Geography
Surčin is located in the eastern Syrmia region, 20 kilometers west of downtown Belgrade. It borders the municipalities of Zemun (north) and Novi Beograd (east). Entire western border of the municipality is the administrative border of the province of Vojvodina while the Sava river formes the border to the municipalities of Čukarica (south-east) and Obrenovac (south).
The area of the municipality is flat and marshy as the entire southern section belongs to the floodplain of the Sava. Numerous smaller streams (mostly channeled) flow through the municipality, most notably the Galovica and Jarčina.
Other distinct geographical features are the ponds of Fenek and Živača, a large woody area od Bojčin (Serbian: Bojčinska šuma) and Progarska ada, one of the largest islands in the Sava.
Surčin lies just south of the Belgrade–Zagreb highway, on the Belgrade beltway which, when finished in 2011, will bypass the heavy traffic from the Belgrade's urban core to the city's southern outskirts (for now, it is the only case among European capitals that highway passes right through the city)[citation needed]. The Syrmian section of the beltway (which separates from the highway at Dobanovci, then goes Surčin–Jakovo–Ostružnica) is already built and operational. An internal Belgrade's freight railway goes parallel to the beltway.
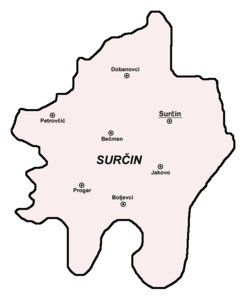
Settlements
Urban (towns):
- Surčin
- Dobanovci
Rural (villages):
Demographics
Surčin and the majority of the settlements in the municipality are growing fast. Though in the past, it had no urban connection with Belgrade on the east (that is, Novi Beograd's westernmost neighborhood of Ledine through which it is connected to the city), an urban zone is developed along that road, turning Belgrade and Surčin into one continuous built-up area. Similar process develops on all sides of Surčin which, with the growth of population, grows into one urban area with Dobanovci (north), Jakovo (south) and Bečmen (west).
Population of the town of Surčin according to the official censuses:
- 1921 - 3,250
- 1931 - 3,502
- 1961 - 6,160
- 1971 - 10,550
- 1981 - 12,575
- 1991 - 11,826
- 2002 - 14,292
Ethnic structure of the town (2002 census):
- Serbs = 12,358 (86.47%)
- Roma = 702 (4.91%)
- Croats = 377 (2.64%)
- Yugoslavs = 79 (0.55%)
- Montenegrins = 75 (0.53%)
Ethnic structure of the municipality (2002 census)
- Serbs = 34,055 (88.01%)
- Slovaks = 1,417 (3.66%)
- Roma = 922 (2.38%)
- Croats = 460 (1.19%)
- Yugoslavs = 223 (0.58%)
All settlements in the municipality have an ethnic Serb majority.
History
The area of the town was settled through the most of the early human history. Being an old settlement, findings from prehistoric times are quite common. So far, it is established that a previous settlements existed in the neolithic, bronze age, stone age and Roman era.[3]
In period 1991 to 2002, population of the municipality grew from 35,591 to 38,695. Majority of that growth came from the refugees from Yugoslav Wars (mostly Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina). Since many of the refugees were integrated into the Serbian citizenship after 2002, it is to be expected the official number of population is much higher now.
Surčin was the seat of its own municipality until 1965 when it was annexed to the municipality of Zemun (prior to that, municipalities of Boljevci and Dobanovci were annexed to the municipality of Surčin). A movement for splitting from Zemun was very vocal since the 1990s and even though it did not fulfil some of the conditions required by the Belgrade City Statute for creation of new municipality (mainly, the population of over 50,000), Belgrade City assembly voted to detach Surčin from Zemun (officially on November 24, 2003) but the newly formed municipality remained under the administration of the municipality of Zemun until next municipal elections and finally got its own administration on November 3, 2004. However, municipal administration and the overall political situation in Surčin is highy unstable ever since.[4][5]
President of the local community of Surčin:
- November 24, 2003 - November 3, 2004: Vojislav Janošević (b. 1946) (Democratic Party)
Presidents of the municipality:
- November 3, 2004 - November 24, 2005: Rajko Matović (b. 1960) (Serbian Radical Party)
- August 13, 2004 - November 24, 2005: Vladimir Aleksandrov (b. 1940) (former Serbian Radical Party; not confirmed by the Ministry for the local self-rule)
- November 24, 2005 - (present): Vojislav Janošević (Democratic Party)
Economy
The majority of population is into the agriculture. Extensive farms for the pig breeding are located in Surčin itself while in the smaller settlements the production is mostly for the Belgrade's market ("suburban agriculture" - fruits, early vegetables, etc.).
The most important facility is the Belgrade Nikola Tesla airport, opened on April 28, 1962, instead of the old one in Bežanija. The new and modern airport put the small village on the map. The aeronautics museum is also located in the airport's complex.
See also
- List of cities in Serbia
- Subdivisions of Belgrade
- List of Belgrade neighborhoods and suburbs
References
- Mala Prosvetina Enciklopedija, Third edition (1985); Prosveta; ISBN 86-07-00001-2
- Jovan Đ. Marković (1990): Enciklopedijski geografski leksikon Jugoslavije; Svjetlost-Sarajevo; ISBN 86-01-02651-6
- ^ "Municipalities of Serbia, 2006". Statistical Office of Serbia. http://webrzs.stat.gov.rs/axd/en/Zip/OG2006webE.zip. Retrieved 2010-11-28.
- ^ "2011 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Serbia – FIRST RESULTS". Bulletin (Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia) 540. 2011. ISSN 0354-3641. http://media.popis2011.stat.rs/2011/prvi_rezultati.pdf. Retrieved 2011-11-21.
- ^ http://www.balkaninstitut.com/pdf/izdanja/balcanica/Balcanica_XXXVI_2005.pdf
- ^ "Surčinski obračun" (in Serbian). Press. 2008-03-20. http://www.pressonline.co.rs/sr/vesti/vesti_dana/story/32604. Retrieved 2010-11-30.
- ^ "Ruše me mafijaši!" (in Serbian). Press. 2008-03-20. http://www.pressonline.co.rs/sr/vesti/vesti_dana/story/32654. Retrieved 2010-11-30.
External links
Municipalities of Belgrade Municipalities Barajevo · Čukarica · Grocka · Lazarevac · Mladenovac · Novi Beograd · Obrenovac · Palilula · Rakovica · Savski Venac · Sopot · Stari Grad · Surčin · Voždovac · Vračar · Zemun · Zvezdara
Municipalities and cities of Serbia Central Serbia Belgrade (Barajevo • Čukarica • Grocka • Lazarevac • Mladenovac • Novi Beograd • Obrenovac • Palilula • Rakovica • Savski Venac • Sopot • Stari Grad • Surčin • Voždovac • Vračar • Zemun • Zvezdara) • Čačak • Jagodina • Kragujevac (Aerodrom • Pivara • Stanovo • Stari Grad • Stragari) • Kraljevo • Kruševac • Leskovac • Loznica • Niš (Crveni Krst • Medijana • Niška Banja • Palilula • Pantelej) • Novi Pazar • Požarevac • Smederevo • Šabac • Užice • Valjevo • Vranje • Zaječar Aleksandrovac • Aleksinac • Aranđelovac • Arilje • Babušnica • Bajina Bašta • Batočina • Bela Palanka • Blace • Bogatić • Bojnik • Boljevac • Bor • Bosilegrad • Brus • Bujanovac • Crna Trava • Čajetina • Ćićevac • Ćuprija • Despotovac • Dimitrovgrad • Doljevac • Gadžin Han • Golubac • Gornji Milanovac • Ivanjica • Kladovo • Knić • Knjaževac • Koceljeva • Kosjerić • Krupanj • Kučevo • Kuršumlija • Lajkovac • Lapovo • Lebane • Lučani • Ljig • Ljubovija • Majdanpek • Mali Zvornik • Malo Crniće • Medveđa • Merošina • Mionica • Negotin • Nova Varoš • Osečina • Paraćin • Petrovac • Pirot • Požega • Preševo • Priboj • Prijepolje • Prokuplje • Rača • Raška • Ražanj • Rekovac • Sjenica • Smederevska Palanka • Sokobanja • Surdulica • Svilajnac • Svrljig • Topola • Trgovište • Trstenik • Tutin • Ub • Varvarin • Velika Plana • Veliko Gradište • Vladičin Han • Vladimirci • Vlasotince • Vrnjačka Banja • Žabari • Žagubica • Žitorađa
Aleksandrovac • Aleksinac • Aranđelovac • Arilje • Babušnica • Bajina Bašta • Batočina • Bela Palanka • Blace • Bogatić • Bojnik • Boljevac • Bor • Bosilegrad • Brus • Bujanovac • Crna Trava • Čajetina • Ćićevac • Ćuprija • Despotovac • Dimitrovgrad • Doljevac • Gadžin Han • Golubac • Gornji Milanovac • Ivanjica • Kladovo • Knić • Knjaževac • Koceljeva • Kosjerić • Krupanj • Kučevo • Kuršumlija • Lajkovac • Lapovo • Lebane • Lučani • Ljig • Ljubovija • Majdanpek • Mali Zvornik • Malo Crniće • Medveđa • Merošina • Mionica • Negotin • Nova Varoš • Osečina • Paraćin • Petrovac • Pirot • Požega • Preševo • Priboj • Prijepolje • Prokuplje • Rača • Raška • Ražanj • Rekovac • Sjenica • Smederevska Palanka • Sokobanja • Surdulica • Svilajnac • Svrljig • Topola • Trgovište • Trstenik • Tutin • Ub • Varvarin • Velika Plana • Veliko Gradište • Vladičin Han • Vladimirci • Vlasotince • Vrnjačka Banja • Žabari • Žagubica • ŽitorađaVojvodina  Ada • Alibunar • Apatin • Bač • Bačka Palanka • Bačka Topola • Bački Petrovac • Bečej • Bela Crkva • Beočin • Čoka • Inđija • Irig • Kanjiža • Kikinda • Kovačica • Kovin • Kula • Mali Iđoš • Nova Crnja • Novi Bečej • Novi Kneževac • Odžaci • Opovo • Pećinci • Plandište • Ruma • Sečanj • Senta • Šid • Srbobran • Sremski Karlovci • Stara Pazova • Temerin • Titel • Vrbas • Vršac • Žabalj • Žitište
Ada • Alibunar • Apatin • Bač • Bačka Palanka • Bačka Topola • Bački Petrovac • Bečej • Bela Crkva • Beočin • Čoka • Inđija • Irig • Kanjiža • Kikinda • Kovačica • Kovin • Kula • Mali Iđoš • Nova Crnja • Novi Bečej • Novi Kneževac • Odžaci • Opovo • Pećinci • Plandište • Ruma • Sečanj • Senta • Šid • Srbobran • Sremski Karlovci • Stara Pazova • Temerin • Titel • Vrbas • Vršac • Žabalj • ŽitišteKosovo Dečani • Đakovica • Dragaš • Glogovac • Gnjilane • Istok • Kačanik • Klina • Kosovo Polje • Kosovska Kamenica • Kosovska Mitrovica • Leposavić • Lipljan • Mališevo • Novo Brdo • Obilić • Orahovac • Peć • Podujevo • Priština • Prizren • Štimlje • Srbica • Štrpce • Suva Reka • Uroševac • Vitina • Vučitrn • Zubin Potok • Zvečan New Municipalities: Đeneral Janković • Gračanica • Junik • Klokot-Vrbovac • Mamuša • Parteš • RanilugCategories:
New Municipalities: Đeneral Janković • Gračanica • Junik • Klokot-Vrbovac • Mamuša • Parteš • RanilugCategories:- Populated places in Central Serbia
- Suburbs of Belgrade
- Municipalities of Belgrade
- Places in Syrmia
- Roman towns and cities in Serbia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.