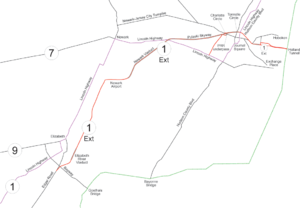
- New Jersey Route 25
-
Route 25 Route information Existed: 1927 – 1953 Major junctions South end:  US 30 at Ben Franklin Bridge in Camden
US 30 at Ben Franklin Bridge in Camden


 US 30 / US 130 / Route 43 / Route 45 in Pennsauken Township
US 30 / US 130 / Route 43 / Route 45 in Pennsauken Township
 Route S41 in Palmyra
Route S41 in Palmyra

 US 206 / Route 39 in Bordentown
US 206 / Route 39 in Bordentown
 Route 33 in Hightstown
Route 33 in Hightstown

 US 1 / Route S26 in New Brunswick
US 1 / Route S26 in New Brunswick

 US 9 / Route 35 in Woodbridge
US 9 / Route 35 in Woodbridge
 Route 4 in Woodbridge
Route 4 in Woodbridge
 Route 28 in Elizabeth
Route 28 in Elizabeth

 US 22 / Route 29 in Newark
US 22 / Route 29 in Newark


 US 1 / US 9 / Route 1 in Jersey City
US 1 / US 9 / Route 1 in Jersey CityNorth end: Holland Tunnel in Jersey City Highway system New Jersey State Highway Routes
Interstate and US←  Route 24
Route 24Route 26  →Route 1 Extension
→Route 1 ExtensionLocation: US 1 and 9 milepoint: 51.25-54.55, NJ 139 milepoint 0-4.5
Jersey City, Kearny Point, NewarkArchitect: New Jersey State Highway Commission Governing body: State NRHP Reference#: 05000880[1] Added to NRHP: August 12, 2005 Route 25 was a major state highway in New Jersey, United States prior to the 1953 renumbering, running from the Benjamin Franklin Bridge in Camden to the Holland Tunnel in Jersey City. The number was retired in the renumbering, as the whole road was followed by various U.S. Routes - U.S. Route 30 coming off the bridge in Camden, US 130 from the Camden area north to near New Brunswick, US 1 to Tonnelle Circle in Jersey City, and US 1 Business (since renamed NJ 139) to the Holland Tunnel.
Contents
History
Routes 1 and 2: 1916-1927
In 1916, two routes were defined by the state legislature:
- Route 1, from the south border of Elizabeth via Rahway and Metuchen to the north border of New Brunswick, and from the south border of New Brunswick via Hightstown and Robbinsville to the east border of Trenton.
- Route 2, from the south border of Trenton via White Horse, Bordentown and Burlington to the north border of Camden.
Route 1 used the existing Lincoln Highway from Elizabeth to New Brunswick, except for two sections between Rahway and New Brunswick (where the Lincoln Highway largely used the old Essex and Middlesex Turnpike). A new alignment was built on the northwest side of the Pennsylvania Railroad (now Amtrak's Northeast Corridor) in Woodbridge Township and Edison to avoid two grade crossings, and a detour over existing streets was made in Metuchen to avoid another one in favor of an underpass. This route, including the realignments, was taken over in 1919, except between the south border of Rahway and downtown Metuchen, which was acquired in 1918.
South of New Brunswick, Route 1 used the old New Brunswick and Cranbury Turnpike (Georges Road) to Cranbury and the Bordentown and South Amboy Turnpike to Robbinsville. At Robbinsville it turned west on Nottingham Way, running to the Trenton line on Greenwood Avenue. This section was all taken over in 1919.
Route 2 left Trenton on Broad Street, known as the White Horse Road to White Horse. At White Horse it turned south on what was known as the White Horse Road Extension and Trenton Road, intersecting the Bordentown and South Amboy Turnpike northeast of Bordentown. There it turned southwest along the turnpike, named Park Street in Bordentown, continuing on the Florence Road (old Burlington Turnpike) through Florence Township to Burlington. From Burlington Route 2 kept going southwest on the Westfield and Camden Turnpike, ending at the Camden border at Westfield Avenue. This was also taken over in 1919.
Several amendments in 1922 added to the routes. Route 2 was extended southwest through Camden to the proposed Ben Franklin Bridge, and a spur was added from Five Points northwest to the Tacony-Palmyra Ferry. More important was the extension of Route 1 north to the planned Holland Tunnel.
Route 1 Extension: 1922-1932
The Route 1 Extension is considered to be the first "super highway" in the United States. [1] The highway was built to carry large amounts of traffic from the Holland Tunnel to the rest of the country. The south end of the extension was at Edgar Road in Linden, just south of Elizabeth and the Bayway Circle. Edgar Road had been built as a turnpike in the 19th century, and now serves as part of U.S. Route 1/9 south of the extension.
The road was built from 1927 to 1932, with all but the Pulaski Skyway finished by 1930. It was a full freeway, mostly elevated, from four blocks west of the Holland Tunnel to Newark Airport, and a high-speed surface road from there to Elizabeth (and beyond).
In summer 1923 the Highway Commission decided that it would be an entirely new route, from the Lincoln Highway (Route 1) southwest of Elizabeth to the Holland Tunnel. Existing roads, which passed through downtown Newark, were already experiencing major congestion. Frederick Lavis, Assistant Construction Engineer of the New Jersey State Highway Department, explained this decision:
- The new highway will be the easterly end of the Lincoln Highway and will carry the greater part of the travel between New Jersey coast resorts, and Trenton, Philadelphia and points south of New York. It was to be made part of one of the main through routes from and to New York. It was stated that this route would undoubtedly be used as a main artery of transportation by trucks carrying freight from New Jersey, Pennsylvania and adjacent points to and from New York.
- It was reported that the highway will assume many of the characteristics of a railway, except that the rolling stock will be autos and auto trucks. It was pointed out that in order that the maximum amount of traffic could pass, the highway would have to be free from interruption.
It was also decided that the road would have a minimum width of 50 feet (15 m), which would be enough room for five lanes (presumably with a center suicide lane). At the time, it often took two or three hours to go the fifteen miles (24 km) from New York City to the far border of Elizabeth, and the new highway would take off over an hour. Grades would be at most 3.5%, and curves would have radii of at least 1,000 feet (300 m).
Construction
As part of the Holland Tunnel project, the Interstate Tunnel Commission widened the four blocks of 12th and 14th Streets in Jersey City from Jersey Avenue to Provost Street. 12th Street was widened to 100 feet (30 m) west of Grove Street, with the remaining block, at the toll plaza, being 160 feet (49 m) wide. 14th Street, and the two blocks of Jersey Avenue carrying westbound traffic to the 12th Street Viaduct, were widened to 100 feet (30 m). The Port of New York Authority later built the 14th Street Viaduct to avoid the turns to and from Jersey Street, but turned it over to the New Jersey State Highway Commission.
As part of the project, current U.S. Route 1-9 Truck was built under the Pennsylvania Railroad at Charlotte Circle and east to Tonnelle Circle. This was bypassed by the Pulaski Skyway, the last part of the route to be built; prior to its completion, traffic used what is now US 1-9 Truck.
The city of Elizabeth opposed the alignment along Spring Street, preferring the use of Division Street, but lost the argument.
section opening date Section 20 - Edgar Road to Jersey Street, including the Elizabeth River Viaduct between June 29 and July 4, 1930 Jersey Street to North Avenue used the existing Spring Street North Avenue Elizabeth to South Street Newark
Section 5 - from South Street to Wilson Avenue
Section 4 - north of Wilson AvenueDecember 16, 1928 (northbound side 1949) Pulaski Skyway November 24, 1932 The underpass under the Pennsylvania Railroad at Charlotte Circle, now U.S. 1-9 Truck soon before March 17, 1929 Section 3 - now U.S. Route 1-9 Truck from Charlotte Circle to Tonnelle Circle
Section 2 - cut through the Palisades (now NJ 139)December 16, 1928 Section 1 - 12th Street Viaduct July 4, 1927 (parallel 14th Street Viaduct February 13, 1951) Holland Tunnel November 13, 1927 Route 25: 1927-1953
In the 1927 renumbering, the majority of the Jersey City-Camden corridor, made of Routes 1 and 2, was assigned Route 25. The one major difference was near Trenton; the new Route 25 bypassed Trenton via the old Bordentown and South Amboy Turnpike, cutting from Route 1 at Robbinsville southwest to Route 2 at Bordentown. Route 1 west from Robbinsville to Trenton became part of Route 33, and Route 2 became part of Route 37 from Trenton to White Horse and Route 39 from White Horse to Bordentown. Additionally, the former Route 1 between Elizabeth and New Brunswick became part of Route 27; a new alignment was planned from Elizabeth to south of New Brunswick, running east of the existing road and connecting directly with the Route 1 Extension. The short spur to the Tacony-Palmyra Ferry became Route S41N.
Also in 1927, U.S. Route 1 was assigned to Route 25 north of the New Brunswick area (temporarily signed along Route 27 until Route 25 was finished) and U.S. Route 130 was assigned south to Camden.
North of New Brunswick, the new 50 foot (15 m) wide alignment was completed September 27, 1930; the last part to open was the reconstruction of Edgar Road through Linden, held up by a grade crossing elimination with the Baltimore and New York Railroad. The part of old Route 1 to the south border of New Brunswick became Route 25M. The Pulaski Skyway opened in 1932; sources disagree about whether the old route (U.S. Route 1-9 Truck) became another Route 25M, Route 25T, or an un-suffixed section of 25. (The eastern half of the old road was part of post-1927 New Jersey Route 1.)
The embankment in Newark was doubled ca. 1949, with a new four-lane northbound roadway. The 12th Street Viaduct in Jersey City was supplemented with the 14th Street Viaduct, opened on February 13, 1951.
Many bypasses were built south of New Brunswick:
- Burlington, ca. 1925 (as Route 2)
- Pennsauken Township to Airport Circle east of Camden, ca. 1927
- Bordentown, ca. 1928
- Completed from Airport Circle west to the Ben Franklin Bridge, ca. 1929 (now U.S. Route 30)
- Hightstown and Cranbury, ca. 1937
- South Brunswick Township, ca. 1942
- Yardville, ca. 1952 (the old road became Route 156)
In the 1953 renumbering, the whole route was decommissioned in favor of the U.S. Routes that were signed along it - US 30, US 130, US 1 and US 1 Business.
Major intersections
County Location Mile Destinations Notes Camden Camden Benjamin Franklin Bridge Southern terminus, south end of US 30 overlap  Route 151 west (Flanders Avenue)
Route 151 west (Flanders Avenue)Pennsauken Township 


 US 30 east / US 130 south / Route 43 east / Route 45 south (Crescent Boulevard)
US 30 east / US 130 south / Route 43 east / Route 45 south (Crescent Boulevard)

 Route 38 / Route 40 east
Route 38 / Route 40 eastAirport Circle, north end of US 30 overlap, south end of US 130 overlap  Route S41
Route S41Burlington Cinnaminson Township  Route S41N north (Cinnaminson Avenue)
Route S41N north (Cinnaminson Avenue)Burlington  Route S25 west
Route S25 westBordentown Township 
 US 206 / Route 39 south
US 206 / Route 39 southSouth end of US 206/NJ 39 overlap 
 US 206 / Route 39 north
US 206 / Route 39 northNorth end of US 206/NJ 39 overlap Mercer Washington Township  Route 33 west
Route 33 westSouth end of NJ 33 overlap East Windsor Township  Route 33 east (Mercer Street)
Route 33 east (Mercer Street)North end of NJ 33 overlap Middlesex North Brunswick Township 


 US 1 / Route S26 south / US 130 / Route 25M north
US 1 / Route S26 south / US 130 / Route 25M northNorth end of US 130 overlap, south end of US 1 overlap New Brunswick  Route S28
Route S28Woodbridge Township  G.S. Pkwy.
G.S. Pkwy.Interchange 
 US 9 / Route 35 south
US 9 / Route 35 southSouth end of US 9 overlap  Route 4
Route 4Interchange Union Elizabeth  Route 28 (South Elmora Avenue/Bayway Avenue)
Route 28 (South Elmora Avenue/Bayway Avenue)Essex Newark 

 US 22 west / Route 29 south / Route 21 north
US 22 west / Route 29 south / Route 21 northInterchange  Route 25B north (Port Street)
Route 25B north (Port Street)Airport Circle  NJ Turnpike
NJ TurnpikeNJTP exit 14  Route 25T north
Route 25T northInterchange Hudson Jersey City 

 US 1 / US 9 north / Route 1
US 1 / US 9 north / Route 1Tonnele Circle, north end of US 1/US 9 overlap Holland Tunnel Northern terminus 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi See also
 U.S. Roads portal
U.S. Roads portal New Jersey portal
New Jersey portal- Route 25A, a spur from Jersey City west into Newark
- Route 25AD, a bridge over the Passaic River between Harrison and Newark
- Route 25B, a spur to Port Newark
- Route 25M, a spur to New Brunswick (part of pre-1927 Route 1)
- Route S25, a spur to the Burlington-Bristol Bridge
- Route 25T, part of the truck route from Newark to Jersey City
References
- ^ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. 2009-03-13. http://nrhp.focus.nps.gov/natreg/docs/All_Data.html.
- Vehicular Tunnels Need Broad Roads, New York Times March 15, 1925 page RE2
- Great Express Highways for New York Zone, New York Times November 21, 1926 page XX3
- Jersey Road Link Will Open July 4, New York Times June 19, 1927 page E21
- Reported from the Road, New York Times September 21, 1930 page XX7
- New Jersey Opens New Auto Route, New York Times September 28, 1930 page N5
- US 30 straight line diagram (PDF)
- US 130 straight line diagram (PDF)
- US 1 straight line diagram (PDF)
- NJ 1920s Route 1
- NJ 1920s Route 2
U.S. National Register of Historic Places Topics Lists by states Alabama • Alaska • Arizona • Arkansas • California • Colorado • Connecticut • Delaware • Florida • Georgia • Hawaii • Idaho • Illinois • Indiana • Iowa • Kansas • Kentucky • Louisiana • Maine • Maryland • Massachusetts • Michigan • Minnesota • Mississippi • Missouri • Montana • Nebraska • Nevada • New Hampshire • New Jersey • New Mexico • New York • North Carolina • North Dakota • Ohio • Oklahoma • Oregon • Pennsylvania • Rhode Island • South Carolina • South Dakota • Tennessee • Texas • Utah • Vermont • Virginia • Washington • West Virginia • Wisconsin • WyomingLists by territories Lists by associated states Other Categories:- Historic districts in New Jersey
- State highways in New Jersey
- Lincoln Highway
- U.S. Route 1
- National Register of Historic Places in New Jersey
- Roads on the National Register of Historic Places
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.