- Phragmites
-
This article is about the common reed. For other plants called reed, see Reed (plant).
Phragmites 
Phragmites australis seed head in winter Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae (unranked): Angiosperms (unranked): Monocots (unranked): Commelinids Order: Poales Family: Poaceae Subfamily: Arundinoideae Tribe: Arundineae[1] Genus: Phragmites Species: P. australis Binomial name Phragmites australis
(Cav.) Trin. ex Steud.Phragmites, the Common reed, is a large perennial grass found in wetlands throughout temperate and tropical regions of the world. Phragmites australis is sometimes regarded as the sole species of the genus Phragmites, though some botanists divide Phragmites australis into three or four species. In particular the South Asian Khagra Reed – Phragmites karka – is often treated as a distinct species.[2]
Contents
Taxonomy
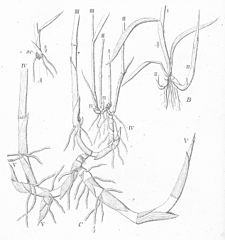 Three Phragmites australis seedlings: A.) very young, B.) juvenile, C.) the oldest (3-4 months). Roman numerals denote different shoot generations.
Three Phragmites australis seedlings: A.) very young, B.) juvenile, C.) the oldest (3-4 months). Roman numerals denote different shoot generations.
Sc = scutellum.
From (Warming 1884.
[clarification needed])The generally accepted botanical name of Common reed is Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud.. However, it is still often known as Phragmites communis Trin.; other synonyms include Arundo phragmites L. (the basionym), Phragmites altissimus, P. berlandieri, P. dioicus, P. maximus, P. vulgaris[clarification needed].
Subspecies
Recent studies have characterised morphological distinctions between the introduced and native stands of Phragmites in North America. The Eurasian genotype can be distinguished from the North American genotype by its shorter ligules of up to 0.9 millimetres (0.04 in) as opposed to over 1.0 millimetre (0.04 in), shorter glumes of under 3.2 millimetres (0.13 in) against over 3.2 millimetres (0.13 in) (although there is some overlap in this character), and in culm characteristics.
- Phragmites australis subsp. americanus - Recently, the North American genotype has been described as a distinct subspecies, subsp. americanus,[3] and
- Phragmites australis subsp. australis - the Eurasian variety is referred to as subsp. australis.[4]
Native and introduced species
In North America, the status of Phragmites australis was a source of confusion and debate. It was commonly considered an exotic species and often invasive species, introduced from Europe. However, there is evidence of the existence of Phragmites as a native plant in North America long before European colonization of the continent[citation needed]. It is now known that the North American native forms of P. a. subsp. americanus are markedly less vigorous than European forms. The recent marked expansion of Phragmites in North America may be due to the more vigorous, but similar-looking European subsp. australis.[4]
Phragmites australis subsp. australis is causing serious problems for many other North American hydrophyte wetland plants, including the native Phragmites australis subsp. americanus. Gallic acid released by Phragmites is degraded by ultraviolet light to produce mesoxalic acid, effectively hitting susceptible plants and seedlings with two harmful toxins.[5][6] Phragmites are so difficult to control that one of the most effective methods of eradicating the plant is to burn it over 2-3 seasons. The roots grow so deep and strong that one burn is not enough.[7]
Growth and habitat
Phragmites australis, Common reed, commonly forms extensive stands (known as reed beds), which may be as much as 1 square kilometre (0.39 sq mi) or more in extent. Where conditions are suitable it can spread at 5 metres (16 ft) or more per year by horizontal runners, which put down roots at regular intervals. It can grow in damp ground, in standing water up to 1 metre (3 ft 3 in) or so deep, or even as a floating mat. The erect stems grow to 2–6 metres (6 ft 7 in–19 ft 8 in) tall, with the tallest plants growing in areas with hot summers and fertile growing conditions.
The leaves are long for a grass, 20–50 centimetres (7.9–20 in) and 2–3 centimetres (0.79–1.2 in) broad. The flowers are produced in late summer in a dense, dark purple panicle, about 20–50 cm long. Later the numerous long, narrow, sharp pointed spikelets appear greyer due to the growth of long, silky hairs.
It is a halophyte, especially common in alkaline habitats, and it also tolerates brackish water,[5] and so is often found at the upper edges of estuaries and on other wetlands (such as grazing marsh) which are occasionally inundated by the sea.
Common reed is suppressed where it is grazed regularly by livestock. Under these conditions it either grows as small shoots within the grassland sward, or it disappears altogether.
In Europe, common reed is rarely invasive, except in damp grasslands where traditional grazing has been abandoned.
Wildlife in reed beds
Main article: Reed bedCommon reed is very important (together with other reed-like plants) for wildlife and conservation, particularly in Europe and Asia, where several species of birds are strongly tied to large Phragmites stands. These include:
- Bearded Reedling (Panurus biarmicus)
- Reed Warbler (Acrocephalus scirpaceus)
- Great Bittern (Botaurus stellaris)
Uses
Phytoremediation water treatment
Main article: Constructed wetlandPhragmites australis is one of the main wetland plant species used for phytoremediation water treatment.
Waste water from lavatories and greywater from kitchens is routed to an underground septic tank-like compartment where the solid waste is allowed to settle out. The water then trickles through a constructed wetland or artificial reed bed, where bioremediation bacterial action on the surface of roots and leaf litter removes some of the nutrients in biotransformation. The water is then suitable for irrigation, groundwater recharge, or release to natural watercourses.
Thatching
Main article: ThatchingReed is used in many areas for thatching roofs. In the British Isles, common reed used for this purpose is known as Norfolk reed or water reed. However "wheat reed" and "Devon reed", also used for thatching, are not in fact reed, but long-stemmed wheat straw.
Other uses
Some other uses for Phragmites australis and other reeds in various cultures include baskets, mats, pen tips, and a rough form of paper.[8] Additionally, the reeds are used as nesting tubes by individuals keeping solitary bees such as Mason Bees.
In the Philippines, Phragmites is known by the local name "tambo". Reed stands flower in December, and the blooms are harvested and bundled into brooms called "walis". Hence the common name of household brooms is "walis tambo".
In Australian Aboriginal cultures, reeds were used to make weapons like spears for hunting game.[9]
Food
Numerous parts of Phragmites can be prepared for consumption. For example, the young stems "while still green and fleshy, can be dried and pounded into a fine powder, which when moistened is roasted [sic] like marshmallows." Also, the wheat-like seeds on the apex of the stems "can be ground into flour or made into gruel." Rootstocks are used similarly.[10]
Legend and literature
When Midas had his ears transformed into donkey's ears, he concealed the fact and his barber was sworn to secrecy. However the barber could not contain himself and rather than confiding in another human, he spoke the secret into a hole in the ground. The reeds that grew in that place then repeated the secret in whispers.
Moses was "drawn out of the water where his mother had placed him in a reed basket to save him from the death that had been decreed by the Pharaoh against the firstborn of all of the children of Israel in Egypt" (Exodus 2:10).[11] However, the plant concerned may have been another reed-like plant, such as papyrus, which is still used for making boats.
One reference to reeds in European literature is Frenchman Blaise Pascal's saying that Man is but a 'thinking reed' — roseau pensant. In Jean de La Fontaine's famous fable The Oak and the Reed — Le chêne et le roseau, the reed tells the proud oak: "I bend, and break not" —"Je plie, et ne romps pas", "before the tree's fall."
-
Reed stems in flower, in France
-
Roadside reed left from previous year, in Hungary
-
Reed stems in autumn, in Virginia
-
Phragmites in Juybar, Iran
See also
References
- ^ "Phragmites australis". Germplasm Resources Information Network. United States Department of Agriculture. 2007-05-09. http://www.ars-grin.gov/cgi-bin/npgs/html/taxon.pl?28091. Retrieved 2009-02-10.
- ^ "Phragmites". Germplasm Resources Information Network. United States Department of Agriculture. 2007-05-09. http://www.ars-grin.gov/cgi-bin/npgs/html/genus.pl?9280. Retrieved 2009-02-10.
- ^ Saltonstall, Peterson, and Soreng
- ^ a b Catling, P.M.; Mitrow, G.l. (2011). "Major invasive alien plants of natural habitats in Canada. 1. European Common Reed (often just called Phragmites), Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. subsp. australis". CBA Bulletin 44 (2): 52–61.
- ^ a b issg Database: Ecology of Phragmites australis
- ^ Changing Climate May Make 'Super Weed' Even More Powerful Newswise, Retrieved on June 4, 2009.
- ^ Stop Invasive Species - Phragmites
- ^ Phragmite
- ^ Unaipon, D. (2001) Legendary Tales of the Australian Aborigines, p. 138, The Miegunyah Press, Melbourne. ISBN 0 522 85246 7.
- ^ Peterson, Lee, "A Field Guide to Edible Wild Plants of Eastern and Central North America",page 228, Houghton Mifflin Company, New York City,accessed the sixth of September, 2010. ISBN 0 395 20445 3
- ^ usu.edu
External links
- Online Field guide to Common Saltmarsh Plants of Queensland
- Invading Species.com Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources and Ontario Federation of Anglers and Hunters
- Species Profile- Common Reed (Phragmites australis), National Invasive Species Information Center, United States National Agricultural Library. Lists general information and resources for Common Reed.
- Cryptic invasion by a non-native genotype of the common reed, Phragmites australis, into North America (pdf file)
- Phragmites australis swamp and reed beds. On the MarLIN website.
- Brandweiner O. et al., Phragmites australis as Alternative Fuel for Clinker Production, DeopTech 2006, Leoben, Austria
Coastal geography Landforms - Anchialine pool
- Avulsion
- Archipelago
- Atoll
- Ayre
- Barrier bar
- Barrier island
- Bay
- Baymouth bar
- Bight
- Brackish marsh
- Cape
- Channel
- Cliff
- Cliff-top dune
- Coast
- Coastal plain
- Coastal waterfall
- Continental margin
- Continental shelf
- Coral reef
- Cove
- Dune
- Estuary
- Firth
- Fjard
- Freshwater marsh
- Fundus
- Geo
- Gulf
- Headland
- Inlet
- Intertidal wetland
- Island
- Islet
- Isthmus
- Lagoon
- Marine terrace
- Mouth bar
- Raised shorelines
- Machair
- Mega delta
- Mudflat
- Natural arch
- Peninsula
- Reef
- Ria
- River delta
- Rocky shore
- Salt marsh
- Shore
- Sound
- Stack
- Strait
- Strand plain
- Submarine canyon
- Tied island
- Tidal island
- Tidal marsh
- Tide pool
- Tombolo
- More...

Beaches Processes - Blowhole
- Coastal erosion
- Concordant coastline
- Current
- Cuspate foreland
- Discordant coastline
- Emergent coastline
- Feeder bluff
- Fetch
- Headlands and bays
- Large scale coastal behaviour
- Longshore drift
- Marine regression
- Marine transgression
- Rip current
- Sea cave
- Sea foam
- Shoal
- Spit
- Submergent coastline
- Surf break
- Surf zone
- Surge channel
- Swash
- Volcanic arc
- Wave-cut platform
- Wave shoaling
- Wind wave
- Wrack zone
Management Related Sustainability Philosophy and
definitionEnvironmentalism · Environmental ethics · Rio Declaration on Environment and Development · Ecological modernization · Stewardship · Sustainable development · Human impact on the environmentPopulation Consumption Anthropization · Anti-consumerism · Ecological footprint · Ethical consumerism · Overconsumption · Sustainability advertising · Sustainable consumption · Tragedy of the commonsTechnology Resource use and conservation Food Food security · Local food · Permaculture · Sustainable agriculture · Sustainable fisheries · Urban horticultureWater Energy Materials Biodiversity Sustainability disciplines and activities Disciplines Sustainable
activitiesSustainable advertising / architecture / art / business / city (infrastructure / drainage) / community / design / education / fashion / gardening / landscape architecture / living / industries / packaging / procurement / tourism / transportManagement Environmental Environmental biotechnology / chemistry / design / economics / engineering / ethics / history / law / psychology / science / sociologyInternational reports and agreements UN Conference on the Human Environment (Stockholm 1972) · Brundtlandt Commission Report, 1983 (Our Common Future, 1987) · Earth Summit (1992) · Agenda 21 (1992) · Convention on Biological Diversity (1992) · ICPD Programme of Action (1994) · Earth Charter · Lisbon Principles · Millennium Declaration (2000) · Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005)Lists and glossaries Lists Climate change topics · Conservation issues / topics · Environmental agreements / health hazards / issues / organisations / topics (studies topics) · Global sustainability statisticsGlossaries Categories:- Arundinoideae
- Halophytes
- Salt marsh plants
- Poaceae genera
- Grasses of the United States
- Grasses of Canada
- Grasses of Mexico
- Flora of Central Mexico
- Flora of Canada
- Flora of the United States
- Flora of the Sierra Nevada region (U.S.)
- Flora of the Rocky Mountains
- Flora of California chaparral and woodlands
- Flora of the California desert regions
- Native grasses of the Great Plains region
- Native grasses of California
- Grasses of Alabama
- Invasive plant species
- Edible plants
- Herbal and fungal hallucinogens
- Psychedelic tryptamine carriers
- Phytoremediation plants
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.









