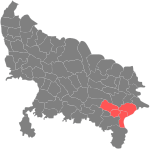
- Divisions of Uttar Pradesh
-
The Indian state of Uttar Pradesh borders with Nepal and the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, Uttarakhand and National Capital Territory of Delhi. The Himalayas lies in the north of the state and the Deccan Plateau is at the south. In between them, the river Ganges, Yamuna, Ghaghra flow eastwards. Uttar Pradesh can be divided into two distinct regions, Southern hills and Gangetic plain
In 1947, when India gained independence, the state of United Provinces was renamed as Uttar Pradesh.[1] The former princely state of Tehri Garhwal joined on 1 August 1949[2] and Rampur joined as a district on 1 December 1949.[3] The States Reorganisation Act of 1956 had no major effect on status of Uttar Pradesh. On 9 November 2000 State of Uttaranchal (having Pauri Garhwal, Tehri Garhwal, Uttar Kashi, Chamoli, Dehradun, Nainital, Almora, Pithoragarh, Udham Singh Nagar, Bageshwar, Champawat, Rudraprayag and Hardwar districts) was carved out of Uttar Pradesh.[4]
Uttar Pradesh is now divided into seventy one districts under eighteen divisions. Districts are administered by District Magistrates, and divisions are administered by Divisional Commissioners. Lucknow, the capital of the state, constitutes the Lucknow district. Other districts are further divided into administrative units such as subdivisions and blocks, administered by SDO and BDO, respectively. The Panchayati Raj has a three-tier structure in the state. The atomic unit is called a Gram Panchayat, which is the Panchayat organization for a collection of villages. The block-level organizations are called Panchayat Samiti, and the district-level organizations are named Zilla Parishad.
Contents
Geography
Main article: Geography of Uttar PradeshUttar Pradesh is India's fifth largest and most populous state, located in the north-western part of the country. It spreads over a large area, and the plains of the state are quite distinctly different from the high mountains in the north. The climate of Uttar Pradesh can also vary widely, with temperatures as high as 47 °C in summer, and as low as −1 °C in winter.
Uttar Pradesh can be divided into two distinct hypsographical regions :
- The Gangetic Plain in the centre – Highly fertile alluvial soils; flat topography broken by numerous ponds, lakes and rivers; slope 2 m/km
- The Vindhya Hills and plateau in the south – Hard rock Strata; varied topography of hills, plains, valleys and plateau; limited water availability.
The climate of the state is tropical monsoon, but variations exist because of difference in altitudes. The Himalayan region is cold. The average temperature varies in the plains from 3 to 4 °C in January to 43 to 45 °C in May and June. There are three distinct seasons – winter from October to February, summer from March to mid-June, and the rainy season from June to September.
Tropical Monsoon Climate Marked By Three Distinct Seasons:
- Summer (March–June): Hot & dry (temperatures rise to 45 °C, sometimes 47–48 °C); low relative humidity (20%); dust laden winds.
- Monsoon (June–September): 85% of average annual rainfall of 990 mm. Fall in temperature 40–45° on rainy days.
- Winter (October–February): Cold (temperatures drop to 3–4 °C, sometimes below −1 °C); clear skies; foggy conditions in some tracts.
Administrative structure
A district is monitored by a District Collector, who is better known as a District Magistrate (DM) in the state of Uttar Pradesh. A DM is an officer from Indian Administrative Service (IAS) or a PCS who gets promoted as an IAS officer on the basis of tenure in Provincial Civil Services Uttar Pradesh Public Service Commission (UPPSC), and is appointed by the Government of Uttar Pradesh. Each district is divided into subdivisions. A subdivision is observed by a sub-divisional magistrate (SDM), better known as a Sub-Divisional Officer (SDO).[5] Other than urban units such as town municipalities, a subdivision contains 'community development blocks' (also known as CD blocks or blocks). A block consists of urban units such as census towns and rural units called gram panchayats. A block is administered by a Block Development Officer (BDO), who is appointed by the Government of Uttar Pradesh.
A gram panchayat, which consists of a group of villages, is administered by a village council headed by a Pradhan.
A District Superintendent of Police, better known as a Superintendent of Police, heads the District Police organization of Uttar Pradesh Police. This is as per the Police Act of 1861, which is applicable to the whole of India.[6] The Superintendents of Police are officers of the Indian Police Service.[7] For every subdivision, there is a Subdivision Police, headed by a Police officer of the rank of Assistant Superintendent of Police or Deputy Superintendent of Police.[8] Under subdivisions, there are Police Circles, each headed by an Inspector of Police.[8] A Police Circle consists of Police Stations, each headed by an Inspector of Police, or in case of rural areas, by a Sub-Inspector of Police.[8]
The Allahabad High Court has the jurisdiction of the state of Uttar Pradesh. Though most of the districts have more courts other than a District Court, not every subdivision of the state has a Court.
A group of districts forms a division, which is administered by a 'Divisional Commissioner'. Uttar Pradesh is now divided in seventy one districts, grouped under eighteen divisions:
Alphabetical listing of divisions
See also
References
- ^ http://www.indiademocracy.org/resource/22
- ^ http://flagspot.net/flags/in-tehri.html
- ^ http://www.manupatrainternational.in/supremecourt/1950-1979/sc1979/s790550.htm
- ^ http://www.helplinelaw.com/docs/THE%20UTTAR%20PRADESH%20REORGANISATION%20ACT,%202000
- ^ Ramesh Kumar Arora, Ramesh Kumar Arora Rajni Goyal. Indian Public Administration: Institutions and Issues. New Age Publishers. p. 298. ISBN 8173280681. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=nvzcy7o4sgAC&pg=PA298&dq=collector+SDO+BDO#PPA297,M1. Retrieved 2008-12-09.
- ^ "The Police Act, 1861". India Code Legislative Department. http://indiacode.nic.in/fullact1.asp?tfnm=186105. Retrieved 2008-12-14.
- ^ "Indian Police Service (Uniform) Rules". Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions, Government of India. http://persmin.nic.in/ais/B11new.htm#s17. Retrieved 2008-12-14.[dead link]
- ^ a b c "Police Organization of India" (PDF). Commonwealth Human Rights Initiative. p. 9. http://www.humanrightsinitiative.org/publications/police/police_organisations.pdf. Retrieved 2008-12-14.
Districts of States of India States Andhra Pradesh · Arunachal Pradesh · Assam · Bihar · Chhattisgarh · Goa · Gujarat · Haryana · Himachal Pradesh · Jammu and Kashmir · Jharkhand · Karnataka · Kerala · Madhya Pradesh · Maharashtra · Manipur · Meghalaya · Mizoram · Nagaland · Orissa · Punjab · Rajasthan · Sikkim · Tamil Nadu · Tripura · Uttar Pradesh · Uttarakhand · West Bengal
Union Territories Andaman and Nicobar Islands · Chandigarh · Dadra and Nagar Haveli · National Capital Territory of Delhi · Daman and Diu · Lakshadweep · PuducherryRelated topics List of states and territories of India · District collector · Sub-Divisional Magistrate · Community Development Block · Block Development Officer · Gram panchayatDivisions and Districts of Uttar Pradesh, India Agra division Aligarh division Aligarh · Etah · Mahamaya Nagar · Kanshi Ram Nagar
Allahabad division Azamgarh division Bareilly division Badaun · Bareilly · Pilibhit · Shahjahanpur
Basti division Chitrakoot division Banda · Chitrakoot · Hamirpur · Mahoba
Devipatan division Faizabad division Gorakhpur division Deoria · Gorakhpur · Kushinagar · Maharajganj
Jhansi division Kanpur division Auraiya · Etawah · Farrukhabad · Kannauj · Kanpur Nagar · Ramabai Nagar
Lucknow division Meerut division Bagpat · Bulandshahr · Gautam Buddha Nagar · Ghaziabad · Meerut · Panchsheel Nagar
Mirzapur division Moradabad division Bhimnagar · Bijnor · Jyotiba Phule Nagar · Moradabad · Rampur
Saharanpur division Prabuddhanagar · Muzaffarnagar · Saharanpur
Varanasi division Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.