- Medial medullary syndrome
-
Medial medullary syndrome Classification and external resources 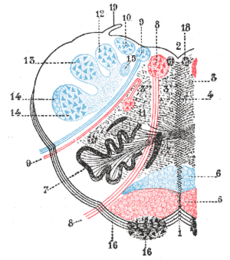
Medulla oblongata, shown by a transverse section passing through the middle of the olive. (Medial medullary syndrome can affect structures in lower left: especially #5, #6, #8.)ICD-10 G46.3 eMedicine emerg/834 Medial medullary syndrome, also known as inferior alternating syndrome, hypoglossal alternating hemiplegia, lower alternating hemiplegia,[1] or Dejerine syndrome,[2] is a type of alternating hemiplegia characterized by a set of clinical features resulting from occlusion of the anterior spinal artery. This results in the infarction of medial part of the medulla oblongata.
Contents
Pathophysiology
The infarction leads to death of the ipsilateral medullary pyramid, the medial leminiscus, and hypoglossal nerve fibers that pass through the medulla. The spinothalamic tract is spared because it is located more laterally in the brainstem and is not supplied by the anterior spinal artery, but rather by the vertebral and posterior inferior cerebellar arteries. The trigeminal nucleus is also spared, since most of it is higher up in the pons, and the spinal part of it found in the medulla is lateral to the infarct.
Presentation
The condition usually consists of:
Description Source of damage Number on diagram a deviation of the tongue to the ipsilateral side of the infarct on attempted protrusion, caused by muscle weakness on the ipsilateral side hypoglossal nerve fibers #8 limb weakness (or hemiplegia, depending on severity), on the contralateral side of the infarct medullary pyramid and hence to the corticospinal fibers of the pyramidal tract #5 a loss of discriminative touch, conscious proprioception, and vibration sense on the contralateral side of the infarct medial leminiscus #6 Sensation to the face is preserved, due to the sparing of the trigeminal nucleus.
The syndrome is said to be "alternating" because the lesion causes symptoms both contralaterally and ipsilaterally. Sensation of pain and temperature is preserved, because the spinothalamic tract is located more laterally in the brainstem and is also not supplied by the anterior spinal artery (instead supplied by the posterior inferior cerebellar arteries and the vertebral arteries).
See also
References
- ^ "Atlas of Microscopic Anatomy: Section 17 - Central Nervous System. Plate 17.330 Medulla Oblongata". http://www.anatomyatlases.org/MicroscopicAnatomy/Section17/Plate17330.shtml. Retrieved 2007-06-07.
- ^ Yokota J, Amakusa Y, Tomita Y, Takahashi S (February 2003). "[The medial medullary infarction (Dejerine syndrome) following chiropractic neck manipulation]" (in Japanese). No To Shinkei 55 (2): 121–5. PMID 12684991.
External links
- http://isc.temple.edu/neuroanatomy/lab/lesions/14.htm
- http://www.neuropat.dote.hu/table/kereszt7.htm
CNS disease, Vascular disease: Cerebrovascular diseases (G45–G46 and I60–I69, 430–438) Brain ischemia/
cerebral infarction
(ischemic stroke/TIA)precerebral: Anterior spinal artery syndrome · Vertebrobasilar insufficiency (Subclavian steal syndrome)brainstem: medulla (Medial medullary syndrome, Lateral medullary syndrome) · pons (Medial pontine syndrome/Foville's, Lateral pontine syndrome/Millard-Gubler) · midbrain (Weber's, Benedikt, Claude's)GeneralIntracranial hemorrhage
(hemorrhagic stroke)Extra-axialBrainstemAneurysm Other/general Categories:- Disease stubs
- Neuroscience stubs
- Brain disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.