- Lateral medullary syndrome
Infobox_Disease
Name = PAGENAME
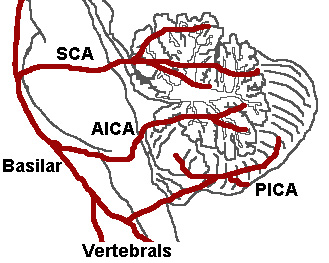
Caption = The three major arteries of the cerebellum: the SCA, AICA, and PICA. (Posterior inferior cerebellar artery is PICA.)
DiseasesDB = 10449
ICD10 = ICD10|G|46|3|g|40
ICD9 =
ICDO =
OMIM =
MedlinePlus =
eMedicineSubj = emerg
eMedicineTopic = 834
MeshID = D014854Lateral medullary syndrome (also called Wallenberg's syndrome and posterior inferior cerebellar artery syndrome) is a disease in which the patient has difficulty with swallowing or speaking or both owing to one or more patches of dead tissue (known as an "infarct") caused by interrupted blood supply to parts of the brain.
igns and symptoms
This syndrome is characterized by sensory deficits affecting the trunk and extremities on the opposite side of the infarct and sensory and motor deficits affecting the face and cranial nerves on the same side with the infarct. Other clinical symptoms and findings are
ataxia , facial pain, vertigo,nystagmus ,Horner's syndrome ,diplopia anddysphagia . The cause of this syndrome is usually the occlusion of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) at its origin.The affected persons have difficulty in swallowing (
dysphagia ) resulting from involvement of thenucleus ambiguus , and slurred speech (dysphonia ,dysarthria ). Damage to the spinaltrigeminal nucleus causes absence of pain on the ipsilateral side of the face, as well as an absentcorneal reflex .The
spinothalamic tract is damaged, resulting in loss of pain and temperature sensation to the opposite side of the body. The damage to thecerebellum or theinferior cerebellar peduncle can cause ataxia.Nystagmus and vertigo, which may result in falling, caused from involvement of the region of
Deiters' nucleus and other vestibular nuclei. Onset is usually acute with severe vertigo.Cause
It is the clinical manifestation resulting from occlusion of the
posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA ) or one of its branches or of thevertebral artery , in which the lateral part of themedulla oblongata infarcts, resulting in a typical pattern. The most commonly affected artery is the vertebral artery, followed by the PICA, superior middle and inferior medullary arteries.Treatment
Treatment for lateral medullary syndrome is symptomatic. A feeding tube may be necessary if swallowing is very difficult. Speech/swallowing therapy may be beneficial. In some cases, medication may be used to reduce or eliminate pain. Some doctors report that the anti-epileptic drug gabapentin appears to be an effective medication for individuals with chronic pain. The small size of the affected PICA does not lend itself to surgical recanalisation.
Prognosis
The outlook for someone with lateral medullary syndrome depends upon the size and location of the area of the brain stem damaged by the stroke. Some individuals may see a decrease in their symptoms within weeks or months. Others may be left with significant neurological disabilities for years after the initial symptoms appeared.
History
This syndrome was first described in 1808 by
Gaspard Vieusseux , [WhoNamedIt|synd|1778] . First descriptions by Wallenberg were in 1895 (clinical) and 1901 (autopsy findings).ee also
* Stroke Recovery
*Weber's syndrome
*Benedikt's syndrome References
External links
*
*
* [http://www.bme.jhu.edu/labs/chb/disorders/wallenbe.html Department of Biomedical Engineering] atJohns Hopkins University
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
