- Close-mid back unrounded vowel
-
Close-mid back unrounded vowel ɤ Image 
IPA number 315 Encoding Entity (decimal) ɤUnicode (hex) U+0264 X-SAMPA 7Kirshenbaum o-Sound
The close-mid back unrounded vowel, or high-mid back unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. Its symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is ɤ, called "ram's horns". It is distinct from the symbol for the voiced velar fricative, ɣ, which has a descender.
The IPA prefers terms "close" and "open" for vowels, and the name of the article follows this. However, a large number of linguists, perhaps a majority, prefer the terms "high" and "low", and these are the only terms found in introductory textbooks on phonetics such as those by Peter Ladefoged.
Before 1989, the symbol for this sound was
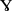 , sometimes called "baby gamma", which has a flat top. Now the symbol is
, sometimes called "baby gamma", which has a flat top. Now the symbol is 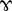 , "ram's horns", with a rounded top. Unicode provides only U+0264 ɤ latin small letter rams horn (HTML:
, "ram's horns", with a rounded top. Unicode provides only U+0264 ɤ latin small letter rams horn (HTML: ɤ), but in some fonts this character may appear as a "baby gamma" instead.Features
IPA vowel chart Front Near-front Central Near-back Back Close Near-close Close-mid Mid Open-mid Near-open Open Paired vowels are: unrounded • rounded This table contains phonetic symbols. They may not display correctly in some browsers (Help).
IPA help • IPA key • chart • chart with audio • view
chart with audio • view- Its vowel height is close-mid, also known as high-mid, which means the tongue is positioned halfway between a close vowel (a high vowel) and a mid vowel.
- Its vowel backness is back, which means the tongue is positioned as far back as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant.
- Its vowel roundedness is unrounded, which means that the lips are not rounded.
Occurrence
Language Word IPA Meaning Notes Alekano gamó [ɣɑmɤʔ] 'cucumber' Chinese Mandarin 喝/hē  [xɤ˥] (help·info)
[xɤ˥] (help·info)'to drink' See Mandarin phonology Taiwanese Hokkien 蚵/ô [ɤ˧] 'oyster' Mostly southern Taiwanese speech Estonian kõrv [kɤrv] 'ear' Irish Uladh [ɤlˠu] 'Ulster' See Irish phonology Korean Gyeongsang dialect 거기/geogi [ˈɡ̊ɤ̘ɡɪ] 'there' See Korean phonology Onge önge [ˈɤŋe] 'man' Scottish Gaelic doirbh [d̪̊ɤrʲɤv] 'difficult' See Scottish Gaelic phonology Thai เธอ [tʰɤː] 'you' Vietnamese tơ [tɤ] 'silk' See Vietnamese phonology International Phonetic Alphabet IPA topics IPA International Phonetic Association · History of the IPA · Kiel convention (1989) · Journal of the IPA (JIPA) · Naming conventionsPhonetics Special topics Encodings Consonants IPA pulmonic consonants chartchart image •  audio
audioPlace → Labial Coronal Dorsal Radical Glottal ↓ Manner Bilabial Labiodental Dental Alveolar Postalv. Retroflex Palatal Velar Uvular Pharyngeal Epiglottal Glottal Nasal m ɱ n̪ n ɳ ɲ ŋ ɴ Plosive p b p̪ b̪ t̪ d̪ t d ʈ ɖ c ɟ k ɡ q ɢ ʡ ʔ Fricative ɸ β f v θ ð s z ʃ ʒ ʂ ʐ ç ʝ x ɣ χ ʁ ħ ʕ ʜ ʢ h ɦ Approximant ʋ ɹ ɻ j ɰ Trill ʙ r ɽ͡r ʀ я * Flap or tap ⱱ̟ ⱱ ɾ ɽ ɢ̆ ʡ̯ Lateral Fric. ɬ ɮ ɭ˔̊ ʎ̥˔ ʟ̝̊ Lateral Appr. l ɭ ʎ ʟ Lateral flap ɺ ɺ̠ ʎ̯ Non-pulmonic consonants Clicks ʘ ǀ ǃ ǂ ǁ Implosives ɓ ɗ ʄ ᶑ ɠ ʛ Ejectives pʼ tʼ cʼ ʈʼ kʼ qʼ fʼ θʼ sʼ ɬʼ xʼ χʼ tsʼ tɬʼ cʎ̝̥ʼ tʃʼ ʈʂʼ kxʼ kʟ̝̊ʼ Affricates p̪f ts dz tʃ dʒ tɕ dʑ ʈʂ ɖʐ tɬ dɮ cç ɟʝ Co-articulated consonants Fricatives ɕ ʑ ɧ Approximants ʍ w ɥ ɫ Stops k͡p ɡ͡b ŋ͡m These tables contain phonetic symbols, which may not display correctly in some browsers. [Help] Where symbols appear in pairs, left—right represent the voiceless—voiced consonants. Shaded areas denote pulmonic articulations judged to be impossible. * Symbol not defined in IPA. Chart image Vowels Vowels: IPA help • chart •  chart with audio • viewCategories:
chart with audio • viewCategories:- Vowels
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.