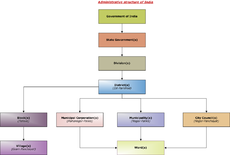
- Administrative divisions of India
-
Republic of India Part of the series
Politics and Government of IndiaLocal & State Govt.- Governor
- State Legislature:
- Vidhan Sabha
- Vidhan Parishad
- Panchayat
- Gram panchayat
- Panchayat samiti
- Zilla Parishad
- Other countries
- Politics Portal
- Government of India Portal
Indian subnational administrative units; they compose a nested hierarchy of country subdivisions. Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision (e.g., the mandals of Andhra Pradesh correspond to tehsils of Uttar Pradesh and other Hindi-speaking states and taluka of Gujarat and Maharashtra). The smaller subdivisions (villages and blocks) exist only in rural areas. In urban areas Urban Local Bodies exist instead of these rural subdivisions.
In the context of the Indian Constitution, local government bodies are the subject of the State List and are thereby governed by State Statutes, or in the case of Union Territories, by the Union Parliament. Federal recognition of local government was substantively expressed in the 74th Constitution Amendment Act of 1992.
The States have been grouped into five zones having an Advisory Council 'to develop the habit of cooperative working” among these States. Five Zonal Councils were set up vide Part-III of the States Re-organisation Act, 1956. The present composition of each of these Zonal Councils is as under:
The Northern Zonal Council, comprising the States of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, National Capital Territory of Delhi and Union Territory of Chandigarh;
The Central Zonal Council, comprising the States of Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh;
The Eastern Zonal Council, comprising the States of Bihar, Jharkhand,Orissa, Sikkim and West Bengal;
The Western Zonal Council, comprising the States of Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra and the Union Territories of Daman & Diu and Dadra & Nagar Haveli; and
The Southern Zonal Council, comprising the States of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
Contents
States and union territories
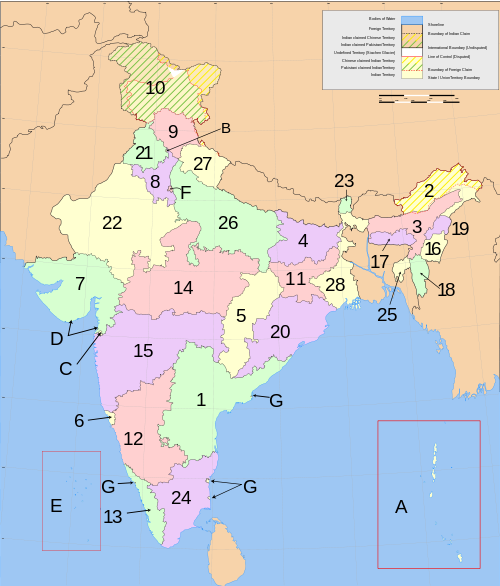
Main article: States and territories of IndiaIndia is composed of 28 states and 7 union territories (including a national capital territory).[1] The union territories are governed by administrators, appointed by the President of India. Two of the territories (Delhi and Puducherry) have been given partial statehood, with elected legislatures and executive councils of ministers, but limited powers.
- States
Number State Code Capital 1 Andhra Pradesh AP Hyderabad 2 Arunachal Pradesh AR Itanagar 3 Assam AS Dispur 4 Bihar BR Patna 5 Chhattisgarh CG Raipur 6 Goa GA Panaji 7 Gujarat GJ Gandhinagar 8 Haryana HR Chandigarh 9 Himachal Pradesh HP Shimla 10 Jammu and Kashmir JK Srinagar 11 Jharkhand JH Ranchi 12 Karnataka KA Bangalore 13 Kerala KL Thiruvananthapuram 14 Madhya Pradesh MP Bhopal 15 Maharashtra MH Mumbai 16 Manipur MN Imphal 17 Meghalaya ML Shillong 18 Mizoram MZ Aizawl 19 Nagaland NL Kohima 20 Orissa OR Bhubaneswar 21 Punjab PB Chandigarh 22 Rajasthan RJ Jaipur 23 Sikkim SK Gangtok 24 Tamil Nadu TN Chennai 25 Tripura TR Agartala 26 Uttar Pradesh UP Lucknow 27 Uttarakhand UK Dehradun 28 West Bengal WB Kolkata - Union territories
Number Union territory Code Capital A Andaman and Nicobar Islands AN Port Blair B Chandigarh CH Chandigarh C Dadra and Nagar Haveli DN Silvassa D Daman and Diu DD Daman E Lakshadweep LD Kavaratti F National Capital Territory ND New Delhi G Puducherry PY Puducherry - See also:
- List of states and union territories of India by population (area can also be found)
- Official languages of India#Languages currently used In Indian states and union territories
Regions
Some of the states of India are divided into regions. The Regions of India are not official administrative divisions. They have no official administrative governmental status. They are purely geographic regions; some correspond to historic countries, states or provinces. A region may comprise one or more divisions, averaging about three divisions per region. However, the boundaries of the regions and the boundaries of the divisions do not always coincide exactly. So far there has been no movement to give the regions official administrative status. If this was to be done, it would presumably require that the boundaries of the regions be slightly modified so that they correspond exactly with their constituent districts.
- Regions of Gujarat
- Regions of Kerala
- Regions of Maharashtra
- Regions of Uttar Pradesh
Divisions
Some of the Indian states are subdivided into divisions, each comprising several districts:
- Divisions of Andhra Pradesh
- Divisions of Arunachal Pradesh
- Divisions of Assam
- Divisions of Bihar
- Divisions of Chhattisgarh
- Divisions of Goa
- Divisions of Gujarat
- Divisions of Haryana
- Divisions of Himachal Pradesh
- Divisions of Jammu and Kashmir
- Divisions of Jharkhand
- Divisions of Karnataka
- Divisions of Kerala
- Divisions of Madhya Pradesh
- Divisions of Maharashtra
- Divisions of Manipur
- Divisions of Meghalaya
- Divisions of Mizoram
- Divisions of Nagaland
- Divisions of Orissa
- Divisions of Punjab (India)
- Divisions of Rajasthan
- Divisions of Sikkim
- Divisions of Tamil Nadu
- Divisions of Tripura
- Divisions of Uttar Pradesh
- Divisions of Uttarakhand
- Divisions of West Bengal
- Divisions of Delhi
Districts
Main article: Districts of IndiaStates and territories (or divisions) are further subdivided into Districts (zilla), of which there are 640.
Sub-Districts
Tehsils, talukas, blocks or mandals (sub-districts), headed by a Tehsildar or Talukdar, comprise several villages or village clusters. The governmental bodies at the Tehsil level are called the panchayat samiti.
States use varying names for their sub-districts. Detailed information is as follows:[2]
State or U.T. Name for sub-district Number of sub-districts Jammu and Kashmir Tahsil 59 Himachal Pradesh Tahsil/Sub-Tahsil 109 Punjab Tahsil 72 Chandigarh Tahsil 1 Uttaranchal Tahsil 49 Haryana Tahsil 67 Delhi Tahsil 27 Rajasthan Tahsil 241 Uttar Pradesh Tahsil 300 Bihar C.D.Block 533 Sikkim Sub-Division 9 Arunachal Pradesh Circle 149 Nagaland Circle 93 Manipur Sub-Division 38 Mizoram R.D.Block 22 Tripura C.D.Block 38 Meghalaya C.D.Block 32 Assam Circle 155 West Bengal C.D.Block 341 Jharkhand C.D.Block 210 Orissa Police Station 485 Chhatisgarh Tahsil 97 Madhya Pradesh Tahsil 259 Gujarat Taluk 226 Daman & Diu Taluk 2 Dadra & Nagar Haveli Taluk 1 Maharashtra Tahsil 353 Andhra Pradesh Mandal 1125 Karnataka Taluk 175 Goa Taluk 11 Lakshadweep Sub-Division 4 Kerala Taluk 63 Tamil Nadu Taluk 201 Pondicherry Commune Panchayat 10 Andaman & Nicobar Islands Tahsil 7 Local level
Blocks
The block is often the next level of administrative division after the tehsil.
Hoblis
A hobli is a subdivision of a taluka which groups adjoining villages in the state of Karnataka. They may have been made for administrative purposes by the revenue department of the state.
Villages
Villages are often the lowest level of subdivisions in India. The governmental bodies at the village level are called Gram Panchayat, of which there were an estimated 256,000 in 2002. Each Gram Panchayat covers a large village or a cluster of smaller villages with a combined population exceeding 500 (Gram Group). Clusters of villages are also sometimes called Hobli.
Habitations
Certain governmental functions and activities - including clean water availability, rural development, and education - are tracked at a sub-village level.[3] These hamlets are termed "habitations". India is composed of approximately 1.6 million habitations.[4] In some states, most villages have a single habitation; in others (notably Kerala and Tripura) there is a high ratio of habitations to villages.[5]
Municipalities
Municipalities of India are governed by Municipal Corporations (Mahanagar Paalika) for large urban areas, Municipal Council (Nagar Paalika) for smaller urban areas, and Town Councils (Nagar Panchayats) for suburban areas. Municipalities can be as large as a district or smaller than a Tehsil.
Historic
See also
- Autonomous regions of India
- Indian states rankings
- Local Governance in India
External links
- Explore places from India hierarchically leading to local information and geographic location on map
- Citymayors.com
- Example of district with different subdivisions
- Seasons, Climate, Global Warming in India - Reference Links Students Project
- Municipal Elections
References
- ^ [1] States and Union Territories of India - Source - Government of India Official Website
- ^ "Statement showing the Nomenclature and Number of Sub-Districts in States/UTs". Office of The Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India, New Delhi. 2010-2011. http://www.censusindia.gov.in/Tables_Published/Admin_Units/Admin_links/subdistrict_nomeclature.html. Retrieved 2011-10-03.
- ^ Indian Department of Drinking Water Supply
- ^ Indian Department of Drinking Water Supply
- ^ Indian Department of Education
v · d · eAdministration in India States Andhra Pradesh · Arunachal Pradesh · Assam · Bihar · Chhattisgarh · Goa · Gujarat · Haryana · Himachal Pradesh · Jammu and Kashmir · Jharkhand · Karnataka · Kerala · Madhya Pradesh · Maharashtra · Manipur · Meghalaya · Mizoram · Nagaland · Orissa · Punjab · Rajasthan · Sikkim · Tamil Nadu · Tripura · Uttar Pradesh · Uttarakhand · West BengalNCT DelhiTerritories Andaman and Nicobar Islands · Chandigarh · Dadra and Nagar Haveli · Daman and Diu · Lakshadweep · Puducherryv · d · eTopics related to Geography of India Climate Geology Geology · Geological historyLandforms Beaches · Desert · Extreme points · Glaciers · Islands · Lakes · Mountains · Rivers · Valleys · Volcanoes · Waterfalls
Plains (Gangetic Plains · Eastern Coastal · Western Coastal)Regions Subdivisions Environment Biosphere Reserves · Ecoregions · Fauna · Flora · National Parks · Protected Areas · Sanctuaries · Wildlifev · d · eSubdivisions of Asia Sovereign
states- Afghanistan
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- Brunei
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Cambodia
- People's Republic of China
- Cyprus
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Egypt
- Georgia
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Israel
- Japan
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- North Korea
- South Korea
- Kuwait
- Kyrgyzstan
- Laos
- Lebanon
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mongolia
- Nepal
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Philippines
- Qatar
- Russia
- Saudi Arabia
- Singapore
- Sri Lanka
- Syria
- Tajikistan
- Thailand
- Turkey
- Turkmenistan
- United Arab Emirates
- Uzbekistan
- Vietnam
- Yemen
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- Palestine
- Republic of China (Taiwan)
- South Ossetia
Dependencies and
other territories- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Hong Kong
- Macau
Categories:- Subdivisions of India
- Divisions of India
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Administrative divisions of France — Politics of France Metropolitan France As of January 1, 2008, metropolitan France is divided into: [fr icon cite web|url=http://www.insee.fr/fr/methodes/nomenclatures/cog/documentation.asp| title=Code officiel géographique… … Wikipedia
Administrative divisions of Portugal — The border between the municipalities of Lisbon and Oeiras; shared also by the civil parishes of Santa Maria de Belém (Lisbon) and Algés (Oeiras) Administratively, Portugal is a unitary and decentralized State. Nonetheless, operationally, it is… … Wikipedia
Administrative divisions of the Republic of China — This article is part of a series on the Administrative divisions of the Republic of China (Taiwan) In effect 1st Provinces (省 shěng) (streamlined) … Wikipedia
Administrative divisions of Burma — … Wikipedia
Administrative divisions of Singapore — While the small physical size of Singapore does not justify the creation of national subdivisions in the form of provinces, states, and other national political divisions found in larger countries, the city state is nonetheless subdivided in… … Wikipedia
Administrative divisions of Azerbaijan — Map of the administrative divisions of Azerbaijan. Note that the divisions of the Nakhchivan exclave are listed in the next section. 1. Absheron Rayon 2. Aghjabadi Rayon 3. Agdam Rayon 4. Agdash Rayon 5. Agstafa Rayon 6 … Wikipedia
Administrative divisions of Armenia — Subdivisions of Armenia Legend Map ref. Administrative division Provincial capital 1 Aragatsotn Ashtarak … Wikipedia
Administrative divisions of Mumbai — The city of Mumbai, India, is divided into administrative divisions. Greater Mumbai is the urban agglomeration of 18 million people (largest in India and one of the six largest in the world) which comes under the Municipal Corporation of Greater… … Wikipedia
List of second-level administrative divisions of North Korea — This is a list of all second level administrative divisions of North Korea, including cities, counties, workers districts, districts, and wards, organized by province or directly governed city. The second level divisions of North Korea as of 2011 … Wikipedia
Divisions of Pakistan — Divisions are the third tier of government in Pakistan, between the provinces and districts. They were abolished in 2000 by the government of former president Pervez Musharraf to make way for local governance via district governments. As of… … Wikipedia
18+© Academic, 2000-2025- Contact us: Technical Support, Advertising
Dictionaries export, created on PHP, Joomla, Drupal, WordPress, MODx.Share the article and excerpts
Administrative divisions of India
- Administrative divisions of India
-
Republic of India Part of the series
Politics and Government of IndiaLocal & State Govt.- Governor
- State Legislature:
- Vidhan Sabha
- Vidhan Parishad
- Panchayat
- Gram panchayat
- Panchayat samiti
- Zilla Parishad

- Other countries
- Politics Portal
- Government of India Portal