- Repaglinide
-
Repaglinide 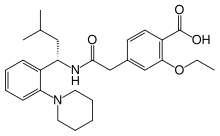
Systematic (IUPAC) name (S)-(+)-2-ethoxy-4-[2-(3-methyl-1-[2-(piperidin-1-yl)phenyl]butylamino)-2-oxoethyl]benzoic acid Clinical data Trade names Prandin AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a600010 Licence data EMA:Link, US FDA:link Pregnancy cat. C (AU, US) Legal status POM (UK) ℞-only (US) Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 56% (oral) Protein binding >98% Metabolism Hepatic oxidation and glucuronidation (CYP3A4-mediated) Half-life 1 hour Excretion Fecal (90%) and renal (8%) Identifiers CAS number 135062-02-1 ATC code A10BX02 PubChem CID 65981 DrugBank APRD00439 ChemSpider 59377 
UNII 668Z8C33LU 
KEGG D00594 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1272 
Chemical data Formula C27H36N2O4 Mol. mass 452.586 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Repaglinide (Prandin in the U.S., GlucoNorm in Canada, Surepost in Japan,Repaglid in Egypt, NovoNorm elsewhere) is for the treatment of type II diabetes. It is supplied by Novo Nordisk. In Japan, Dainippon Sumitomo pharma sells.
Repaglinide belongs to the meglitinide class of blood glucose-lowering drugs.
Contents
Pharmacology
Repaglinide lowers blood glucose by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas. It achieves this by closing ATP-dependent potassium channels in the membrane of the beta cells. This depolarizes the beta cells, opening the cells' calcium channels, and the resulting calcium influx induces insulin secretion.
History
Precursor drugs to repaglinide were invented in late 1983 by scientists at Dr Karl Thomae GmbH, a German drug manufacturer located at Biberach an der Riß in southern Germany which was acquired by Boehringer Ingelheim in 1990. The drug that became repaglinide was later licensed by Boehringer to Novo Nordisk, which filed an Investigational New Drug application for the compound with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 1992. Novo Nordisk filed its New Drug Application (NDA) for Prandin in July 1997 and it was quickly approved, gaining FDA approval in December 1997. The drug was the first of the meglitinide class. It was branded Prandin because its quick onset and short duration of action concentrates its effect around meal time (the prandium was the Roman meal which is comparable to the modern lunch).
Intellectual property
After several attempts to file for U.S. patent protection, a filing was made in March 1990 which eventually became U.S. Patents 5,216,167 (June 1993), 5,312,924 (May 1994) and 6,143,769 (November 2000). After filing its NDA for repaglinide in 1997, Novo Nordisk applied for patent extension under the Hatch-Waxman Act. This process, called patent term restoration, allows drug patents to be extended based on the time that a drug spent in clinical trials and in the approval process. Previously it had been decided by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office that the expiration date of U.S. Patents 5,216,167 and 5,312,924 would be 5 September 2006. In February 2001 Prandin's patent life was extended to 14 March 2009 in response to Novo Nordisk's patent term restoration application, with U.S. Patent 5,216,167 having been reissued as RE37035.[1]
Prior to the end of repaglinide's patent term, Novo Nordisk obtained a new patent, U.S. Patent 6,677,358 (January 2004), covering the combination therapy of repaglinide together with the generic anti-diabetic drug metformin. This new patent was due to expire June 2018. In January 2011, a federal court ruled Novo Nordisk's new patent invalid on the grounds of obviousness, and unenforceable on the grounds of inequitable conduct on the part of Novo Nordisk's patent attorneys.[2]
Generic status
Per the above paragraph, repaglinide will not become available as a generic drug in the United States before March 2009.
Supply
Repaglinide is available in 0.5 mg, 1 mg and 2 mg tablets.
Drug interactions
Repaglinide should not be administered concomitantly with gemfibrozil, clarithromycin or azole antifungals such as itraconazole or ketoconazole[citation needed]. Administration of both repaglinide and one or more of these drugs results in an increase in plasma concentration of repaglinide and may lead to hypoglycemia.
See also
References
- ^ "Details for Patent: RE37035". http://www.drugpatentwatch.com/ultimate/preview/patent/index.php?query=RE37035.
- ^ Frankel, Alison (2011-01-27). "Judge Finds Novo Nordisk Diabetes Drug Patent Invalid and Unenforceable, Questions In-House Patent Lawyer's Conduct". http://www.law.com/jsp/cc/PubArticleCC.jsp?id=1202479538382. Retrieved 2011-02-05.
External links
- Prandin's label
- Prandin Repaglinide Tablets (manufacturer's website)
- RE37035, the reissued U.S. Patent 5,216,167
- U.S. Patent 5,312,924
- U.S. Patent 6,143,769
- U.S. Patent 6,677,358
Oral anti-diabetic drugs and Insulin analogs (A10) Insulin K+ ATPMeglitinides/"glinides"Nateglinide • Repaglinide • MitiglinideGLP-1 analogsExenatide • Liraglutide • Taspoglutide† • Albiglutide† • LixisenatideAnalogs/other insulinsfast-acting (Insulin lispro • Insulin aspart • Insulin glulisine) • short-acting (Regular insulin) • long-acting (Insulin glargine • Insulin detemir • NPH insulin) • ultra-long-acting (Insulin degludec†) • inhalable Exubera‡Other Amylin analogSGLT2 inhibitorsCanagliflozin† • Dapagliflozin† • Remogliflozin§ • Sergliflozin§OtherBenfluorex‡ • Tolrestat‡Categories:- Meglitinides
- Piperidines
- Phenol ethers
- Acetamides
- Benzoic acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
