- Glipizide
-
Glipizide 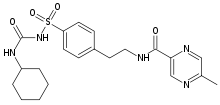
Systematic (IUPAC) name N-(4-[N-(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl]phenethyl)-5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxamide Clinical data Trade names Glucotrol AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a684060 Pregnancy cat. C (Au, U.S.) Legal status POM (UK), ℞-only (U.S.) Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 100% (regular formulation)
90% (extended release)Protein binding 98 to 99% Metabolism Hepatic hydroxylation Half-life 2 to 5 hours Excretion Renal and fecal Identifiers CAS number 29094-61-9 ATC code A10BB07 PubChem CID 3478 DrugBank DB01067 ChemSpider 3359 
UNII X7WDT95N5C 
KEGG D00335 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1073 
Chemical data Formula C21H27N5O4S Mol. mass 445.536 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Glipizide is an oral medium-to-long acting anti-diabetic drug from the sulfonylurea class. It is classified as a second generation sulfonylurea, which means that it undergoes enterohepatic circulation. The structure on the R2 group is a much larger cyclo or aromatic group compared to the 1st generation sulfonylureas. This leads to a once a day dosing that is much less than the first generation, about 100 fold.
Mechanism of action is produced by blocking potassium channels in the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans. By partially blocking the potassium channels, it will increase the time the cell spends in the calcium release stage of cell signaling leading to an increase in calcium. The increase in calcium will initiate more insulin release from each beta cell.
Originally available in 1984, it is marketed by Pfizer under the brand name Glucotrol in the USA, where Pfizer sells Glucotrol in doses of 5 and 10 milligrams and Glucotrol XL (an extended release form of glipizide) in doses of 2.5, 5, and 10 milligrams. Other companies also market glipizide, most commonly extended release tablets of 5 and 10 milligrams.
External links
- Glucotrol XL Full U.S. Prescribing Information. Accessed on July 26, 2005.
Oral anti-diabetic drugs and Insulin analogs (A10) Insulin K+ ATP1st generation: Acetohexamide • Carbutamide • Chlorpropamide • Tolbutamide • Tolazamide
2nd generation: Glibenclamide (Glyburide)# • Glipizide • Gliquidone • Glyclopyramide • Glimepiride • Gliclazide •Meglitinides/"glinides"GLP-1 analogsfast-acting (Insulin lispro • Insulin aspart • Insulin glulisine) • short-acting (Regular insulin) • long-acting (Insulin glargine • Insulin detemir • NPH insulin) • ultra-long-acting (Insulin degludec†) • inhalable Exubera‡Other Amylin analogSGLT2 inhibitorsOtherBenfluorex‡ • Tolrestat‡
This drug article relating to the gastrointestinal system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
