- Dapagliflozin
-
Dapagliflozin 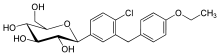
Systematic (IUPAC) name (2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-[4-chloro-3- Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Routes Oral Identifiers CAS number 461432-26-8 
ATC code None PubChem CID 9887712 ChemSpider 8063384 
UNII 1ULL0QJ8UC 
ChEMBL CHEMBL429910 
Synonyms BMS-512148 Chemical data Formula C21H25ClO6 Mol. mass 408.873 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Dapagliflozin (rINN/USAN)[1] is an experimental drug being studied by Bristol-Myers Squibb in partnership with AstraZeneca as a potential treatment for type 1[1] and 2 diabetes. Although dapagliflozin's method of action would operate on either type of diabetes or other conditions resulting in hyperglycemia, the current clinical trials specifically exclude participants with Type 1 diabetes.[2][3]
In July 2011 an FDA committee recommended against approval until more data was available.[4] The Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) date for dapagliflozin for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes was extended three months by the FDA to January 28, 2012.[citation needed]
Method of action
Dapagliflozin inhibits subtype 2 of the sodium-glucose transport proteins (SGLT2), which is responsible for at least 90% of the glucose reabsorption in the kidney. Blocking this transporter causes blood glucose to be eliminated through the urine.[5]
Selectivity
The IC50 for SGLT2 is less than one thousandth of the IC50 for SGLT1 (1.1 versus 1390 nmol/l), so that the drug does not interfere with the intestinal glucose absorption.[6]
References
- ^ a b Statement on a nonproprietory name adopted by the USAN council
- ^ Efficacy and Safety of Dapagliflozin, Added to Therapy of Patients With Type 2 Diabetes With Inadequate Glycemic Control on Insulin, ClinicalTrials.gov, April 2009
- ^ Trial Details for Trial MB102-020, Bristol-Myers Squibb, May 2009
- ^ "FDA panel advises against approval of dapagliflozin". 19 July 2011. http://www.hemonctoday.com/article.aspx?rid=85812.
- ^ Prous Science: Molecule of the Month November 2007
- ^ Schubert-Zsilavecz, M, Wurglics, M, Neue Arzneimittel 2008/2009
Oral anti-diabetic drugs and Insulin analogs (A10) Insulin K+ ATPMeglitinides/"glinides"GLP-1 analogsfast-acting (Insulin lispro • Insulin aspart • Insulin glulisine) • short-acting (Regular insulin) • long-acting (Insulin glargine • Insulin detemir • NPH insulin) • ultra-long-acting (Insulin degludec†) • inhalable Exubera‡Other Amylin analogSGLT2 inhibitorsOtherBenfluorex‡ • Tolrestat‡
This drug article relating to the gastrointestinal system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
