- N-(S)-Fenchyl-1-(2-morpholinoethyl)-7-methoxyindole-3-carboxamide
-
N-(S)-Fenchyl-1-(2-morpholinoethyl)-7-methoxyindole-3-carboxamide 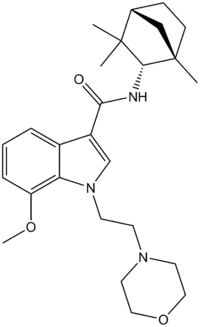
Systematic (IUPAC) name 7-methoxy-1-(2-morpholinoethyl)-N-((1S,2S,4R)-1,3,3-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamide Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status uncontrolled Identifiers ATC code ? PubChem CID 44307202 ChemSpider 26286811 
Chemical data Formula C26H37N3O3 Mol. mass 439.59 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)7-methoxy-1-(2-morpholinoethyl)-N-((1S,4R)-1,3,3-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamide (N-[(S)-fenchyl]-1-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-7-methoxyindole-3-carboxamide) is a drug invented by Bristol-Myers Squibb,[1] that acts as a reasonably selective agonist of peripheral cannabinoid receptors.[2] It has moderate affinity for CB2 receptors with a Ki of 11nM, but 22x lower affinity for the psychoactive CB1 receptors with a Ki of 245nM. The indole 2-methyl derivative has the ratio of affinities reversed however, with a Ki of 8nM at CB1 and 29nM at CB2,[3][4] which contrasts with the usual trend of 2-methyl derivatives having increased selectivity for CB2 (cf. JWH-018 vs JWH-007, JWH-081 vs JWH-098).[5][6]
Chemically, it is closely related to another indole-3-carboxamide synthetic cannabinoid, Org 28611, but with a different cycloalkyl substitution on the carboxamide, and the cyclohexylmethyl group replaced by morpholinylethyl, as in JWH-200 or A-796,260. Early compounds such as these have subsequently led to the development of a large number of related indole-3-carboxamide cannabinoid ligands.[7][8][9][10]
See also
- A-834,735
- AB-001
- AM-1221
- JTE 7-31
- MDA-19
- (1-Pentylindol-3-yl)-(2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropyl)methanone
References
- ^ CANNABINOID RECEPTOR MODULATORS, THEIR PROCESSES OF PREPARATION, AND USE OF CANNABINOID RECEPTOR MODULATORS IN TREATING RESPIRATORY AND NON-RESPIRATORY DISEASES. WO 2001/58869
- ^ Rulin Zhao, Bei Wang, Hong Wu, John Hynes, Jr., Katerina Leftheris, Balu Balasubramanian, Joel C. Barrish and Bang-Chi Chen. Improved procedure for the preparation of 7-methoxy-2-methyl-1-(2-morpholinoethyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid, key intermediate in the synthesis of novel 3-amidoindole and indolopyridone cannabinoid ligands. ARKIVOC 2010 (vi):89-95.
- ^ Hynes, J.; Leftheris, K.; Wu, H.; Pandit, C.; Chen, P.; Norris, D. J.; Chen, B. C.; Zhao, R. et al. (2002). "C-3 Amido-Indole cannabinoid receptor modulators". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 12 (17): 2399. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(02)00466-3.
- ^ Wrobleski, Stephen T.; Chen, Ping; Hynes, John; Lin, Shuqun; Norris, Derek J.; Pandit, Chennagiri R.; Spergel, Steven; Wu, Hong et al. (2003). "Rational Design and Synthesis of an Orally Active Indolopyridone as a Novel Conformationally Constrained Cannabinoid Ligand Possessing Antiinflammatory Properties". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 46 (11): 2110–6. doi:10.1021/jm020329q. PMID 12747783.
- ^ Huffman, J. W.; Padgett, L. W. (2005). "Recent Developments in the Medicinal Chemistry of Cannabimimetic Indoles, Pyrroles and Indenes". Current Medicinal Chemistry 12 (12): 1395–1411. doi:10.2174/0929867054020864. PMID 15974991.
- ^ Manera, C.; Tuccinardi, T.; Martinelli, A. (2008). "Indoles and Related Compounds as Cannabinoid Ligands". Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry 8 (4): 370–387. doi:10.2174/138955708783955935. PMID 18473928.
- ^ Adam, J. M.; Cairns, J.; Caulfield, W.; Cowley, P.; Cumming, I.; Easson, M.; Edwards, D.; Ferguson, M. et al. (2010). "Design, synthesis, and structure–activity relationships of indole-3-carboxamides as novel water soluble cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonists". MedChemComm 1: 54. doi:10.1039/c0md00022a.
- ^ Kiyoi T, York M, Francis S, Edwards D, Walker G, Houghton AK, Cottney JE, Baker J, Adam JM (August 2010). "Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship study of conformationally constrained analogs of indole-3-carboxamides as novel CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonists". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 20 (16): 4918–21. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.06.067. PMID 20634067.
- ^ Moir EM, Yoshiizumi K, Cairns J, Cowley P, Ferguson M, Jeremiah F, Kiyoi T, Morphy R, Tierney J, Wishart G, York M, Baker J, Cottney JE, Houghton AK, McPhail P, Osprey A, Walker G, Adam JM (December 2010). "Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship study of bicyclic piperazine analogs of indole-3-carboxamides as novel cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonists". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 20 (24): 7327–30. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.10.061. PMID 21074434.
- ^ Blaazer, A. R.; Lange, J. H. M.; Van Der Neut, M. A. W.; Mulder, A.; Den Boon, F. S.; Werkman, T. R.; Kruse, C. G.; Wadman, W. J. (2011). "Novel indole and azaindole (pyrrolopyridine) cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonists: Design, synthesis, structure–activity relationships, physicochemical properties and biological activity". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 46 (10): 5086–5098. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.08.021. PMID 21885167.
Further reading
1. John Hynes., Katerina Leftherisa, Hong Wua, Chennagiri Pandita, Ping Chena, Derek J. Norrisa, Bang-Chi Chenb, Rulin Zhaob, Peter A. Kienerc, Xiaorong Chenc, Lori A. Turkc, Vina Patil-Kootac, Kathleen M. Gilloolyc, David J. Shuterc and Kim W. Mclntyrec. C3 AMIDO-INDOLE CANNABINOID RECEPTOR MODULATORS. Bioorganic and Medical Chemistry Letters. Volume 12 issue 17, 2 September 2002 pages 2399-2402
2. Frost, J. M.; Dart, M. J.; Tietje, K. R.; Garrison, T. R.; Grayson, G. K.; Daza, A. V.; El- Kouhen, O. F.; Yao, B. B. et al. (2010) . "Indol -3-ylcycloalkyl Ketones: Effects of N1 Substituted Indole Side Chain Variations on CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Activity" . Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 53 (1 ): 295. doi :10.1021/ jm901214q . PMID 19921781
3. Chin CL, Tovcimak AE, Hradil VP, Seifert TR, Hollingsworth PR, Chandran P, Zhu CZ, Gauvin D, Pai M, Wetter J, Hsieh GC, Honore P, Frost JM, Dart MJ, Meyer MD, Yao BB, Cox BF, Fox GB (January 2008). "Differential effects of cannabinoid receptor agonists on regional brain activity using pharmacological MRI" . British Journal of Pharmacology 153 (2) : 367– 79. doi :10.1038/ sj.bjp .0707506 . PMC 2219521 . PMID 17965748
Cannabinoids Plant cannabinoids Cannabinoid metabolites 8,11-DiOH-THC · 11-COOH-THC · 11-OH-THC
Endogenous cannabinoids Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (Anandamide or AEA) · 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) · 2-Arachidonyl glyceryl ether (noladin ether) · Virodhamine · Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) · N-Arachidonoyl dopamine (NADA) · Oleamide · RVD-Hpα
Synthetic cannabinoid
receptor agonistsClassical cannabinoids
(Dibenzopyrans)A-40174 · A-41988 · A-42574 · Ajulemic acid · AM-087 · AM-411 · AM-855 · AM-905 · AM-906 · AM-919 · AM-926 · AM-938 · AM-4030 · AMG-1 · AMG-3 · AMG-36 · AMG-41 · Dexanabinol (HU-211) · DMHP · Dronabinol · HHC · HU-210 · JWH-051 · JWH-133 · JWH-139 · JWH-161 · JWH-229 · JWH-359 · KM-233 · L-759,633 · L-759,656 · Levonantradol (CP 50,5561) · Nabazenil · Nabidrox (Canbisol) · Nabilone · Nabitan · Naboctate · O-581 · O-774 · O-806 · O-823 · O-1057 · O-1125 · O-1238 · O-2365 · O-2372 · O-2373 · O-2383 · O-2426 · O-2484 · O-2545 · O-2694 · O-2715 · O-2716 · O-3223 · O-3226 · Parahexyl · Perrottetinene · Pirnabine · THC-O-acetate · THC-O-phosphate
Nonclassical cannabinoidsBenzoylindoles1-Butyl-3-(2-methoxybenzoyl)indole · 1-Butyl-3-(4-methoxybenzoyl)indole · 1-Pentyl-3-(2-methoxybenzoyl)indole · AM-630 · AM-679 · AM-694 · AM-1241 · AM-2233 · GW-405,833 (L-768,242) · Pravadoline · RCS-4 · WIN 54,461
NaphthoylindolesNaphthylmethylindolesJWH-175 · JWH-184 · JWH-185 · JWH-192 · JWH-194 · JWH-195 · JWH-196 · JWH-197 · JWH-199
PhenylacetylindolesCannabipiperidiethanone · JWH-167 · JWH-203 · JWH-249 · JWH-250 · JWH-251 · JWH-302 · RCS-8
NaphthoylpyrrolesEicosanoidsAM-883 · Arachidonyl-2'-chloroethylamide (ACEA) · Arachidonylcyclopropylamide (ACPA) · Methanandamide (AM-356) · O-585 · O-689 · O-1812 · O-1860 · O-1861
Others(1-Pentylindol-3-yl)-(2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropyl)methanone · N-(S)-Fenchyl-1-(2-morpholinoethyl)-7-methoxyindole-3-carboxamide · A-796,260 · A-834,735 · A-836,339 · Abnormal cannabidiol · AB-001 · AM-1248 · AZ-11713908 · BAY 38-7271 · BAY 59-3074 · CB-13 · CB-86 · GW-842,166X · JWH-171 · JWH-176 · JTE 7-31 · Leelamine · MDA-19 · O-1918 · O-2220 · Org 28312 · Org 28611 · SER-601 · VSN-16 · WIN 56,098
Allosteric modulators of
cannabinoid receptorsOrg 27569 · Org 27759 · Org 29647
Endocannabinoid
activity enhancersAM-404 · CAY-10401 · CAY-10429 · JZL184 · JZL195 · N-arachidonoyl-serotonin · O-1624 · PF-04457845 · PF-622 · PF-750 · PF-3845 · PHOP · URB-447 · URB-597 · URB-602 · URB-754 · Genistein · Arvanil · Olvanil · Kaempferol · Biochanin A
Cannabinoid receptor
antagonists and
inverse agonistsAM-251 · AM-281 · AM-630 · BML-190 · CAY-10508 · CB-25 · CB-52 · CB-86 · Drinabant · Hemopressin · Ibipinabant (SLV319) · JTE-907 · LY-320,135 · Taranabant (MK-0364) · MK-9470 · NESS-0327 · O-1184 · O-1248 · O-2050 · O-2654 · Otenabant · Rimonabant (SR141716) · SR144528 · Surinabant (SR147778) · TM-38837 · VCHSR
This cannabinoid related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.

