- Sideband
-
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, containing power as a result of the modulation process. The sidebands consist of all the Fourier components of the modulated signal except the carrier. All forms of modulation produce sidebands.[1]
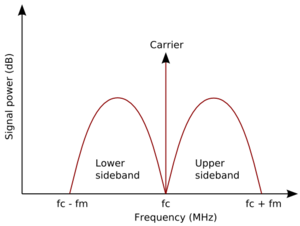
Amplitude modulation of a carrier wave normally results in two mirror-image sidebands. The signal components above the carrier frequency constitute the upper sideband (USB), and those below the carrier frequency constitute the lower sideband (LSB). In conventional AM transmission, the carrier and both sidebands are present, sometimes called double sideband amplitude modulation (DSB-AM).
In some forms of AM, the carrier may be removed, producing double sideband with suppressed carrier (DSB-SC). An example is the stereophonic difference (L-R) information transmitted in stereo FM broadcasting on a 38 kHz subcarrier. The receiver locally regenerates the subcarrier by doubling a special 19 kHz pilot tone, but in other DSB-SC systems, the carrier may be regenerated directly from the sidebands by a Costas loop or squaring loop. This is common in digital transmission systems such as BPSK where the signal is continually present.
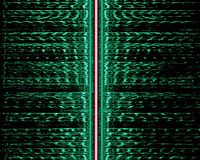 Sidebands are evident in this spectrogram of an AM broadcast (The carrier is highlighted in red, the two mirrored audio spectra (green) are the lower and upper sideband).
Sidebands are evident in this spectrogram of an AM broadcast (The carrier is highlighted in red, the two mirrored audio spectra (green) are the lower and upper sideband).
If part of one sideband and all of the other remain, it is called vestigial sideband, used mostly with television broadcasting, which would otherwise take up an unacceptable amount of bandwidth. Transmission in which only one sideband is transmitted is called single-sideband transmission or SSB. SSB is the predominant voice mode on shortwave radio other than shortwave broadcasting. Since the sidebands are mirror images, which sideband is used is a matter of convention. In amateur radio, LSB is traditionally used below 10 MHz and USB is used above 10 MHz.
In SSB, the carrier is suppressed, significantly reducing the electrical power (by up to 12 dB) without affecting the information in the sideband. This makes for more efficient use of transmitter power and RF bandwidth, but a beat frequency oscillator must be used at the receiver to reconstitute the carrier. Another way to look at an SSB receiver is as an RF-to-audio frequency transposer: in USB mode, the dial frequency is subtracted from each radio frequency component to produce a corresponding audio component, while in LSB mode each incoming radio frequency component is subtracted from the dial frequency.
Sidebands can also interfere with adjacent channels. The part of the sideband that would overlap the neighboring channel must be suppressed by filters, before or after modulation (often both). In Broadcast band frequency modulation (FM), subcarriers above 75 kHz are limited to a small percentage of modulation and are prohibited above 99 kHz altogether to protect the ±75 kHz normal deviation and ±100 kHz channel boundaries. Amateur radio and public service FM transmitters generally utilize ±5 kHz deviation.
See also
- Independent sideband
- Single-sideband modulation for more technical information about sideband modulation
- Sideband computing is a distributed computing method using a separate channel than the main communication channel.
- Out-of-band communications involve a separate channel other than the main communication channel.
- Side lobe
- TV transmitter
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C" (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C" (in support of MIL-STD-188).- partly from Department of The Army Technical Manual TM 11-685 "Fundamentals of Single Sideband Communications"
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.