- Disopyramide
-
Disopyramide 
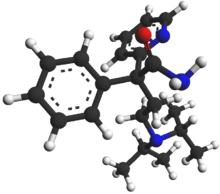
Systematic (IUPAC) name 4-(diisopropylamino)-2-phenyl-2-(pyridin-2-yl)butanamide Clinical data Trade names Norpace AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a682408 Pregnancy cat. B2(AU) C(US) Legal status POM (UK) ℞-only (US) Routes Oral, intravenous Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability High Protein binding 50% to 65%
(concentration-dependent)Metabolism Hepatic (CYP3A4-mediated) Half-life 6.7 hours (range 4 to 10 hours) Excretion Renal (80%) Identifiers CAS number 3737-09-5 
ATC code C01BA03 PubChem CID 3114 DrugBank APRD00507 ChemSpider 3002 
UNII GFO928U8MQ 
KEGG D00303 
ChEBI CHEBI:4657 
ChEMBL CHEMBL517 
Chemical data Formula C21H29N3O Mol. mass 339.475 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Disopyramide (INN, trade names Norpace and Rythmodan) is an antiarrhythmic medication. It is a Class Ia antiarrhythmic (sodium channel blocker) used in the treatment of ventricular tachycardias. It has no effect on alpha or beta adrenergic receptors. It resembles quinidine but it has a marked anti-muscarinic effect on the heart, for this reason, it is not considered as a drug of 1st choice. It is also used in ventricular arrhythmia and supraventricular arrhythmia that might follow myocardial infarctions.
Contents
Cardiac adverse effects
- Acute heart failure[1]
- Severe hypotension
Extracardiac effects
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Urinary retention
- Blurred vision
- Glaucoma
- Rash
- Agranulocytosis
Additionally, disopyramide may enhance the hypoglycaemic effect of gliclazide, insulin, and metformin.
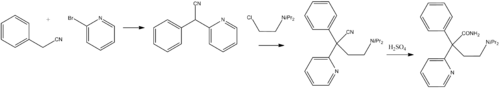
Chemistry
External links
Antiarrhythmic agents (C01B) Channel blockers class Ib (Phase 3←)class Ic (Phase 0→)Amiodarone • Dronedarone • Bretylium • Bunaftine • Dofetilide • Ibutilide • Nifekalant • Sotalol • Tedisamil • Vernakalant • E-4031Receptor agonists
and antagonistsIon transporters 
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.