- Mexiletine
-
Mexiletine 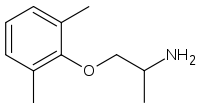
Systematic (IUPAC) name (RS)-1-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)propan-2-amine
OR
2-(2-aminopropoxy)-1,3-dimethylbenzeneClinical data AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a607064 Pregnancy cat. B1(AU) C(US) Legal status POM (UK) Routes Oral, IV Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 90% Protein binding 50-60% Metabolism Hepatic (CYP2D6 and 1A2- mediated) Half-life 10-12 hours Excretion Renal (10%) Identifiers CAS number 31828-71-4 
ATC code C01BB02 PubChem CID 4178 IUPHAR ligand 2629 DrugBank APRD00242 ChemSpider 4034 
UNII 1U511HHV4Z 
KEGG D08215 
ChEBI CHEBI:6916 
ChEMBL CHEMBL558 
Chemical data Formula C11H17NO Mol. mass 179.259 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Mexiletine (INN, sold under the trade name Mexitil) belongs to the Class IB anti-arrhythmic group of medicines. It is used to treat arrhythmias within the heart, or seriously irregular heartbeats. It slows conduction in the heart and makes the heart tissue less sensitive. Dizziness, heartburn, nausea, nervousness, trembling, unsteadiness are common side effects. It is available in injection and capsule form.
Class IB antiarrhythmics decrease action potential duration by shortening the repolarization phase. This is achieved by blocking sodium channels.[1]
Mexiletine may also be of use in patients experiencing refractory pain[2] and is also effective for treating muscle stiffness resulting from myotonia congenita (Thomsen disease) or myotonic dystrophy (Steinert's disease).
References
- ^ Mexiletine, RxList.com
- ^ Sweetman S (ed.) (2002). Martindale: The complete drug reference (33rd ed. ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 0-85369-499-0.
Further reading
- Peck T; Hill S, Williams M (eds.) (2004). Pharmacology for Anaesthesia and Intensive Care (2nd ed. ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-68794-2.
External links
Antiarrhythmic agents (C01B) Channel blockers class Ib (Phase 3←)class Ic (Phase 0→)Amiodarone • Dronedarone • Bretylium • Bunaftine • Dofetilide • Ibutilide • Nifekalant • Sotalol • Tedisamil • Vernakalant • E-4031Receptor agonists
and antagonistsIon transporters 
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
