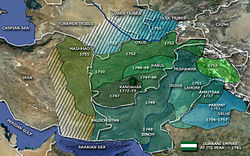
- Durrani Empire
-
Durrani Empire
د درانیانو واکمني← 
←
←
1747–1826  →
→
 →
→
 →
→
 →
→Flag
Capital Kandahar (first)
Kabul (second, summer capital)
Peshawar (second, winter capital)Language(s) Pashto
Dari
UrduGovernment Monarchy History - Established 1747 - Disestablished 1826 Today part of  Afghanistan
Afghanistan
 Iran
Iran
 Pakistan
Pakistan
 India
India
 Tajikistan
Tajikistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Turkmenistan
TurkmenistanThe Durrani Empire (Pashto: د درانیانو واکمني, also referred to as the Afghan Empire[1][2]) was a Pashtun dynasty[3] centered in Afghanistan and included northeastern Iran, the Kashmir region, the modern state of Pakistan, and northwestern India. It was established at Kandahar in 1747 by Ahmad Shah Durrani, an Afghan military commander under Nader Shah of Persia and chief of the Abdali tribe.[4] After the death of Ahmad Shah in about 1773, the Emirship was passed onto his children followed by grandchildren and its capital was shifted to Kabul. Ahmad Shah and his descendants were from the Sadozai line of the Abdalis (later called Durranis), making them the second Pashtun rulers of Kandahar, after the Ghilzai Hotakis.[5][6]
With the support of tribal leaders, Ahmad Shah Durrani extended Afghan control from Meshed to Kashmir and Delhi, from the Amu Darya to the Arabian Sea.[7] Next to the Ottoman Empire, the Durrani was the greatest Muslim Empire in the second half of the eighteenth century.[7] The Durrani Empire is considered the foundation of the current state of Afghanistan,[8] with Ahmad Shah Durrani being credited as "Father" of Afghanistan.[6][9] Even before the death of Nader Shah of Persia in 1747, tribes around the Hindu Kush region had been growing stronger and were beginning to take advantage of the waning power of their distant rulers.[6]
Contents
Reign of Ahmad Shah Durrani (1747-1772)
Main article: Ahmad Shah DurraniNader Shah's Turkmen Afsharid rule ended in June 1747 after being murdered by his Persian soldiers.[10] In October of 1747, when the chiefs of the Afghans met at a loya jirga (grand council) in Kandahar to select a new ruler for the Abdali confederation, the young 25-year-old Ahmad Shah Abdali was chosen. Despite being younger than other claimants, Abdali had several overriding factors in his favor:
- He was a direct descendant of Asadullah Khan, patriarch of the Sadozai clan, the most prominent tribe amongst the Pashtun people at the time;
- He was unquestionably a charismatic leader and seasoned warrior who had at his disposal a trained, mobile force of 4,000 loyal cavalrymen;[7]
- Not least, he possessed a substantial part of Nadir Shah's treasury.
One of Abdali's first acts as chief was to adopt the title Padshah durr-i durrān ('King, "pearl of the age"[11] or "pearl of pearls").[7] The name may have been suggested, as some claim, from Abdali's dream, or as others claim, from the pearl earrings worn by the royal guard of Nadir Shah. The Abdali Pashtuns were known thereafter as the Durrani, and the name of the Abdali confederation was changed to Durrani.
Early victories
 Kabul silver rupee under the Durrani Shahs of Afghanistan, 18th century.
Kabul silver rupee under the Durrani Shahs of Afghanistan, 18th century.
Ahmad Shah began his rule by capturing Ghazni from the Ghilzais, and then wresting Kabul from the local ruler. In 1749, the Mughal ruler was induced to cede Sindh, the Punjab region and the important trans Indus River to Ahmad Shah in order to save his capital from Afghan attack. Having thus gained substantial territories to the east without a fight, Ahmad Shah turned westward to take possession of Herat, which was ruled by Nader Shah's grandson, Shah Rukh of Persia. Herat fell to Ahmad after almost a year of siege and bloody conflict, as did Mashhad (in present-day Iran). Ahmad Shah next sent an army to subdue the areas north of the Hindu Kush mountains. In short order, the powerful army brought under its control the Turkmen, Uzbek, Tajik and Hazaras tribes of northern Afghanistan. Ahmad invaded the remnants of the Mughal Empire a third time, and then a fourth, consolidating control over the Punjab and Kashmir regions. Then, early in 1757, he sacked Delhi, but permitted the Mughal dynasty to remain in nominal control of the city as long as the ruler acknowledged Ahmad Shah's suzerainty over Punjab, Sindh, and Kashmir. Leaving his second son Timur Shah to safeguard his interests, Ahmad Shah left India to return to Afghanistan.
East Turkistan and the Uyghurs
Sympathizing with the plight of the Uyghurs, whose lands were conquered by the Qing dynasty, Ahmad Shah attempted to rally neighboring Muslim nations to check Qing expansion.[12] Ahmad Shah halted trade with Qing China and dispatched troops to Kokand.[13] However, with his campaigns in India exhausting the state treasury, and with his troops stretched thin throughout Central Asia, Ahmad Shah lacked sufficient resources to check the advance of Qing forces. In an effort to alleviate the situation in East Turkistan, Ahmad Shah sent envoys to Beijing, but the talks did not yield favorable results for the Uyghurs.
Third Battle of Panipat
Main article: Third Battle of PanipatThe Mughal power in northern India had been declining since the reign of Aurangzeb, who died in 1707; In 1751-52, Ahamdiya treaty was signed between the Marathas and Mughals, when Balaji Bajirao was the Peshwa.[14] Through this treaty, the Marathas controlled virtually the whole of India from their capital at Pune and Mughal rule was restricted only to Delhi (the Mughals remained the nominal heads of Delhi). Marathas were now straining to expand their area of control towards the Northwest of India. Ahmad Shah sacked the Mughal capital and withdrew with the booty he coveted. To counter the Afghans, Peshwa Balaji Bajirao sent Raghunathrao. He succeeded in ousting Timur Shah and his court from India and brought Lahore, Multan, Kashmir and other subahs on the Indian side of Attock under Maratha rule.[15] Thus, upon his return to Kandahar in 1757, Ahmad was forced to return to India and face the formidable attacks of the Maratha Confederacy.
Ahmad Shah declared a jihad (or Islamic holy war) against the Marathas, and warriors from various Pashtun tribes, as well as other tribes such as the Baloch, Tajiks, and Nawabs in India, answered his call. Early skirmishes were followed by victory for the Afghans against the smaller Maratha garrisons in Northwest India and by 1759 Ahmad and his army had reached Lahore and were poised to confront the Marathas. By 1760, the Maratha groups had coalesced into a big enough army under the command of Sadashivrao Bhau. Once again, Panipat was the scene of a confrontation between two warring contenders for control of northern India. The Third Battle of Panipat (January 1761), fought between largely Muslim and largely Hindu armies was waged along a twelve-kilometer front. Despite decisively defeating the Marathas, what might have been Ahmad Shah's peaceful control of his domains was disrupted by other challenges.
Decline
The victory at Panipat was the high point of Ahmad Shah's—and Afghan—power. His Durrani empire was one of the largest Islamic empires in the world at that time.[16] However, even prior to his death, the empire began to unravel. In 1762, Ahmad Shah crossed the passes from Afghanistan for the sixth time to subdue the Sikhs. He assaulted Lahore and, after taking their holy city of Amritsar, massacred thousands of Sikh inhabitants, destroying their revered Golden Temple. Within two years, the Sikhs rebelled again and rebuilt their holy city of Amritsar. Ahmad Shah tried several more times to subjugate the Sikhs permanently, but failed.
Ahmad Shah also faced other rebellions in the north, and eventually he and the Uzbek Emir of Bukhara agreed that the Amu Darya would mark the division of their lands. Ahmad Shah retired to his home in the mountains east of Kandahar, where he died on (April 14, 1773).[17] He had succeeded to a remarkable degree in balancing tribal alliances and hostilities, and in directing tribal energies away from rebellion. He earned recognition as Ahmad Shah Baba, or "Father" of Afghanistan.[6][9]
The main cause of the decline of the Durrani Empire was relentless efforts of the Sikhs. After suffering at the hands of the Afghans the Sikhs reunited, and as more and more Hindus converted to Sikhism, their army increased and they were able to re-capture Amritsar (1802), Ludhiana (1806), Multan, Kashmir, Laddakh, Peshawar, the Khyber Pass and Lahore. By the time Ranjit Singh of the Sikh Empire died, the Sikhs had taken almost all of Pakistan and Kashmir from the Afghans. Dost Mohammad of the Afghans put up much resistance, even defeating Ranjit Singh in Kandahar, but that did not stop the Sikhs from capturing Peshawar. Dost Mohammad and the Afghans were defeated in 1814, giving the Sikhs control of the strategically important Khyber Pass.[18][19]
The last Sikh-Afghan battle was fought in 1837. The construction of Fort Jamrud next to Afghanistan made the Durrani rulers feel that Kabul was insecure, so Dost Muhammad and Akbar Khan led an attack on that fort. This failed however, and the Sikhs not only saved Fort Jamrud but also captured the Khyber Pass, which connects Pakistan and Afghanistan. The death of Hari Singh was the only solace for the Afghans. After this, the death of Ranjit Singh and the Sikh-Anglo war stopped the Sikh Empire from growing any further.
Forming a nation
By the time of Ahmad Shah's ascendancy, the Pashtuns included many groups whose origins were obscure; it is commonly believed they descended from ancient Aryan tribes, some, such as the Ghilzai, believe they may have intermingled with Turks, and some believe to be descendents of the Israelites that might have settled in the Pashtun areas. The Durranis are Persianized in culture due to their contacts with the nearby Persians. What they had in common was their education and love of Islam. To the east, the Waziris and their close relatives, the Mahsuds, had lived in the hills of the central Sulaiman Mountains since the 14th century. By the end of the 16th century, when the final Turkish-Mongol invasions occurred, tribes such as the Shinwaris, Yusufzais and Mohmands had moved from the upper Kabul River valley into the valleys and plains west, north, and northeast of Peshawar. The Afridis had long been established in the hills and mountain ranges south of the Khyber Pass. By the end of the eighteenth century, the Durranis had blanketed the area west and north of Kandahar and were to be found as far east as Quetta, Baluchistan.
Other Durrani rulers (1772-1826)
History of Afghanistan Timeline Bronze age and Proto-Elamite culture in Nimruz area (2300–1800 BC) Bronze age and Indus valley civilization in Mundigak (Kandahar area) (2200–1800 BC) Bronze age and Oxus civilization in northern Afghanistan (2100–1800 BC) Late Bronze age and Iron age and coming of Aryans (1700–700 BC) Median Empire (728–550 BC) Achaemenids (550–330 BC) Seleucids (330–150 BC) Mauryans (305–180 BC) Greco-Bactrians (256–125 BC) Indo-Greeks (180–130 BC) Indo-Scythians (Sakas) (155–80? BC) Indo-Parthians (20 BC–50? AD) Kushans (135 BC–248 AD) Sassanids (230–565) Indo-Sassanids (248–410) Kidarites (320–465) Hephthalites (410–557) Kabul Shahi (565–879) Rashidun Caliphate (642–641) Umayyads (661–750) Abbasids (750–821) Tahirids (821–873) Saffarids (863–900)) Samanids (875–999) Ghaznavids (963–1187) Seljukids (1037–1194) Khwarezmids (1077–1231) Ghorids (1149–1212) Ilkhanate (1258–1353) Kartids (1245–1381) Timurids (1370–1506) Arghun (1479-1522) Mughals (1501–1738) Safavids (1510–1709) Hotaki dynasty (1709–1738) Afsharids (1738–1747) Modern historyDurrani Empire (1747–1826) Emirate of Afghanistan (1826–1919) Kingdom of Afghanistan (1919–1973) Republic of Afghanistan (1973–1978) Democratic Republic (1978–1992) Islamic State (1992–1996) Islamic Emirate (1996–2001) Islamic Republic (2001–) Afghan Civil War 1979–1989 1989–1992 1992–1996 1996–2001 2001–present

Part of a series on
PashtunsKingdoms (Lodi · Suri
Hotaki · Durrani)
Afghanistan · Pakistan
Pashtunistan · Pakhtunkhwa
Pashtunization
Ahmad Shah's successors governed so ineptly during a period of profound unrest that within fifty years of his death, the Durrani empire per se was at an end, and Afghanistan was embroiled in civil war. Much of the territory conquered by Ahmad Shah fell to others in this half century. By 1818, the Sadozai rulers who succeeded Ahmad Shah controlled little more than Kabul and the surrounding territory within a 160-kilometer radius. They not only lost the outlying territories but also alienated other tribes and lineages among the Durrani Pashtuns.
Timur Shah (1772-1793)
Main article: Timur Shah DurraniAhmad Shah was succeeded by his son, Timur Shah, who had been deputed to administer his fathers conquests in northern India, but had been driven out by the Marathas. Upon Ahmad Shah's death, the Durrani chieftains only reluctantly accepted Timur's accession. Most of his reign was spent fighting a civil war and resisting rebellion; Timur was even forced to move his capital from Kandahar to Kabul due to insurgency. Timur Shah proved an ineffectual ruler, during whose reign the Durrani empire began to crumble. He is notable for having had 24 sons, several of whom became rulers of the Durrani territories. Timur died in 1793, and was then succeeded by his fifth son Zaman Shah
Zaman Shah (1793-1801)
Main article: Zaman Shah DurraniAfter the death of Timur Shah, three of his sons, the governors of Kandahar, Herat and Kabul, contended for the succession. Zaman Shah, governor of Kabul, held the field by virtue of being in control of the capital, and became shah at the age of twenty-three. Many of his half-brothers were imprisoned on their arrival in the capital for the purpose, ironically, of electing a new shah. The quarrels among Timur's descendants that threw Afghanistan into turmoil also provided the pretext for the intervention of outside forces.
The efforts of the Sadozai heirs of Timur to impose a true monarchy on the truculent Pashtun tribes, and their efforts to rule absolutely and without the advice of the other major Pashtun tribal leaders, were ultimately unsuccessful. The Sikhs became particularly troublesome, and after several unsuccessful efforts to subdue them, Zaman Shah made the mistake of appointing a forceful young Sikh chief, Ranjit Singh, as his governor in the Punjab. This "one-eyed" warrior would later become an implacable enemy of Pashtun rulers in Afghanistan.
Zaman's downfall was triggered by his attempts to consolidate power. Although it had been through the support of the Barakzai chief, Painda Khan Barakzai, that he had come to the throne, Zaman soon began to remove prominent Barakzai leaders from positions of power and replace them with men of his own lineage, the Sadozai. This upset the delicate balance of Durrani tribal politics that Ahmad Shah had established and may have prompted Painda Khan and other Durrani chiefs to plot against the shah. Painda Khan and the chiefs of the Nurzai and the Alizai Durrani clans were executed, as was the chief of the Qizilbash clan. Painda Khan's son fled to Iran and pledged the substantial support of his Barakzai followers to a rival claimant to the throne, Zaman's older brother, Mahmud Shah. The clans of the chiefs Zaman had executed joined forces with the rebels, and they took Kandahar without bloodshed.
Mahmud Shah (first reign, 1801-1803)
Main article: Mahmud Shah DurraniZeman Shah's overthrow in 1801 was not the end of civil strife in Afghanistan, but the beginning of even greater violence. Mahmud Shah's first reign lasted for only two years before he was replaced by Shuja Shah.
Shuja Shah (1803-1809)
Main article: Shuja Shah DurraniYet another of Timur Shah's sons, Shuja Shah (or Shah Shuja), ruled for only six years. On June 7, 1809, Shuja Shah signed a treaty with the British, which included a clause stating that he would oppose the passage of foreign troops through his territories. This agreement, the first Afghan pact with a European power, stipulated joint action in case of Franco-Persian aggression against Afghan or British dominions. Only a few weeks after signing the agreement, Shuja was deposed by his predecessor, Mahmud. Much later, he was reinstated by the British, ruling during 1839-1842. Two of his sons also ruled for a brief period in 1842.
Mahmud Shah (second reign, 1809-1818)
Main article: Mahmud Shah DurraniMahmud's second reign lasted nine years. Mahmud alienated the Barakzai, especially Fateh Khan, the son of Painda Khan, who was eventually seized and blinded. Revenge would later be sought and obtained by Fateh Khan's youngest brother, Dost Mohammad Khan.
Sultan Ali Shah (1818-1819)
Main article: Ali Shah DurraniAli Shah was another son of Timur Shah. He seized power for a brief period in 1818-19.
Ayub Shah (1819-1823?)
Main article: Ayub Shah DurraniAyub Shah was another son of Timur Shah, who deposed Sultan Ali Shah. He was himself later deposed, and presumably killed in 1823. The loss of Kashmir during his reign opened a new chapter in South Asian history.
See also
- History of Afghanistan
- History of Pakistan
- History of Iran
- List of Sunni Muslim dynasties
Notes
- ^ "Last Afghan empire". Louis Dupree, Nancy Hatch Dupree and others. Encyclopædia Britannica. 2010. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/7798/Afghanistan/21392/Last-Afghan-empire. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ "Afghanistan (Archived)". John Ford Shroder. University of Nebraska. 2010. http://www.webcitation.org/5kwDUj6WJ. Retrieved 2010-03-21.
- ^ Jaffrelot, Christophe, A History of Pakistan and its Origins, (Anthem Press, 2002), 200.
- ^ "Aḥmad Shah Durrānī". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2010. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/10162/Ahmad-Shah-Durrani. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ Malleson, George Bruce (1984). History of Afghanistan, from the earliest period to the outbreak of the war of 1878. Adegi Graphics LLC. p. Chapter 7: The Ghilzai Rule. ISBN 1402172788, 9781402172786. http://books.google.com/books?id=pqNGBEmHUd4C. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ a b c d "Ahmad Shah and the Durrani Empire". Library of Congress Country Studies on Afghanistan. 1997. http://lcweb2.loc.gov/cgi-bin/query/r?frd/cstdy:@field(DOCID+af0010). Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ a b c d "The Durrani dynasty". Louis Dupree, Nancy Hatch Dupree and others. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 2010. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/7798/Afghanistan/21396/The-Durrani-dynasty. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ "Afghanistan". CIA. The World Factbook. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/af.html. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ a b Ganḍā, Singh (1959). Ahmad Shah Durrani: Father of Modern Afghanistan. Asia Pub. House. pp. 457. ISBN 1402172788, 9781402172786. http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=F_A8AAAAMAAJ. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ Vogelsang, Willem (2003). The Afghans. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 228. ISBN 0631198415, 9780631198413. http://books.google.com/books?id=9kfJ6MlMsJQC. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ Vogelsang, Willem (2003). The Afghans. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 229. ISBN 0631198415, 9780631198413. http://books.google.com/books?id=9kfJ6MlMsJQC. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ Kim, Ho-dong (2004). Holy war in China: the Muslim rebellion and state in Chinese Central Asia, 1864-1877. Stanford University Press. p. 20. ISBN 0804748845, 9780804748841. http://books.google.com/books?id=9kfJ6MlMsJQC. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ Newby, Laura J. (2005). The Empire and the Khanate: a political history of Qing relations with Khoqand c. 1760-1860. BRILL. p. 34. ISBN 9004145508, 9789004145504. http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=KTmO416hNQ8C. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ Patil, Vishwas. Panipat.
- ^ Roy, Kaushik. India's Historic Battles: From Alexander the Great to Kargil. Permanent Black, India. pp. 80–1. ISBN 978-8178241098.
- ^ "Afghanistan and the Search for Unity" Omrani, Bijan, published in Asian Affairs, Volume 38, Issue 2, 2007, pp. 145–157.
- ^ Reddy, L. R (2002). Inside Afghanistan: end of the Taliban era?. APH Publishing. p. 65. ISBN 8176483192, 9788176483193. http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=NubtDf2T3cAC. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ http://books.google.co.in/books?id=2wANAAAAIAAJ&q=ranjit+singh+defeated+dost+mohammad+khyber+pass&dq=ranjit+singh+defeated+dost+mohammad+khyber+pass&hl=en&ei=7nYpTuOMHs6HmQWdysiNDA&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=5&ved=0CEMQ6AEwBA
- ^ http://books.google.co.in/books?id=29bg7g1U6coC&pg=PA43&dq=sikh+empire+in+peshawar,attock&hl=en&ei=RHcpTvawIu-OmQWmj92dDA&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=4&ved=0CEEQ6AEwAw#v=onepage&q=sikh%20empire%20in%20peshawar%2Cattock&f=false
References
- Malleson, George Bruce (1879) History of Afghanistan, from the Earliest Period to the Outbreak of the War of 1878 W.H. Allen & Co., London, OCLC 4219393, limited view at Google Books
- Singh, Ganda (1959) Ahmad Shah Durrani: Father of Modern Afghanistan Asia Publishing House, London, OCLC 4341271
- Fraser-Tytler, William Kerr (1953) Afghanistan: A Study of Political Developments in Central and Southern Asia Oxford University Press, London, OCLC 409453
- Tanner, Stephen (2002) Afghanistan : a military history from Alexander the Great to the fall of the Taliban Da Capo Press, New York, ISBN 0-306-81164-2, also available from NetLibrary
External links
- Afghanistan 1747-1809: Sources in the India Office Records
- Some details and images of Durrani coins
- Biography of Ahmad Shah Abdali (Durrani)
- Ahmad Shah Baba
- History of Abdali tribe
- Detailed genealogy of the Durrani dynasty
- Afghanistan and the Search for Unity Article on Durrani methods of government, published in Asian Affairs, Volume 38, Issue 2, 2007, pp. 145–157.
 Iran topics
Iran topicsHistory Pre-IslamicPrehistory · Proto-Elamite civilization BCE 3200– BCE 2800 · Elamite dynasties BCE 2800– BCE 550 · Bactria-Margiana Complex BCE 2200– BCE 1700 · Kingdom of Mannai BCE 10th– BCE 7th cent. · Median Empire BCE 728– BCE 550 · Achaemenid Empire BCE 550– BCE 330 · Seleucid Empire BCE 330– BCE 150 · Greco-Bactrian Kingdom BCE 250– BCE 125 · Parthian Empire BCE 248–CE 224 · Kushan Empire CE 30–CE 275 · Sassanid Empire CE 224–CE 651 · Hephthalite Empire CE 425–CE 557 · Kabul Shahi kingdom CE 565–CE 879
IslamicPatriarchal Caliphate 637–651 · Umayyad Caliphate 661–750 · Abbasid Caliphate 750–1258 · Tahirid dynasty 821–873 · Alavid dynasty 864–928 · Saffarid dynasty 861–1003 · Samanid dynasty 819–999 · Ziyarid dynasty 928–1043 · Buyid dynasty 934–1055 · Ghaznavid Empire 975–1187 · Ghori dynasty 1149–1212 · Seljuk Empire 1037–1194 · Khwarezmid dynasty 1077–1231 · Ilkhanate 1256–1335 · Kartids dynasty 1231–1389 · Ottoman Empire 1299–1923 · Muzaffarid dynasty 1314–1393 · Chupanid dynasty 1337–1357 · Jalayerid dynasty 1339–1432 · Timurid Empire 1370–1506 · Qara Qoyunlu Turcomans 1407–1468 · Aq Qoyunlu Turcomans 1378–1508 · Safavid Empire 1501–1722 or 1736 · Hotaki dynasty 1722–1729 · Afsharid dynasty 1736–1750 · Zand Dynasty 1750–1794 · Durrani Empire 1794–1826 · Qajar Dynasty 1794–1925
ModernSee also: Greater Iran · Ancient Iran · Iranian Cultural Continent · Indo-Iranians (languages) · Jiroft civilization · Aryans · Persian peoples · Iranian peoples · Tajiks · Kings of Persia · Military history · Years in IranPolitics
GovernmentIntellectual movements · Women's movement · Elections · Constitution · Supreme Leader · President · Judicial system · Assembly of Experts · Parliament · Guardian Council · Expediency Discernment Council · Supreme National Security Council · City and Village Councils · Human rights (LGBT) · Officials · Provincial governors · Reformists · Principlists · United Nations Security Council Resolution 1747 · Ambassadors · Foreign relations · Ministry of Intelligence · Terrorism · Military (Army · Air Force · Navy) · Censorship · Nuclear program · Allegations of state terrorism · Iranian Green Revolution Anglo-Iranian Oil Company · Operation Ajax · White Revolution · Iranian Revolution · Embassy siege · Iran-Iraq war · Iran Air Flight 655 · 1987 massacre of Iranian pilgrims · Chicago's Persian heritage crisis · History of the Islamic Republic of Iran · Iranian Presidential Election, 2009 · Persian Constitutional Revolution ·Demographics Iranian citizens (abroad) · Religion · Muslims · Bahá'ís · Christians · Armenians · Jews · Ethnic minorities · Religious minorities · Zoroastrians (persecution) · WomenLanguages Geography Cities (list) · Iranian Azerbaijan · Iranian Balochistan · Iranian Kurdistan · Iranian Plateau · Islands · Mountains · Provinces · Earthquakes · WildlifeEconomy Economic history of Iran · Agriculture · Fruit · Industry · Water and sanitation · Health care · Central bank · Companies (automobile manufacturers - Banks) · Research centers · Brain drain · Iran Electronics Industries (IEI) · Military equipment · IDRO · National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) · Iran Aviation Industries Organization (IAIO) · Space · Milad Tower and complex · Military exports · Rial · Tehran Stock Exchange · Electronic banking · Intellectual property · International Oil Bourse · Bonyad · Asalouyeh industrial corridor · Kish Island Free Trade Zone · Chabahar Free Trade-Industrial Zone · Labor and tax laws · Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO) · Mining · Construction · Privatization · Foreign Direct Investment · Supreme Audit Court · Communications · Telecommunication Company of Iran (TCI) · Transport · Railways · Metro · Airlines · Iran Shipping Lines · Energy · Petroleum industry · Nuclear program · Tourism · Environmental issues · Economic Reform Plan · Middle East economy · List of major economic laws in Iran · Iran and WTO · Economic history of IranSociety
CultureIranian nationality · Iranology · Education (Higher · Science · Scientists and scholars · Universities) · Philosophy · List of Iranians · Literature · Media (News agencies (student) · newspapers) · Architecture (architects) · Achaemenid architecture · Art (modern/contemporary) · Persian gardens · Cinema · Cuisine · Public holidays · National symbols · Opium consumption · Music (Ey Iran · Heavy metal · Persian traditional music · Folk · Pop · Rap and hip-hop · Rock and alternative) · Blogs · Mythology · Folklore · Islam · Islamization · Scouting · Sport (Football)Other topics Calendar · Crown jewels · Anti-Iranianism · Persian names · Tehrangeles · International rankings of Iran · Sorood-e Shahanshahi IranDurrani Empire (1747–1823) Rulers Events Architecture Adversaries Categories:- Former countries in Asia
- States and territories established in 1747
- States and territories disestablished in 1826
- History of Afghanistan
- History of Iran
- 1823 disestablishments
- Durrani Empire
- Empires and kingdoms of Pakistan
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.