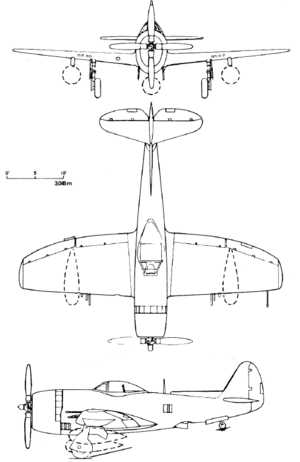
- Republic P-47 Thunderbolt
-
P-47 Thunderbolt In-flight view of a prototype of the Republic P-47N Thunderbolt Role Fighter-bomber Manufacturer Republic Aviation Designer Alexander de Seversky
Alexander KartveliFirst flight 6 May 1941 Introduction 1942 Retired 1966, Peruvian Air Force Primary users United States Army Air Forces
United States Air ForceNumber built 15,686 Unit cost US$85,000 in 1945 ($1.04 million in today's dollars)[1] Variants Republic XP-72 Republic Aviation's P-47 Thunderbolt, also known as the "Jug", was the largest, heaviest, and most expensive fighter aircraft in history to be powered by a single reciprocating engine.[2] It was heavily armed with eight .50-caliber machine guns, four per wing. When fully loaded, the P-47 weighed up to eight tons. The P-47, based on the powerful Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp engine, was very effective in high-altitude air-to-air combat and proved especially adept at ground attack.
The P-47 was one of the main United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) fighters of World War II, and served with other Allied air forces such as France, the UK and the USSR. Mexican and Brazilian squadrons fighting alongside the U.S. were equipped with the P-47.
The sturdy and rugged aircraft was designed by expatriate Russians Alexander de Seversky and Alexander Kartveli. The armored cockpit was roomy inside, comfortable for the pilot, and offered good visibility. A modern-day U.S. ground attack aircraft, the Fairchild Republic A-10 Thunderbolt II, takes its name from the P-47.[N 1]
Contents
Development
The P-47 Thunderbolt was the product of Russian immigrant Alexander P. de Seversky and Georgian immigrant Alexander Kartveli, who had left their homelands to escape the Bolsheviks.
P-43 Lancer / XP-47B
 P-47 firing its M2 machine guns during night gunnery
P-47 firing its M2 machine guns during night gunnery
In 1939, Republic Aviation designed the AP-4 demonstrator powered by a Pratt & Whitney R-1830 radial engine with a belly-mounted turbocharger. While the resulting Republic P-43 Lancer was in limited production, Republic had been working on an improved P-44 Rocket with a more powerful engine, as well as on a fighter designated the AP-10. The latter was a lightweight aircraft powered by the Allison V-1710 liquid-cooled V-12 engine and armed with eight .50 in (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine guns. The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) backed the project and gave it the designation XP-47.
As the war in Europe escalated in spring 1940, Republic and the USAAC concluded that the XP-44 and the XP-47 were inferior to the German fighters. Republic unsuccessfully attempted to improve the design, proposing the XP-47A. Kartveli subsequently came up with an all-new and much larger fighter which was offered to the USAAC in June 1940. The Air Corps ordered a prototype in September, to be designated the XP-47B. The XP-47A, which had almost nothing in common with the new design, was abandoned.
The XP-47B was all-metal construction (except for fabric-covered tail control surfaces) with elliptical wings, with a straight leading edge that was slightly swept back. The cockpit was roomy and the pilot's seat was comfortable—"like a lounge chair", as one pilot later put it. The pilot was provided with every convenience, including cabin air conditioning. The canopy doors hinged upward. Main and auxiliary self-sealing fuel tanks were placed under the cockpit, giving a total fuel capacity of 305 U.S. gal (1,155 l).
 A P-47 engine with the cowling removed. Uncompressed air enters through an intake under the engine, and is carried to the turbosupercharger behind the pilot via the silver duct at the bottom. The olive–green pipe returns the compressed air to the engine [4]
A P-47 engine with the cowling removed. Uncompressed air enters through an intake under the engine, and is carried to the turbosupercharger behind the pilot via the silver duct at the bottom. The olive–green pipe returns the compressed air to the engine [4]
Power came from a Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp two-row 18-cylinder radial engine producing 2,000 hp (1,500 kW) and turning a four-bladed Curtiss Electric constant-speed propeller 146 in (3.7 m) in diameter. The loss of the AP-4 prototype to an engine fire ended Kartveli's experiments with tight-fitting cowlings, so the engine was placed in a broad cowling that opened at the front in a "horse collar"-shaped ellipse. The cowling admitted cooling air for the engine, left and right oil coolers, and the turbosupercharger intercooler system. The engine exhaust gases were routed into a pair of wastegate-equipped pipes that ran along each side of the cockpit to drive the turbosupercharger turbine at the bottom of the fuselage about halfway between cockpit and tail. At full power, the pipes glowed red at their forward ends and the turbine spun at 21,300 rpm.[5] The complicated turbosupercharger system with its ductwork gave the XP-47B a deep fuselage, and the wings had to be mounted in a relatively high position. This was problematic since long landing gear were needed to provide ground clearance for the propeller. To reduce the size and weight of the long landing gear and so that wing-mounted machine guns could be fitted, each main gear strut was fitted with a mechanism by which it telescoped out 9 in (23 cm) when extended.
The XP-47B was a very large aircraft for its time with an empty weight of 9,900 lb (4,490 kg), or 65 percent more than the YP-43. Kartveli is said to have remarked, "It will be a dinosaur, but it will be a dinosaur with good proportions."[6] The armament consisted of eight .50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns, four in each wing. The guns were staggered to allow feeding from side-by-side ammunition boxes, each with a 350-round capacity. Although the British already possessed eight-gun fighters, the Hurricane and the Spitfire, and even the 12-gun Typhoon, they used the smaller 0.303 in (7.7 mm) guns.
The XP-47B first flew on 6 May 1941 with Lowry P. Brabham at the controls. Although there were minor problems, such as some cockpit smoke that turned out to be due to an oil drip, the aircraft proved impressive in its first trials. It was eventually lost in an accident on 8 August 1942, but before that mishap, the prototype had achieved a level speed of 412 mph (663 km/h) at 25,800 ft (7,864 m) altitude, and had demonstrated a climb from sea level to 15,000 ft (4,600 m) altitude in five minutes.[7]
P-47B / RP-47B and XP-47E / XP-47F
The XP-47B gave the newly reorganized United States Army Air Forces cause for both optimism and apprehension. While possessing good performance and firepower, the XP-47B had its share of teething problems:
- Its sheer size and limited ground-propeller clearance in a fuselage-level attitude made for challenging takeoffs which required long runways—the pilot had to hold the tail low until considerable speed was attained on the initial run.
- The sideways-opening canopy covers had a tendency to jam.
- The multiple-gun installation, with its tight fit and cramped ammunition belt tracks, experienced jamming problems, especially during and after hard maneuvering.
- Maneuverability was less than desired when compared to the Supermarine Spitfire and Messerschmitt Bf 109.
- The ignition system arced at high altitude.
- Access to the rear engine accessory pad was difficult due to the short engine mount used.
- At high altitude the ailerons "snatched and froze".
- At high speeds the control loads were deemed excessive.
Republic addressed the problems with a sliding canopy that could be jettisoned in an emergency, a pressurized ignition system, and new all-metal control surfaces (improved engine-accessory access had to wait until the P-47C introduced a new engine mount). While the engineers worked frantically to get their "dinosaur" to fly right, the USAAF ordered 171 P-47Bs. An engineering prototype P-47B was delivered in December 1941, with a production prototype following in March 1942, and the first production model provided in May. Republic continued to improve the design as P-47Bs were produced, and although all P-47Bs had the sliding canopy and the new General Electric turbosupercharger regulator for the R-2800-21 engine, features such as all-metal control surfaces were not standard at first. A modification unique to the P-47B was the radio mast behind the cockpit that was slanted forward to maintain the originally designed antenna wire length in spite of the new sliding canopy.
The P-47B led to a few "one off" variants. A single reconnaissance aircraft designated RP-47B was built. In September 1942, the 171st and last P-47B (41-6065) was also used as a test platform under the designation XP-47E to evaluate the R-2800-59 engine, a pressurized cockpit with a hinged canopy and, eventually, a new Hamilton Standard propeller. The plans for production were cancelled after increased emphasis on low-level operations over Europe.[8][9] Another P-47B was later fitted with a new laminar flow wing in search of higher performance and redesignated XP-47F.
P-47C
Production changes gradually addressed the problems with P-47B, and on balance, with experience the USAAF decided that the P-47 was worthwhile, quickly following the initial order for P-47Bs for 602 more examples of a improved model, named P-47C, with the first of this variant delivered in September 1942. The initial P-47Cs were very similar to the P-47B.
Initial deliveries of the Thunderbolt to the USAAF were to the 56th Fighter Group, which was also on Long Island. The 56th served as an operational evaluation unit for the new fighter. Teething problems continued. A Republic test pilot was killed in the fifth production P-47B when it went out of control in a dive on 26 March 1942, and crashed due to failure of the tail assembly, after fabric-covered tail surfaces ballooned and ruptured.[10] The introduction of revised rudder and elevator balance systems and other changes corrected these problems. In spite of the problems, the USAAF was interested enough to order an additional 602 examples of the refined P-47C, with the first of the variant delivered in September 1942.
Essentially similar to the P-47B, the initial P-47C featured strengthened all-metal control surfaces, an upgraded GE turbosupercharger regulator, and a short vertical radio mast. After the initial manufacture of a block of 57 P-47Cs, production moved to the P-47C-1, which had a 13 in (33 cm) fuselage extension forward of the cockpit at the firewall to correct centre of gravity problems, ease engine maintenance and allow installation of a new engine mount. There were a number of other changes, such as revised exhausts for the oil coolers, and fixes to brakes, undercarriage and electrical system as well as a redesigned rudder and elevator balance. The 55 P-47C-1s were followed by 128 P-47C-2s which introduced a centerline hardpoint with under-fuselage shackles for either a 500 lb (227 kg) bomb or a 200 U.S. gal (758 l, 167 Imp gal) fuel tank that conformed to the underside of the fuselage. The main production P-47C sub-variant was the P-47C-5 which introduced a new whip antenna and the R-2800-59 engine with water-methanol injection with a war emergency power rating of 2,300 hp (1,716 kW). With the use of pressurized drop tanks, the P-47C was able to extend its range on missions beginning 30 July 1943.[7]
By the end of 1942, most of the troubles with the P-47 had been worked out and P-47Cs were sent to England. The 56th FG was sent overseas to join the Eighth Air Force, whose 4th and 78th Fighter Groups would be equipped with the Thunderbolt as well.
P-47D / P-47G and XP-47K / XP-47L
Refinements of the Thunderbolt continued, leading to the P-47D, which was the most popular version with 12,602 built. The "D" model actually consisted of a series of evolving production blocks, the last of which were visibly different from the first.
The first P-47Ds were actually the same as P-47Cs. Republic could not produce Thunderbolts fast enough at its Farmingdale plant on Long Island, so a new plant was built at Evansville, Indiana. The Evansville plant built a total of 110 P-47Ds, which were completely identical to P-47C-2s. Farmingdale aircraft were identified by the "-RE" suffix after the block number, while Evansville aircraft were given the "-RA" suffix.
The P-47D-1 through P-47D-6, the P-47D-10, and the P-47D-11 successively incorporated changes such as the addition of more engine cooling flaps around the back of the cowl to reduce the engine overheating problems that had been seen in the field. Engines and engine subsystems saw refinement, as did the fuel, oil and hydraulic systems. Additional armor protection was also added for the pilot.
The P-47D-15 was produced in response to requests by combat units for increased range. The internal fuel capacity was increased to 375 U.S. gal (1,421 l) and the bomb racks under the wings were made "wet" (equipped with fuel plumbing) to allow a jettisonable drop tank pressurized by vented exhaust air to be carried under each wing, in addition to the belly tank. Five different auxiliary tanks were fitted to the Thunderbolt during its career:
- 200 U.S. gallon (758 l) ferry tank, a conformal tub-shaped jettisonable tank made of paper, which barely cleared the ground on grass airfields, was used as an interim measure between 30 July and 31 August 1943;
- 75 U.S. gal (284 l) drop tank, a teardrop-shaped steel tank produced for the P-39 Airacobra, was adapted to the P-47 beginning 31 August 1943, initially carried on a belly shackle but used in pairs in 1944 as underwing tanks;
- 108 U.S. gal (409 l) drop tank, a cylindrical paper tank of British design and manufacture, used as a belly tank beginning in September 1943 and a wing tank in April 1944;
- 150 U.S. gal (568 l) drop tank, a steel tank first used as a belly 20 February 1944, and an underwing tank 22 May 1944;
- 215 U.S. gal (810 l) belly tank, a wide, flat steel tank developed by VIII Service Command that allowed performance-degrading wing pylons to be removed, was first used in February 1945.
The tanks made of plastic-impregnated (laminated) paper could not store fuel for an extended period of time, but they worked quite well for the time it took to fly a single mission. These tanks were cheaper, lighter, and were useless to the enemy if recovered after being dropped—not only did they break apart, but they did not provide the enemy with any reusable materials that could be scavenged for their own war effort. With the increased fuel capacity, the P-47 was now able to perform escort missions deep into enemy territory. A drawback to their use was that fighters could not land with the tanks in place because of the hazard of rupture and explosion. Fighters recalled from a mission or that did not jettison for some reason were required to drop paper tanks into a designated "dump" area at their respective fields, resulting in substantial losses of aviation fuel.
The P-47D-16, D-20, D-22 and D-23 were similar to the P-47D-15 with minor improvements in the fuel system, engine subsystems, a jettisonable canopy, and a bulletproof windshield. Beginning with the block 22 aircraft, the original narrow-chorded Curtiss propeller was replaced by propellers with larger blades, the Evansville plant switching to a new Curtiss propeller with a diameter of 13 ft (3.96 m) and the Long Island plant using a Hamilton Standard propeller with a diameter of 13 ft 2 in (4.01 m). With the bigger propellers having barely 6 in (152 mm) of ground clearance, Thunderbolt pilots had to learn to be careful on takeoffs to keep the tail down until they obtained adequate ground clearance, and on landings to flare the aircraft properly. Failure to do so damaged both the propeller and the runway. A modification to the maingear legs was installed to extend the gear legs via an electric motor (un-extending before retract) to accommodate the larger propeller diameter. The P-47D-25 was a model with increased range, firepower, and maneuverability.
Even with two Republic plants rolling out the P-47, the USAAF still was not getting as many Thunderbolts as they wanted. Consequently, an arrangement was made with Curtiss to build the aircraft under license in a plant in Buffalo, New York. The Curtiss plant experienced serious problems and delays in producing Thunderbolts, and the 354 Curtiss-built fighters were relegated to stateside advanced flight training.[11] The Curtiss aircraft were all designated P-47G, and a "-CU" suffix was used to distinguish them from other production. The first P-47G was completely identical to the P-47C, the P-47G-1 was identical to the P-47C-1, while the following P-47G-5, P-47G-10, and P-47G-15 sub-variants were comparable to the P-47D-1, P-47D-5 and P-47D-10 respectively. Two P-47G-15s were built with the cockpit extended forward to just before the leading edge of the wing to provide tandem seating, designated TP-47G, essentially to provide a trainer variant. The second crew position was accommodated by substituting a much smaller main fuel tank. The "Doublebolt" did not go into production but similar modifications were made in the field to older P-47s, which were then used as squadron "hacks" (miscellaneous utility aircraft).
Bubbletop P-47s
All the P-47s to this point had a "razorback" canopy configuration with a tall fuselage spine behind the pilot which resulted in poor visibility to the rear. The British also had this problem with their fighter aircraft, and had devised the bulged "Malcolm hood" canopy for the Spitfire as an initial solution. This was fitted in the field to many North American P-51 Mustangs, and to a handful of P-47Ds (and far more on P-47Bs and P-47Cs). However, the British then came up with a much better solution, devising an all-round vision "bubble canopy" for the Hawker Typhoon. USAAF officials liked the bubble canopy, and quickly adapted it to American fighters, including the P-51 and the Thunderbolt. The first P-47 with a bubble canopy was a modified P-47D-5 completed in the summer of 1943 and redesignated XP-47K. Another older P-47D was modified to provide an internal fuel capacity of 370 U.S. gal (1,402 l) and given the designation XP-47L. The bubble canopy and increased fuel capacity were then rolled into production together, resulting in the block 25 P-47D (rather than a new variant designation). First deliveries to combat groups began in May 1944.
It was followed by similar bubble-top variants, including the P-47D-26, D-27, D-28 and D-30. Improvements added in this series included engine refinements, more internal fuel capacity, and the addition of dive recovery flaps. Cutting down the rear fuselage to accommodate the bubble canopy produced yaw instability, and the P-47D-40 introduced a dorsal fin extension in the form of a narrow triangle running from the vertical tailplane to the radio aerial. The fin fillet was retrofitted in the field to earlier P-47D bubble-top variants. The P-47D-40 also featured provisions for 10 "zero length" stub launchers for 5 in (127 mm) High velocity aircraft rockets (HVARs), as well as the new K-14 computing gunsight. This was a license-built copy of the British Ferranti GGS Mark IID computing gyroscopic sight which allowed the pilot to dial in target wingspan and range, and would then move the gunsight reticle to compensate for the required deflection.
The bubbletop P-47s were nicknamed "Superbolts" by combat pilots in the field.[12]
XP-47H / XP-47J
Republic made several attempts to further improve the P-47D:
Two XP-47Hs were built. They were major reworkings of existing razorback P-47Ds to accommodate a Chrysler IV-2220-11 water-cooled 16-cylinder inverted vee engine. However, such large inline engines did not prove to be especially effective.
The XP-47J began as a November 1942 request to Republic for a high-performance version of the Thunderbolt using a lighter airframe and an uprated engine with water injection and fan cooling. Kartveli designed an aircraft fitted with a tight-cowled Pratt & Whitney R-2800-57(C) with a war emergency rating of 2,800 hp (2,090 kW), reduced armament of six 0.50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns, a new and lighter wing, and many other changes. The only XP-47J was first flown in late November 1943. When fitted with a GE CH-5 turbosupercharger, the XP-47J achieved a top speed of 505 mph (440 kn, 813 km/h) in level flight in August 1944, making it one of the fastest piston engine fighters ever built[citation needed]. However, by that time Republic had moved on to a new concept, the XP-72.
P-47M
 Republic P-47 M-1, 63. FS/56. FG, Boxted/Essex 1945
Republic P-47 M-1, 63. FS/56. FG, Boxted/Essex 1945
The P-47M was a more conservative attempt to come up with a higher-performance ("Sprint") version of the Thunderbolt, seeking parity with the newly introduced German jet aircraft and V-1 flying bombs. Four P-47D-27-RE airframes (s/n 42-27385 / 42-27388) were modified into prototype YP-47Ms by fitting the R-2800-57(C) engine and the GE CH-5 turbo-supercharger, a combination which could produce 2,800 hp (2,089 kW) at 32,500 ft (9,900 m) when using Wartime Emergency Power (water injection). Air brakes were added to the wing's lower surfaces to allow braking after a dive onto its prey. The YP-47M had a top speed of 473 mph (410 kn, 761 km/h) and it was put into limited production with 130 (sufficient for one group) built. However, the type suffered serious teething problems in the field due to the highly tuned engine. Engines were unable to reach operating temperatures and power settings and frequently failed in early flights from a variety of causes: ignition harnesses cracked at high altitudes, severing electrical connections between the magneto and distributor, and carburetor valve diaphragms also failed. Persistent oil tank ruptures in replacement engines were found to be the result of inadequate protection against salt water corrosion during transshipment. In the end it was simply errors made by the R-2800-57(C) model engine's manufacturers which led to these issues with the P-47M. By the time the bugs were worked out, the war in Europe was nearly over. However, P-47Ms still destroyed 15 enemy aircraft in aerial combat, normal results for any fighter type in March–May 1945 when aerial encounters with the Luftwaffe were rare. The entire production total of 130 P-47Ms were delivered to the 56th Fighter Group, and were responsible for all seven of that group's jet shoot-downs. Twelve were lost in operational crashes with the 56th Group resulting in 11 deaths, two after VE Day, and two (44-21134 on 13 April 1945 and 44-21230 on 16 April 1945) were shot down in combat, both by ground fire.
The second YP-47M (of the batch of four converted P-47Ds) was later fitted with new wings and served as the prototype for the P-47N.
P-47N
The P-47N was the last Thunderbolt variant to be produced. It was designed as an escort fighter for the Boeing B-29 Superfortress bombers flying raids on the Japanese home islands. Increased internal fuel capacity and drop tanks had done much to extend the Thunderbolt's range during its evolution, and the only other way to expand the fuel capacity was to put fuel tanks into the wings. Thus, a new wing was designed with two 50 U.S. gal (190 l) fuel tanks. The second YP-47N with this wing flew in September 1944. The redesign proved successful in extending range to about 2,000 mi (3,200 km), and the squared-off wingtips improved the roll rate. The P-47N entered mass production with the uprated R-2800-77(C) engine, with a total of 1,816 built.
The very last Thunderbolt to be built, a P-47N-25, rolled off the production line in October 1945. Thousands more had been on order, but production was halted with the end of the war in August. At the end of production, a Thunderbolt cost $83,000 in 1945 U.S. dollars. A total of 15,686 Thunderbolts of all types were built, making it second most produced American fighter of all time—after the 16,766 P-51 Mustangs. Due to continued postwar service with U.S. military (including the ANG) and foreign operators, a number of P-47s have survived to the present day, and a few are still flying.
Operational history
US service
By the end of 1942 P-47Cs were sent to England for combat operations. The initial Thunderbolt flyers, 56th Fighter Group, was sent overseas to join the 8th Air Force. Two Fighter Groups already stationing in England began introducing the Jugs in January 1943: the Spitfire-flying 4th Fighter Group, a unit built around a core of experienced American volunteers of the Eagle Squadrons; and the 78th Fighter Group, formerly using P-38 Lightning.
 P-47 pilot Lt Col Francis S. "Gabby" Gabreski, 56th Fighter Group, leading ace of the 8th Air Force
P-47 pilot Lt Col Francis S. "Gabby" Gabreski, 56th Fighter Group, leading ace of the 8th Air Force
Beginning in January 1943, Thunderbolt fighters were sent to the joint Army Air Forces – civilian Millville Airport in Millville, New Jersey in order to train civilian and military pilots.
The first P-47 combat mission took place 10 March 1943 when the 4th FG took their aircraft on a fighter sweep over France. The mission was a failure due to radio malfunctions. All P-47s were refitted with British radios, and missions resumed 8 April. The first P-47 air combat took place 15 April with Major Don Blakeslee of the 4th FG scoring the Thunderbolt's first air victory (a Fw 190). On 17 August, P-47s performed their first large-scale escort missions, providing B-17 bombers with both penetration and withdrawal support of the Schweinfurt-Regensburg mission, and claiming 19 kills against three losses.
By mid-1943, the Jug was also in service with the 12th Air Force in Italy, and it was fighting against the Japanese in the Pacific with the 348th Fighter Group flying escort missions out of Brisbane, Australia. By 1944, the Thunderbolt was in combat with the USAAF in all its operational theaters, except Alaska.
Although the North American P-51 Mustang replaced the P-47 in the long-range escort role in Europe, the Thunderbolt still ended the war with 3,752 air-to-air kills claimed in over 746,000 sorties of all types, at the cost of 3,499 P-47s to all causes in combat.[13] In Europe during the critical first three months of 1944 when the German aircraft industry and Berlin were heavily attacked, the P-47 shot down more German fighters than did the P-51 (570 out of 873), and shot down approximately 900 of the 1,983 claimed during the first six months of 1944. In Europe, Thunderbolts flew more sorties (423,435) than P-51s, P-38s and P-40s combined. Indeed, it was the P-47 which broke the back of the Luftwaffe in the critical period of January–May 1944.[14]
By the end of the war, the 56th FG was the only 8th Air Force unit still flying the P-47, by preference, instead of the P-51. The unit claimed 677.5 air victories and 311 ground kills, at the cost of 128 aircraft.[15] Lieutenant Colonel Francis S. Gabreski scored 31 victories,[16] including three ground kills, Captain Bob Johnson scored 27 (with one unconfirmed probable kill leading to some giving his tally as 28),[17] and 56th FG Commanding Officer Colonel Hubert Zemke scored 17.75 kills.[N 2] Despite being the sole remaining P-47 group in the 8th Air Force, the 56th FG remained its top-scoring group in aerial victories throughout the war.
With increases in fuel capacity as the type was refined, the range of escort missions over Europe steadily increased until the P-47 was able to accompany bombers in raids all the way into Germany. On the way back from the raids, pilots shot up ground targets of opportunity, and also used belly shackles to carry bombs on short-range missions, which led to the realization that the P-47 could perform a dual-function on escort missions as a fighter-bomber. Even with its complicated turbosupercharger system, its sturdy airframe and tough radial engine could absorb a lot of damage and still return home. Some pilots readily chose to belly-land their burning Thunderbolts rather than risk bailing out; there are instances of P-47s crash-landing after being shot down, hitting trees and causing impacts severe enough to snap off wings, tail, and engine, while the pilot escaped with few or no injuries.[19]
The P-47 gradually became the USAAF's best fighter-bomber, normally carrying 500 lb (227 kg) bombs, M8 4.5 in (115 mm) or 5 in (127 mm) High velocity aircraft rockets (HVARs, or Holy Moses). From the invasion of Europe on 6 June 1944 to VE day on 7 May 1945, the Thunderbolt units claimed destroyed: 86,000 railroad cars, 9,000 locomotives, 6,000 armoured fighting vehicles, and 68,000 trucks.[20]
Postwar service
The USAAF Strategic Air Command had P-47 Thunderbolts in service from 1946 through 1947.
The P-47 served with the Army Air Forces (United States Air Force after 1947) until 1949, and with the Air National Guard until 1953, receiving the designation F-47 in 1948. P-47s also served as spotters for rescue aircraft such as the OA-10 Catalina and Boeing B-17H.
The P-51 Mustang was used by the USAF during the Korean War, mainly in the close air support role with the P-47 not being deployed to Korea. Since the Mustang was more vulnerable to being shot down, (and many were lost due to anti-aircraft fire), some former P-47 pilots suggested the more durable Thunderbolt should have been sent to Korea; however the P-51D was available in greater numbers in the USAF and ANG inventories.[21]
P-47 in Allied, non-U.S. service
 Royal Air Force Republic Thunderbolt Mark I
Royal Air Force Republic Thunderbolt Mark I
 Brazilian P-47s in World War II carried the Senta a Pύa! squadron badge, along with the national insignia of Brazil painted over USAAF's star and bar.
Brazilian P-47s in World War II carried the Senta a Pύa! squadron badge, along with the national insignia of Brazil painted over USAAF's star and bar.
 P-47D "Kathie" with 75-gallon drop tank buzzes the airfield at Bodney, England
P-47D "Kathie" with 75-gallon drop tank buzzes the airfield at Bodney, England
P-47s were operated by several Allied air arms during World War II. The RAF received 240 razorback P-47Ds which they designated "Thunderbolt Mark I", and 590 bubbletop P-47D-25s, designated "Thunderbolt Mark IIs". With no need for another high-altitude fighter, the RAF adapted their Thunderbolts for ground attack, a task for which the type was well suited. Once the Thunderbolts were cleared for use in 1944, they were used against the Japanese in Burma by 16 RAF squadrons of the South East Asia Command from India. Operations were army support (operating as "cab ranks" to be called in when needed), attacks on enemy airfields and lines of communication, and escort sorties. The Thunderbolts were armed with three 500 lb (227 kg) bombs or, in some cases, British "60 pound" (27 kg) RP-3 rocket projectiles. Long range fuel tanks gave five hours of endurance. Thunderbolts remained in RAF service until October 1946; those squadrons not disbanded outright after the war re-equipped with British-built aircraft.
During the Italian campaign, the "1º Grupo de Caça da Força Aérea Brasileira" (Brazilian Air Force 1st Fighter Squadron) flew a total of 48 P-47Ds in combat (of a total of 67 received, 19 of which were backup aircraft). This unit flew a total of 445 missions from November 1944 to May 1945 over northern Italy and Central Europe, with 15 P-47s lost to German flak and five pilots being killed in action. In the early 1980s, this unit was awarded the "Presidential Unit Citation" by the American government in recognition for its achievements in World War II.
From March 1945 to the end of the war in the Pacific, the Mexican Escuadrón Aéreo de Pelea 201 (201st Fighter Squadron) operated P-47Ds as part of the U.S. 5th Air Force in the Philippines. In 791 sorties against Japanese forces, the 201st lost no pilots or aircraft to enemy action.[22]
The French Air Force received 446 P-47Ds from 1943. These aircraft saw extensive action in France and Germany and again in the 1950s during the Algerian War of Independence.
After World War II, the Italian Air Force (AMI) received 75 P-47D-25s (sent to 5˚ Stormo, and 99 to the 51˚). These machines were delivered between 1947 and 1950. However, they were not well liked, as the Italian pilots were used to much lighter aircraft and found the controls too heavy. Nevertheless, the stability, payload and high speed were appreciated. Most importantly, the P-47 served as an excellent transition platform to heavier jet fighters, including the F-84 Thunderjet, starting in 1953.[23]
The type was provided to many Latin American air forces some of which operated it into the 1960s. Small numbers of P-47s were also provided to China, Iran, Turkey and Yugoslavia.
In Soviet Service
The U.S. sent 203 P-47Ds to the Soviet Union.[24] In mid-1943, the Soviet high command showed an interest in the P-47B. Three P-47D-10-REs were ferried to the Soviet Air Forces (VVS) via Alaska in March 1944. Two of them were tested in April–May 1944. Test pilot Aleksey N. Grinchik noted the spacious cockpit with good ventilation and a good all-around view. He found it easy to fly, and stable upon take-off and landing, but it showed excessive rolling stability and poor directional stability. Soviet engineers disassembled the third aircraft to examine its construction. They appreciated the high production standards and rational design well-suited to mass production, and the high reliability of the hard-hitting Browning machine guns. With its high service ceiling, the P-47 was superior to fighters operating on the Eastern front, yielding a higher speed above 30,000 feet (9,000 m). Still, the Yakovlev Yak-9, Lavochkin La-5FN, Messerschmitt Bf 109G and Focke-Wulf Fw 190A outperformed the P-47 at low and medium altitude, where the P-47 had poor acceleration and performed aerobatics rather reluctantly. In mid-1944, 200 P-47D-22-REs and P-47D-27-REs were ferried to the USSR via Iraq and Iran. Many were sent to training units. Less than half reached operational units, and they were rarely used in combat.[25] The fighters were assigned to high-altitude air defense over major cities in rear areas. Unlike their Western counterparts, the VVS made little use of the P-47 as a ground attack aircraft, depending instead on their own widely produced special-purpose ground-attack aircraft, the Ilyushin Il-2. At the end of the war, Soviet units held 188 P-47s.[25]
In German Service
The Luftwaffe operated at least one captured P-47. In poor weather on 7 November 1943 while flying a P-47F on a bomber escort mission, 2nd Lt. William E. Roach of 358th Squadron, 355th Fighter Group made an emergency landing on a German airfield. Roach was imprisoned at Stalag Luft I. The Thunderbolt was given German markings.[26]
Flying the Thunderbolt
Aerial warfare
Initial response to the P-47 praised its dive speed and high-altitude performance, while criticizing its turning performance and rate of climb (particularly at low altitudes). Some British assumed the American P-47 nickname "Jug" was short for "Juggernaut" and began using the longer word as an alternate nickname.[27] Another nickname that was used for the Thunderbolt was "T-bolt".
The turbosupercharger in the P-47 gave the powerplant its maximum power at 27,000 ft (8,230 m), and in the thin air above 30,000 ft (9,144 m), the Thunderbolt became comparatively fast and nimble relative to other aircraft.[28]
The P-47 first saw action with the 4th Fighter Group. The Group’s pilots were mainly drawn from the three British Eagle Squadrons who had previously flown the British Supermarine Spitfire Mark V - a much smaller and much more slender aircraft in comparison. They viewed their new fighter with misgivings, at first. It was huge. The British joked that a Thunderbolt pilot could defend himself from a Luftwaffe fighter by running around and hiding in the fuselage. Optimized for high altitude work, the Thunderbolt had 5 feet (1.5 m) more wingspan, a quarter more wing area, about four times the fuselage volume and nearly twice the weight of a Spitfire V.[29][30] One Thunderbolt pilot compared it to flying a bathtub around the sky. When his unit (4th Fighter Group) was equipped with Thunderbolts, ace Don Blakeslee said, referring to the P-47's vaunted ability to dive on its prey, "It ought to be able to dive. It certainly can't climb."[31] (Blakeslee's early-model P-47C had not been fitted with the new paddle blade propeller). The 4th Fighter Group's commander hated the P-47, and his prejudices filtered down to the group's pilots; the 4th had the fewest kills of any of the first three P-47 squadrons in Europe.[30] The U.S. ace Jim Goodson, who had flown Spitfires with the RAF and flew a P-47 in 1943, at first shared the skepticism of other pilots for their “seven-ton milk-bottles”. But Goodson learned to appreciate the P-47’s potential: “There were many U.S. pilots who preferred the P-47 to anything else: they do not agree that the (Fw) 190 held an overall edge against it.” [32]
The P-47's initial success in combat was primarily due to tactics, using rolls (the P-47 had an excellent roll rate) and energy-saving dive and zoom climbs from high altitude to outmaneuver German fighters. Both the Bf 109 and Fw 190 could, like the Spitfire, out-turn and out-climb the early model P-47s at low altitude, although at altitudes above 15,000 ft, the P-47 could turn inside both the Bf 109 and Fw 190. Once paddle blade propellers were added to the P-47 in early 1944, climb performance improved tremendously,[33] enabling the P-47 to match the climb performance of any German fighter at all altitudes[citation needed]. While both German fighters could break hard downwards, and leave all models of the Spitfire trailing,[29] no German piston-engined aircraft could out-dive the Thunderbolt. In a "bounce," with their rapid acceleration downhill coupled with the pulverizing effect of eight .50s, these aircraft were deadly.[34] The Thunderbolt was the fastest-diving American aircraft of the war—it could reach speeds of 550 mph (480 kn, 885 km/h). Major Robert S. "Bob" Johnson described the experience of diving the big fighter by writing, "the Thunderbolt 'howled' and ran for the earth".[35] Some P-47 pilots claimed to have broken the sound barrier, but later research revealed that because of the pressure buildup inside the pitot tube at high speeds, airspeed readings became unpredictably exaggerated. But German pilots gradually learned to avoid diving away from a Thunderbolt. Kurt Bühligen, a high-scoring German fighter ace with 112 victories, recalled:
"The P-47 was very heavy, too heavy for some maneuvers. We would see it coming from behind, and pull up fast and the P-47 couldn’t follow and we came around and got on its tail in this way".[36]
The arrival of the new Curtiss paddle blade propeller significantly increased climb rate at lower altitudes, and came as a shock to German pilots who had resorted to steep climbs to evade pursuit by the P-47.[30] Other positive attributes included the P-47's ruggedness; it could sustain a large amount of damage and still be able to get its pilot back to base.[N 3] With eight .50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns, the P-47 did not lack for firepower. German aircraft caught in a well-aimed burst tended to fly apart from the impact of so many armor-piercing projectiles. The P-47 would also claim over 20 Luftwaffe Messerschmitt Me 262 jet fighters, and four Arado Ar 234 jet bombers in aerial combat, proving its effectiveness in combat with the much more advanced and faster German aircraft.
In the Pacific, Colonel Neel E. Kearby of the Fifth Air Force destroyed 22 Japanese aircraft and was awarded the Medal of Honor for an action in which he downed six enemy fighters on a single mission. He was shot down and killed over Biak in March 1944.[37]
Ground attack role
The P-47 proved to be a formidable fighter-bomber due to its impressive armament, bomb load and ability to survive enemy fire. The Thunderbolt's eight .50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns could inflict severe damage on lightly armored targets. In a ground attack role, the armor-piercing (AP), armor-piercing incendiary (API), and armor-piercing incendiary tracer (APIT) ammunition proved useful in penetrating thin-skinned and lightly armored German vehicles and exploding their fuel tanks, as well as occasionally damaging some types of enemy armored fighting vehicles (AFVs).[38]
The dreaded cry of Achtung! Jabos! (fighter-bombers) regularly erupted from German armored columns as the P-47 flights got to work.[39] While the AP projectiles from the .50 in machine guns could not penetrate the front, side, or rear armor of German tanks, analysis of German AFV armor schemes shows that .50 caliber AP rounds could, under optimum circumstances, penetrate the turret roof and rear engine deck armor of all German AFVs, save the Tiger I and II.[40][41] [42] Exposed tank crews were obviously vulnerable to air-to-ground fire, but rounds could also penetrate the unprotected radiator grilles of the German tanks, disabling the vehicle, or even starting engine fires.[38][43][44] On 28 June 1944, General Heinz Guderian, Inspector General of Panzer Troops reported on experiences in opposing the Allied Landing in Normandy: "... Soon the troops will demand protective armor shields be mounted over the rear decks [of tanks] because of the success of fighter-bomber attacks.” [45]
P-47 pilots frequently carried two 500 lb (227 kg) bombs, using skip bombing techniques for difficult targets (skipping bombs into railroad tunnels to destroy hidden enemy trains was a favorite tactic).[39] Tunnel-busting became a fine art. When pilots spotted a train entering a tunnel, they skipped bombs into both ends to seal the train inside, then bombed the tunnel itself. Near Canisy, France, a locomotive was shredded until it looked like a steel broom. A near bomb miss was sufficient to knock a tank on its side, blow off a track or turret, or cause serious damage to tracks, suspension, and turret mechanisms, frequently causing the vehicle to be abandoned by its crew.[46] The adoption of the triple-tube rocket launcher with M8 high-explosive 4.5 in (110 mm) rockets (with an explosive force similar to a 105 mm artillery shell), significantly increased the P-47's ground attack capability.[47] Late in the war, the P-47 was retrofitted with more powerful 5 in (130 mm) HVAR rockets.
Operators
 Thunderbolt F-47D of the Colombian Air Force in 1946
Thunderbolt F-47D of the Colombian Air Force in 1946
 Mexican P-47D Thunderbolt over the Philippines.
Mexican P-47D Thunderbolt over the Philippines.
- Bolivian Air Force (post-war)
- Brazilian Expeditionary Force, Brazilian Air Force
- 85 units 1st Brazilian Fighter Group, 1944–1954
- Colombian Air Force (post-war)
- Cuban Air Force (post-war)
- Dominican Air Force (post war)
- Ecuadorian Air Force (post war)
- Honduran Air Force (post-war)
- Imperial Iranian Air Force (post-war)
- Italian Air Force (post-war)
- Fuerza Aerea de Nicaragua (provided by the CIA post 1954 action in Guatemala)
- Peruvian Air Force (post-war) (56 aircraft) (July 1947 – June 1966)
- Portuguese Air Force (post-war)
- Soviet Air Force
- Turkish Air Force (post-war) (1948)
- Yugoslav Air Force (post-war) (133 aircraft) (1952)
Survivors
Main article: List of surviving P-47 ThunderboltsA large number of surviving airframes exist in flyable condition as well as in museum collections worldwide.
Specifications (P-47D Thunderbolt)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 36 ft 1 in (11.00 m)
- Wingspan: 40 ft 9 in (12.42 m)
- Height: 14 ft 8 in (4.47 m)
- Wing area: 300 ft² (27.87 m²)
- Empty weight: 10,000 lb (4,536 kg)
- Loaded weight: 17,500 lb (7,938 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 17,500 lb (7,938 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney R-2800-59 twin-row radial engine, 2,535 hp (1,890 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 433 mph at 30,000 ft (697 km/h at 9,145 m)
- Range: 800 mi combat, 1,800 mi ferry (1,290 km / 2,900 km)
- Service ceiling: 43,000 ft (13,100 m)
- Rate of climb: 3,120 ft/min (15.9 m/s)
- Wing loading: 58.3 lb/ft² (284.8 kg/m²)
- Power/mass: 0.14 hp/lb (238 W/kg)
Armament
- 8 × .50 in (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine guns (3400 rounds)
- Up to 2,500 lb (1,134 kg) of bombs
- 10 × 5 in (127 mm) unguided rockets
In popular culture
Main article: Aircraft in fiction#P-47 Thunderbolt- Thunderbolt, a 1947 color documentary film directed by John Sturges and William Wyler, featuring James Stewart and Lloyd Bridges and narrated by Robert Lowery.[48]
- "Thunderbolts: The Conquest of the Reich", a 2001 television documentary presented by the History Channel. Director Lawrence Bond depicted the last months of World War II over Germany as told by four P-47 pilots of the 362nd Fighter Group using original, all color 1945 footage.
- The P-47 Thunderbolt was the subject of an episode of the World's Deadliest Aircraft series broadcast by the Military Channel.
- The film Fighter Squadron (1948) depicts a P-47 Thunderbolt unit.[49]
See also
- Related development
- Republic P-43
- Republic XP-72
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Grumman F6F Hellcat
- Focke-Wulf Fw 190
- Hawker Typhoon
- Hawker Tempest
- Kawasaki Ki-100
- Mitsubishi A7M
- North American P-51 Mustang
- Polikarpov I-185
- Vought F4U Corsair
- Related lists
- List of military aircraft of the United States
- List of fighter aircraft
References
- Notes
- ^ Fairchild Republic was the most recent incarnation of the original Republic aerospace company, now considered defunct. [3]
- ^ Zemke flew a P-38 for three of his kills.[18]
- ^ Quentin C. Aanenson documented his experiences flying the Thunderbolt on D-Day and subsequently in the European Theater in his documentary, A Fighter Pilot's Story (also released as Dogfight.).
- Citations
- ^ "Republic P-47 Thunderbolt." National Museum of the United States Air Force.
- ^ Gunston 1980, p. 22.
- ^ Rummerman, Judy. "Fairchild Republic." Centennial of Flight Commission, 2003. Retrieved: 7 August 2011.
- ^ Dwyer, Larry. "Republic P-47 Thunderbolt." Aviation History Online Museum, 11 November 2010.
- ^ "The Turbosupercharger and the Airplane Power Plant." General Electric, January, 1943.
- ^ "P-47 Thunderbolt". Top Fighters.com. Retrieved: 12 July 2006.
- ^ a b Green 1961, p. 173.
- ^ Baugher, Joe. "Republic P-47 Thunderbolt." USAAC/USAAF/USAF Fighter and Pursuit Aircraft, 18 July 1999. Retrieved: 23 January 2011.
- ^ Green 1961, p. 178.
- ^ Lake 2001, p. 143.
- ^ O'Leary, Michael (1986). USAAF fighters of World War Two in action. In Action. Blandford Press. p. 228. ISBN 0713718390.
- ^ Freeman 2000, p. 81.
- ^ "Republic P-47D Thunderbolt". Museum of Flight. Retrieved: 12 July 2006.
- ^ "USAF Historical Study 70." Tactical Operations of the Eighth Air Force 6 June 1944 to 8 May 1945, Appendix 3, p. 241.
- ^ "8th Air Force 56th FG." U.S. Army Air Forces in World War II, 18 June 2004. Retrieved: 14 July 2006.
- ^ "Francis S. 'Gabby' Gabreski". USAF Air University, Maxwell-Gunter AFB, 17 April 2006. Retrieved: 14 July 2006.
- ^ Rose, Scott. "Robert S. Johnson". Warbirds Resource Group, 11 June 2006. Retrieved: 14 July 2006.
- ^ "Col. Hubert 'Hub' Zemke." Acepilots.com, 29 July 2003. Retrieved: 14 July 2006.
- ^ Ryan, Cornelius. A Bridge Too Far. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1974. ISBN 978-0-445-08373-8.
- ^ "Republic P-47D Thunderbolt". Smithsonian National Air & Space Museum. Retrieved: 1 April 2007.
- ^ "Air Power History". goliath.ecnext.com. Retrieved: 21 November 2009.
- ^ Velasco, E. Alfonso, Jr. "Aztec Eagle—P-47D of the Mexican Expeditionary Air Force". IPMS Stockholm, 9 January 2006. Retrieved: 14 July 2006.
- ^ Sgarlato 2005.
- ^ Hardesty 1991, p. 253.
- ^ a b Gordon 2008, p. 449.
- ^ "P-47F-2-RA 'Agnes' SN: 42-22490." Warbirds Resource Group. Retrieved: 14 July 2011.
Stapfer, Hans-Heiri. Strangers In A Strange Land. Carrollton, Texas: Squadron/Signal Publications, 1988. ISBN 0-89747-278-0. - ^ Air Force Association 1998, p. 110.
- ^ Bergerud 2000, pp. 269–270.
- ^ a b Spick 1983, p. 96.
- ^ a b c Caldwell 2007, p. 89.
- ^ Sims, Edward H. American Aces of World War II, London: Macdonald, 1958.
- ^ Sims 1980, pp. 160-161.
- ^ Jordan, C. C. "Pushing The Envelope With Test Pilot Herb Fisher". Planes and Pilots of WW2, 2000. Retrieved: 22 July 2011.
- ^ Spick 1983, p. 99.
- ^ "P-47 Thunderbolt". about.com. Retrieved: 14 July 2006.
- ^ Sims 1980, pp. 134-135.
- ^ "Colonel Neel Earnest Kearby". Air Force History, Air Force Historical Studies Office, 20 January 2004. Retrieved: 14 July 2006.
- ^ a b Barnes 1989, p. 432.
- ^ a b "Achtung! Jabos! The Story of the IX TAC." Stars & Stripes, U.S. Army, 1944.
- ^ Jentz 2008
- ^ Jentz Panzer Truppen 1 2004, pp. 279, 280.
- ^ Jentz Germany’s Panther Tank, p. 86.
- ^ Hallion, Richard P. D-Day 1944: Air Power Over the Normandy Beaches and Beyond. Maxwell AFB AL: Air Force Historical Research Branch, 1994. ISBN 978-0-16-043205-7.
- ^ Collins, J. Lawton. Lightning Joe: An Autobiography. Novato, California: Presidio Press, 1994. ISBN 978-0-89141-530-5.
- ^ Jentz Germany’s Panther Tank 2004, p. 147.
- ^ "The Tank's Formidable Enemies". aero-web.org. Retrieved: 21 November 2009.
- ^ Dunn, Carle E. (LTC). "Army Aviation and Firepower". redstone.army.mil, May 2000. Retrieved: 21 November 2009.
- ^ "Thunderbolt (1947)". imdb.com. Retrieved: 21 November 2009.
- ^ "Fighter Squadron (1948)". imdb.com. Retrieved: 21 November 2009.
- Bibliography
- Air Force Fifty. Nashville, Tennessee: Turner Publishing (Air Force Association), 1998 (limited edition). ISBN 1-56311-409-7.
- Barnes, Frank C. Cartridges of the World. Fairfield, Ohio: DBI Books, 1989. ISBN 978-0-87349-605-6.
- Bergerud, Eric M. Fire in the Sky. Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press, 2000. ISBN 0-8133-3869-7.
- Bodie, Warren M. Republic's P-47 Thunderbolt: From Seversky to Victory. Hiawassee, Georgia: Widewing Publications, 1994. ISBN 0-9629359-1-3.
- Cain, Charles W. and Mike Gerram.Fighters of World War II. London: Profile Publications, 1979.
- Caldwell, Donald. The Luftwaffe Over Germany: Defense of the Reich. St. Paul, Minnesota: MBI Publishing Company, 2007. ISBN 978-1-85367-712-0.
- Davis, Larry. P-47 Thunderbolt in Action, Squadron/Signal Publications (#67). Carrollton, Texas: Squadron/Signal Publications, 1984. ISBN 0-89747-161-X.
- Donald, David, ed. American Warplanes of the Second World War.London: Airtime Publications, 1995. ISBN 1-84013-392-9.
- Freeman, Roger A. 56th Fighter Group. Oxford, UK: Osprey, 2000. ISBN 1-84176-047-1.
- Freeman, Roger A. Camouflage and Markings 15: Republic P-47 Thunderbolt U.S.A.A.F., E.T.O. And M.T.O. 1942–1945 (Ducimus Classic). London: Ducimus Books, 1971.
- Freeman, Roger A. Thunderbolt: A Documentary History of the Republic P-47. London: Macdonald and Jane's, 1978. ISBN 0345-01166-9.
- Goebel, Greg. "The Republic P-47 Thunderbolt." Air Vectors, April 2009.
- Gordon, Yefim. Soviet Air Power in World War 2. Hinkley, UK: Midland/Ian Allan Publishing, 2008. ISBN 978-85780-304-4.
- Graff, Cory. P-47 Thunderbolt at War (The At War Series). St. Paul, Minnesota: Zenith Press, 2007. ISBN 978-07603-2948-1.
- Green, William. Fighters Vol. 2 (Warplanes of the Second World War). New York: Doubleday and Company Inc., 1961.
- Guillemin, Sébastien. Republic P-47 Thunderbolt (Les Materiels de l'Armée de L'Air 4) (in French). Paris: Histoire et Collections, 2007. ISBN 978-2-915239-90-4.
- Gunston, Bill. Aircraft of World War 2. London: Octopus Books Limited, 1980. ISBN 0-7064-1287-7.
- Hagedorn, Dan. Republic P-47 Thunderbolt: The Final Chapter: Latin American Air Forces Service. St. Paul, Minnesota: Phalanx Publishing Co. Ltd., 1991. ISBN 0-9625860-1-3.
- Hardesty, Von. Red Phoenix: The Rise of Soviet Air Power 1941–1945. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution, 1991 (first edition 1982). ISBN 0-87474-510-1.
- Hess, William N. P-47 Thunderbolt (Warbird History). St. Paul, Minnesota: Motorbooks International Publishers, 1994. ISBN 0-87938-899-4.
- Jentz, Thomas L. Germany's Panther Tank: The Quest for Combat Supremacy, Development Modifications, Rare Variants, Characteristics, Combat Accounts (Schiffer Military/Aviation History). Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Publishing Ltd, 2004. ISBN 978-0887408120.
- Jentz, Thomas L. Panzer Tracts No. 8: Sturmgeschuetz - S.Pak TO Sturmmoerser. Winter Park, Florida: Darlington Productions, Inc, 1999. ISBN 978-1892848048.
- Jentz, Thomas L. Panzer Truppen: 1943-1945 v. 2: The Complete Guide to the Creation and Combat Employment of Germany's Tank Force (Schiffer Military History Book). Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Publishing Ltd, 2004. ISBN 978-0764300806.
- Lake, Jon. "P-47 Thunderbolt Part 1: Early development and combat in the ETO". International Air Power Review, Volume 1, Summer 2001. Westport, Connecticut: AIRtime Publishing Inc. ISBN 1473-9917.
- Mondey, David. The Concise Guide to American Aircraft of World War II. London: Chartwell Books Inc., 1994. ISBN 0-7858-0147-2.
- Scutts, Jerry. Republic P-47 Thunderbolt (Combat Legend). Ramsbury, Wiltshire, UK: Airlife Publishing, 2003. ISBN 1-84037-402-0.
- Sims, Edward H. Fighter Tactics and Strategy 1914-1970. Fallbroock, California: Aero publisher Inc., 1980. ISBN 0-8168-8795-0.
- Sgarlato, Nico and Giorgio Gibertini. "P-47" (in Italian). I Grandi Aerei Storici n.14, January 2005. Parma, Italy: Delta Editrice. ISSN 1720-0636.
- Spick, Mike. Fighter Pilot Tactics. The Techniques of Daylight Air Combat. Cambridge, UK: Patrick Stephens, 1983. ISBN 0-85059-617-3.
- Stoff, Joshua. The Thunder Factory: An Illustrated History of the Republic Aviation Corporation. London: Arms & Armour Press, 1990. ISBN 1-85409-040-2.
The initial version of this article was based on a public domain article from Greg Goebel's Vectorsite.
External links
- "It's The Thunderbolt", December 1942 article in "Popular Science"
- P47Pilots.com. P-47 Pilot Biographies, Pilot Stories, Photo Gallery
- The Cradle of Aviation Museum—history of the P-47
- South American 'Jug'. The P-47 Thunderbolt of the Fuerza Aérea de Chile (FACH), IPMS Stockholm
- P-47 Pilot's Flight Operation Instructions, April 10, 1942
Articles and topics related to Republic P-47 Thunderbolt Republic and Seversky aircraft Seversky aircraft Republic aircraft (by role) Republic aircraft (by name) Lancer · Rainbow · Seabee · Thunderbolt · Thunderceptor · Thunderchief · Thunderflash · Thunderjet · Thunderscreech · Thunderstreak · Thunderwarrior
See also: JB-2 Loon USAAS/USAAC/USAAF/USAF fighter designations 1924–1962 Pursuit (pre-1948)
Fighter (post-1948)P-1 • P-2 • P-3 • XP-4 • P-5 • P-6 • XP-7 • XP-8 • XP-9 • XP-10 • P-11 • P-12 • XP-13 • XP-14 • XP-15 • P-16 • XP-17 • XP-18 • XP-19 • YP-20 • XP-21 • XP-22 • XP-23 • YP-24 • Y1P-25 • P-26 • YP-27 • Y1P-28 • P-29 • P-30 • XP-31 • XP-32 • XP-33 • XP-34 • P-35 • P-36 • XP-37 • P-38 • P-39 • P-40 • XP-41 • XP-42 • P-43 • P-44 • XP-45 • XP-46 • P-47 • XP-48 • XP-49 • XP-50 • P-51 • XP-52 • XP-53 • XP-54 • XP-55 • XP-56 • XP-57 • XP-58 • P-59 • YP-60 • P-61/RF-61C • XP-62 • P-63 • P-64 • XP-65 • P-66 • XP-67 • XP-68 • XP-69 • P-70 • XP-71 • XP-72 • XP-73 • (P-74 not assigned) • P-75 • XP-76 • XP-77 • XP-78 • XP-79 • P-80 • XP-81 • P-82 • XP-83 • P-84 • XP-85 • P-86/F-86D • XP-87 • XP-88 • P-89 • XF-90 • XF-91 • XF-92 • YF-93 • F-94 • YF-95 • YF-96 • F-97 • XF-98 • F-99 • F-100 • F-101 • F-102 • XF-103 • F-104 • F-105 • F-106 • F-107 • XF-108 • XF-109 • F-110 • F-111/F-111B
Pursuit, Biplace Fighter, Multiplace YFM-1 • XFM-2
See also: F-24 (redesignation of A-24 in 1948) • F-117 • Post-1962 list Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Propeller aircraft
- Low wing aircraft
- Single-engine aircraft
- United States fighter aircraft 1940–1949
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.