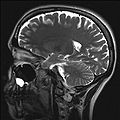
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
-
MRI of brain and brain stem Intervention 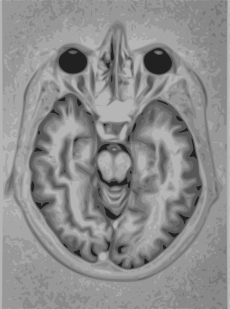
Brain MRIICD-10-PCS B030ZZZ ICD-9-CM 88.91 OPS-301 code: 3-800, 3-820 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and brain stem uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce high quality two- or three-dimensional images of brain structures without use of ionizing radiation (X-rays) or radioactive tracers.
One advantage of MRI of the brain over computed tomography of the head is better tissue contrast,[1] and it has fewer artifacts than CT when viewing the brainstem. MRI is also superior for pituitary imaging.[2] It may however be less effective at identifying early cerebritis.[3]
In analysis of the fetal brain, MRI provides more information about gyration than ultrasound.[4]
A number of different imaging modes can be used with imaging the brain:
- T1: Cerebrospinal fluid is dark. T1 weighting is useful for visualizing normal anatomy.
- T2: CSF is light, but fat (and thus white matter) is darker than with T1. T2 is useful for visualizing pathology.[5]
- PD (proton density): CSF has a relatively high level of protons, making CSF appear bright. Gray matter is brighter than white matter.[6]
- FLAIR: useful for evaluation of white matter plaques near the ventricles.[7] It is useful in identifying demyelination.[8]
Gallery
References
- ^ Ebel, Klaus-Dietrich; Benz-Bohm, Gabriele (1999). Differential diagnosis in pediatric radiology. Thieme. pp. 538–. ISBN 9783131081315. http://books.google.com/books?id=SGMrGn49QZUC&pg=PA538. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ Bradley, William G.; Brant-Zawadzki, Michael; Cambray-Forker, Jane (2001-01-15). MRI of the brain. Surendra Kumar. ISBN 9780781725682. http://books.google.com/books?id=40f2WPdivA8C. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ^ Roos, Karen L.; Tunkel, Allan R. (2010). Bacterial infections of the central nervous system. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 69–. ISBN 9780444520159. http://books.google.com/books?id=GgQshXzR9scC&pg=PA69. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ Garel, Cathérine (2004). MRI of the fetal brain: normal development and cerebral pathologies. Springer. ISBN 9783540407478. http://books.google.com/books?id=Qbd75DzWGh8C. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ^ Butler, Paul; Mitchell, Adam W. M.; Ellis, Harold (2007-11-19). Applied Radiological Anatomy for Medical Students. Cambridge University Press. pp. 12–. ISBN 9780521819398. http://books.google.com/books?id=COrAyvWUt68C&pg=PA12. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ Tofts, Paul (2005-09-01). Quantitative MRI of the Brain: Measuring Changes Caused by Disease. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 86–. ISBN 9780470869499. http://books.google.com/books?id=f5ZPsReoG1IC&pg=PA86. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ Chowdhury, Rajat; Wilson, Iain; Rofe, Christopher; Graham Lloyd-Jones (2010-04-19). Radiology at a Glance. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 95–. ISBN 9781405192200. http://books.google.com/books?id=---xH-DNsrwC&pg=PA95. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ Granacher, Robert P. (2007-12-20). Traumatic brain injury: methods for clinical and forensic neuropsychiatric assessment. CRC Press. pp. 247–. ISBN 9780849381386. http://books.google.com/books?id=xt1YFydzXKQC&pg=PT247. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
Surgery, Nervous system: neurosurgical and other procedures (ICD-9-CM V3 01–05+89.1, ICD-10-PCS 00-01) Skull CNS thalamus and globus pallidus: Thalamotomy · Thalamic stimulator · Pallidotomy
ventricular system: Ventriculostomy · Suboccipital puncture · Intracranial pressure monitoring
cerebrum: Psychosurgery (Lobotomy, Bilateral cingulotomy) · Hemispherectomy · Anterior temporal lobectomy
pituitary: Hypophysectomy
hippocampus: Amygdalohippocampectomy
Brain biopsyCerebral meningesSpinal cord and roots (Cordotomy, Rhizotomy)
Vertebrae and intervertebral discs: see Template:Bone, cartilage, and joint proceduresCT head · Cerebral angiography · Pneumoencephalography · Echoencephalography/Transcranial doppler · MRI of brain and brain stem · Brain PET · SPECT of brain · MyelographyDiagnosticPNS Sympathetic nerves or gangliaNerves (general)DiagnosticCategories:- Medicine stubs
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Neuroimaging
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.