- Sodium chlorite
-
Sodium chlorite 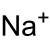
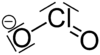

 Sodium chloriteOther namesChlorous acid, sodium salt
Sodium chloriteOther namesChlorous acid, sodium salt
TextoneIdentifiers CAS number 7758-19-2 
PubChem 24452 ChemSpider 22860 
UNII G538EBV4VF 
UN number 1496 KEGG C19523 
RTECS number VZ4800000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Na+].[O-]Cl=O
Properties Molecular formula NaClO2 Molar mass 90.44 g/mol Appearance white solid Density 2.5 g/cm3, solid Melting point 180–200 °C decomp.
Solubility in water 39 g/100 ml (17 °C) Hazards MSDS ICSC 1045 EU Index Not listed NFPA 704 Flash point Non-flammable Related compounds Other anions Sodium chloride
Sodium hypochlorite
Sodium chlorate
Sodium perchlorateOther cations Potassium chlorite
Barium chloriteRelated compounds Chlorine dioxide
Chlorous acid (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Sodium chlorite (NaClO2) is a chemical compound used in the manufacture of paper.
Contents
Use
The main application of sodium chlorite is the generation of chlorine dioxide for bleaching and stripping of textiles, pulp, and paper. It is also used for disinfection of a few municipal water treatment plants after conversion to chlorine dioxide.[1] An advantage in this application, as compared to the more commonly used chlorine, is that trihalomethanes (such as chloroform) are not produced from organic contaminants.[citation needed] . Chlorine dioxide generated from sodium chlorite is approved by FDA under some conditions for disinfecting water used to wash fruits, vegetables, and poultry. [2]
Sodium chlorite, NaClO2, sometimes in combination with zinc chloride, also finds application as a component in therapeutic rinses, mouthwashes,[3][4] toothpastes and gels, mouth sprays,[5] as a teat dip for control of mastitis in dairy cattle,[6] as preservative in eye drops,[7] and in contact lens cleaning solution under the trade name Purite. Under the brand name Oxine it is used for sanitizing air ducts and HVAC/R systems and animal containment areas (walls, floors, and other surfaces).
Chemical reagent
In organic synthesis, sodium chlorite is frequently used as a reagent in the Pinnick oxidation for the oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids. The reaction is usually performed in monosodium phosphate buffered solution in the presence of a chlorine scavenger (usually 2-methyl-2-butene).[8]
Recently, sodium chlorite has been used as an oxidizing agent to convert alkyl furans to the corresponding 4-oxo-2-alkenoic acids in a simple one pot synthesis.[9]
Safety
Sodium chlorite, like many oxidizing agents, should be protected from inadvertent contamination by organic materials to avoid the formation of an explosive mixture. The chemical explodes on percussive impact[10], and will ignite if combined with a strong antioxidant (reducing agent).
Toxicity
Sodium chlorite is a strong oxidant and can therefore be expected to cause clinical symptoms similar to the well known sodium chlorate: methemoglobinemia, hemolysis, renal failure.[11] A dose of 10-15 grams of sodium chlorate can be lethal.[12] Methemoglobemia had been demonstrated in rats and cats [13] and recent studies by the EMEA have confirmed that the clinical symptomatology is very similar to the one caused by sodium chlorate in the rat, mouse, rabbit, and the green monkey. [14]
There is only one human case in the medical literature of chlorite poisoning.[15] It seems to confirm that the toxicity is equal to sodium chlorate. From the analogy with sodium chlorate, even small amounts of about 1 gram can be expected to cause nausea, vomiting and even life-threatening hemolysis in Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase deficient persons.
Manufacture
The free acid, chlorous acid, HClO2, is only stable at low concentrations. Since it cannot be concentrated, it is not a commercial product. However, the corresponding sodium salt, sodium chlorite, NaClO2 is stable and inexpensive enough to be commercially available. The corresponding salts of heavy metals (Ag+, Hg+, Tl+, Pb2+, and also Cu2+ and NH4+) decompose explosively with heat or shock.
Sodium chlorite is derived indirectly from sodium chlorate, NaClO3. First, the explosive (only at concentrations greater than 10% in atmosphere) chlorine dioxide, ClO2 is produced by reducing sodium chlorate in a strong acid solution with a suitable reducing agent (for example, sodium sulfite, sulfur dioxide, or hydrochloric acid). The chlorine dioxide is then absorbed into an alkaline solution and reduced with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), yielding sodium chlorite.
Availability
In the United States sodium chlorite is available in industrial quantities from DuPont.[16]
General references
- "Chemistry of the Elements", N.N. Greenwood and A. Earnshaw, Pergamon Press, 1984.
- "Kirk-Othmer Concise Encyclopedia of Chemistry", Martin Grayson, Editor, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1985
References
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ "New mouthwashes may help take bad breath away" article by Joyce Cohen in USA Today
- ^ SmartMouth 2 Step Mouth Rinse
- ^ Products entry Skin Deep cosmetic safety database
- ^ "Preventing Bovine Mastitis by a Postmilking Teat Disinfectant Containing Acidified Sodium Chlorite" J. Dairy Sci. 90:1201–1208
- ^ Blink Tears
- ^ Bal BS, Childers, Jr. WE, Pinnick HW (1981). "Oxidation of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes" (abstract). Tetrahedron 37: 2091. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)97963-3.
- ^ Annangudi SP, Sun M, Salomon RG (2005). "An efficient synthesis of 4-oxo-2-alkenoic acids from 2-alkyl furans" (abstract). Synlett 9: 1468. doi:10.1055/s-2005-869833. http://www.thieme-connect.com/ejournals/se/abstract/synlett/doi/10.1055/s-2005-869833.
- ^ http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ie50367a007
- ^ Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies, McGraw-Hill Professional; 8th edition (March 28, 2006), ISBN 978-0071437639
- ^ http://www.poisoncentre.be/article.php?id_article=39
- ^ Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. Robert E. Gosselin, Roger P. Smith, Harold C. Hodge, Jeannet Braddock. Uitgever: Williams & Wilkins; 5 edition (September 1984) ISBN 978-0683036329
- ^ Sodium Chlorite - Summary Report of the Europena Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products - Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit [3]
- ^ Acute sodium chlorite poisoning associated with renal failure. Lin JL, Lim PS. Ren Fail. 1993;15(5):645-8. PMID: 8290712
- ^ Chlorine Dioxide and Sodium Chlorite Supply
External links
Sodium compounds NaAlO2 · NaBH3(CN) · NaBH4 · NaBr · NaBrO3 · NaCH3COO · NaCN · NaC6H5CO2 · NaC6H4(OH)CO2 · NaCl · NaClO · NaClO2 · NaClO3 · NaClO4 · NaF · NaH · NaHCO3 · NaHSO3 · NaHSO4 · NaI · NaIO3 · NaIO4 · NaMnO4 · NaNH2 · NaNO2 · NaNO3 · NaN3 · NaOH · NaO2 · NaPO2H2 · NaReO4 · NaSCN · NaSH · NaTcO4 · NaVO3 · Na2CO3 · Na2C2O4 · Na2CrO4 · Na2Cr2O7 · Na2MnO4 · Na2MoO4 · Na2O · Na2O2 · Na2O(UO3)2 · Na2S · Na2SO3 · Na2SO4 · Na2S2O3 · Na2S2O4 · Na2S2O5 · Na2S2O6 · Na2S2O7 · Na2S2O8 · Na2Se · Na2SeO3 · Na2SeO4 · Na2SiO3 · Na2Te · Na2TeO3 · Na2Ti3O7 · Na2U2O7 · NaWO4 · Na2Zn(OH)4 · Na3N · Na3P · Na3VO4 · Na4Fe(CN)6 · Na5P3O10 · NaBiO3
Categories:- Sodium compounds
- Chlorites
- Oxidizing agents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

