- Sodium perchlorate
-
Sodium perchlorate 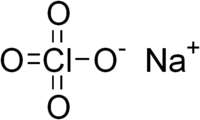
 Other namesSodium chlorate(VII)
Other namesSodium chlorate(VII)
Sodium hyperchlorate
Perchloric acid, sodium saltIdentifiers CAS number 7601-89-0 
PubChem 522606 ChemSpider 22668 
EC number 231-511-9 UN number 1502 ChEMBL CHEMBL1644700 
RTECS number SC9800000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Na+].[O-]Cl(=O)(=O)=O
Properties Molecular formula NaClO4
NaClO4.H2O (monohydrate)Molar mass 122.44 g/mol Appearance White crystalline solid Density 2.4994 g/cm3 Melting point 130 °C (monohydrate)
>400 °C (decomp.)Solubility in water 209.6 g/100 ml at 25 °C Related compounds Other anions Sodium chloride
Sodium hypochlorite
Sodium chlorite
Sodium chlorateOther cations Lithium perchlorate
Potassium perchlorate
Ammonium perchlorate
Caesium perchlorateRelated compounds Perchloric acid  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Sodium perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaClO4. It is the most soluble of the common perchlorate salts. It is a white crystalline, hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and in alcohol. It usually comes as the monohydrate, which has a rhombic crystal structure.[citation needed]
Its heat of formation is −382.75 kJ mol−1.[1]
Contents
Uses
Sodium perchlorate is the precursor to many other perchlorate salts, often taking advantage of their low solubility relative to NaClO4 (209 g/100 ml at 25 °C). Perchloric acid is made by treating NaClO4 with HCl.
NaClO4 finds only minimal use in pyrotechnics because it is hygroscopic; ammonium and potassium perchlorates are preferred. These salts are prepared by double decomposition from a solution of sodium perchlorate and potassium or ammonium chlorides.
Laboratory applications
NaClO4 has a variety of uses in the laboratory, often as a nonreactive electrolyte. For example, it is used in standard DNA extraction and hybridization reactions in molecular biology.
Production
Sodium perchlorate is produced by anodic oxidation of sodium chlorate, not sodium chloride, at a platinum electrode.[2]
- ClO3− + H2O → ClO4− + H2
See also
External links
References
- ^ WebBook page for NaClO4
- ^ Helmut Vogt, Jan Balej, John E. Bennett, Peter Wintzer, Saeed Akbar Sheikh, Patrizio Gallone “Chlorine Oxides and Chlorine Oxygen Acids” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_483
Sodium compounds NaAlO2 · NaBH3(CN) · NaBH4 · NaBr · NaBrO3 · NaCH3COO · NaCN · NaC6H5CO2 · NaC6H4(OH)CO2 · NaCl · NaClO · NaClO2 · NaClO3 · NaClO4 · NaF · NaH · NaHCO3 · NaHSO3 · NaHSO4 · NaI · NaIO3 · NaIO4 · NaMnO4 · NaNH2 · NaNO2 · NaNO3 · NaN3 · NaOH · NaO2 · NaPO2H2 · NaReO4 · NaSCN · NaSH · NaTcO4 · NaVO3 · Na2CO3 · Na2C2O4 · Na2CrO4 · Na2Cr2O7 · Na2MnO4 · Na2MoO4 · Na2O · Na2O2 · Na2O(UO3)2 · Na2S · Na2SO3 · Na2SO4 · Na2S2O3 · Na2S2O4 · Na2S2O5 · Na2S2O6 · Na2S2O7 · Na2S2O8 · Na2Se · Na2SeO3 · Na2SeO4 · Na2SiO3 · Na2Te · Na2TeO3 · Na2Ti3O7 · Na2U2O7 · NaWO4 · Na2Zn(OH)4 · Na3N · Na3P · Na3VO4 · Na4Fe(CN)6 · Na5P3O10 · NaBiO3
Categories:- Perchlorates
- Sodium compounds
- Oxidizing agents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
