- Media, Pennsylvania
-
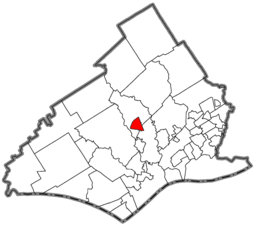
Borough of Media Borough Bank building on State StreetSealNickname: Everybody's Hometown Country United States State Pennsylvania County Delaware Elevation 299 ft (91.1 m) Coordinates 39°55′08″N 75°23′17″W / 39.91889°N 75.38806°W Area 0.8 sq mi (2.1 km2) - land 0.8 sq mi (2 km2) - water 0.0 sq mi (0 km2) Population 5,533 (2000) Density 7,399.0 / sq mi (2,856.8 / km2) Incorporated 1850 Timezone EST (UTC-5) - summer (DST) EDT (UTC-4) ZIP code 19063 Area code 610 Website: http://www.mediaborough.com The borough of Media is the county seat of Delaware County, Pennsylvania[1] and is located 12 miles (19 km) west of Philadelphia. Media was incorporated in 1850 at the same time that it was named the county seat.[2] The population was 5,533 at the 2000 census. Its school district is the Rose Tree Media School District with Penncrest High School and Springton Lake Middle School. In June 2006, it became the first fair trade town in America.[3]
The history of the town goes back to William Penn, but the area remained predominantly rural until the twentieth century, and is suburban today. The Delaware County Institute of Science was founded in Media in 1833, while the Pennsylvania Institute of Technology, a two-year technical college, Williamson Free School of Mechanical Trades a three-year technical college, and Delaware County Community College, a two-year liberal arts college, are located nearby. Media promotes itself as "Everybody's Hometown."
Contents
History
Land in area was sold and settled soon after William Penn was named proprietor of the colony of Pennsylvania in 1681 by King Charles II of England. Peter and Wiliam Taylor bought the land where Media is now located, directly from Penn.[4] Providence Township was organized in 1684, and divided into Upper Providence and Nether Providence Townships by 1690 even though they only had 40 taxable properties at the time.[5][6] The current borough, formed in 1850, sits between the two townships.
In 1683 the Court of Chester County approved the construction of "Providence Great Road" (now Pennsylvania Route 252). The road, which runs north from Chester to within a few blocks from today's downtown, is shown on a 1687 map along with the names of local landowners.[7] It forms the eastern border of the borough.
Thomas Minshall, a Quaker, was an early Media resident, settling just outside the small village then known as Providence, along the Providence Great Road. The village then included a tailor shop, blacksmith shop, wheelwright shop, barn and other buildings.
Minshall bought 625 acres (2.53 km2) from William Penn and arrived in 1682. The Providence Friends Meeting was established at his house in February, 1688, and a meetinghouse was later built on land he donated for the purpose. The original meetinghouse was built out of logs in 1699 or 1700 and the current building dates to 1814. Minshall’s house still stands and was given to the citizens of the borough in 1975. During the American Revolution the Marquis de La Fayette bought a saddle at the Minshall house.[8]
The area remained rural through 1850. On March 11, 1850 the State of Pennsylvania by Special Act of Assembly incorporated the Borough of Media, and made the sale of malt and spirituous liquors unlawful within its borders. At the same time the county seat of Delaware County was moved to Media from Chester. The borough was formed from four farms purchased by the county, totalling only 480 acres (1.9 km2). The borders of the borough have not changed since that time.
Streets were plotted in a rectangular grid around the location of the new courthouse, lots were sold at public auctions, and the construction of houses began. Sources agree that Minshall Painter, a descendant of Thomas Minshall, suggested the name "Media," but do not agree on the reason. The name may come from the city’s central location in Delaware County, or from the biblical area of Medea.
The John J. Tyler Arboretum occupies part of Thomas Minshall’s original 625 acres (2.53 km2). This farm was used by the underground railroad.[9] The land was donated to a public trust in 1944 by an eighth generation descendant. The arboretum was started as a private collection by brothers Jacob and Minshall Painter. In 1825 they began systematically planting over 1,000 varieties of trees and shrubs. Over 20 of their original trees survive including a giant sequoia.[10]
Minshall Painter was also a leader of the Delaware County Institute of Science, which was formed on September 21, 1833 with just four other members: George Miller, John Miller, George Smith, M.D., and John Cassin. The Institute was incorporated in 1836. About 1850, Painter gave the Institute the land where its building currently stands at 11 Veteran's Square, and the building was constructed in 1867.
In the second half of the 19th Century, Media was a summer resort for well-to-do Philadelphians. The borough's large vacation hotels included the Idlewild Hotel (1871) on Lincoln Street at Gayley Terrace, Chestnut Grove House or "The Colonial" (1860) on Orange Street, and Brooke Hall on Lemon Street and Washington Ave. (now Baltimore Ave.). The Chestnut Grove was used for a year by nearby Swarthmore College due to a fire on their campus.
The West Chester and Philadelphia Railroad was built through Media on October 19, 1854. Electrified service was opened on December 2, 1928. Up to 50 trains passed through each day. The railroad became part of the Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad and eventually the Penn Central. SEPTA took over operations in 1983. Woodrow Wilson spoke at the Media Station in 1912 during his first election campaign. Trolley transportation lines spread to and through Media in the 1890s and early 1900s.
The Media Theatre opened as a vaudeville house in 1927.[11] The first talkie film, "The Jazz Singer", was shown there. It remained a popular cinema through the 1970s. In 1994, the theater was refurbished by Walter Strine, Sr. and reopened as a professional live music theater. Shows produced there include "The Full Monty", "Carousel", and "Miss Saigon". Tony Award winners Judy Kaye and David Miller have performed there.
In June 2006, Media became the first US town to follow over three-hundred towns in Europe in attaining fair trade certification. To meet the criteria for certification, Media passed a council resolution in support of fair trade, serve fair-trade coffee and tea in local government meetings and offices, ensure that a range of fair-trade products were available in local restaurants and businesses, raise popular support and provide media coverage for the fair-trade campaign, and convene a fair-trade steering committee to ensure continued commitment.
The Borough of Media, PA is run by a Mayor along with the elected Borough Council. The main responsibility of theirs is to ensure the safety and livelihood of the residents of Media, PA. The Mayor of Media, Bob McMahon, was first elected in 1992; Pete Alyanakian serves as President and Monika Simpson is Media's Vice-President.
Current Borough Council members are as follows: Dr. Eric Stein, Monica G. Simpson, Dawn Roe, Peter Williamson, and James Cunningham.[12]
Media and the FBI
Media may be best known for secret government documents which were illegally seized there by activists in 1971 and distributed nationwide. On March 8 of that year, the Citizens' Commission to Investigate the FBI raided an FBI "resident agency" in Media. They later released thousands of documents to major newspapers around the country. These documents revealed controversial and illegal FBI tactics, like the recruitment of Boy Scouts as informants, and confirmed for the first time the existence of COINTELPRO, an FBI program to "expose, disrupt, misdirect, discredit, or otherwise neutralize" dissident groups in the US.[13]
Landmarks
- Minshall House (1702) on Route 252.
- Media Presbyterian Church (1855) at Baltimore Ave. and Church Street, designed by John McArthur, architect of Philadelphia City Hall.
- Delaware County Institute of Science (1867) on Veterans’ Square. Google Street View
- Cooper House (before 1870) on State Street.
- Delaware County Court House (1871) on Front Street. Google Street View
- Media Monthly Meeting of the Religious Society of Friends (1875) and Media-Providence Friends School (1876), both located at 125 W. 3rd Street.
- Risley House (1877) 430 N. Monroe St.
- Hillhurst (1890) on Orange Street, designed by Addison Hutton.
- Provident National Bank (1900) on State Street at Veterans’ Square, designed by Albert Dilks. Google Street View
- Media Armory (1908) on State Street, designed by William S. Price and M H. McClanahan. It now houses the Pennsylvania Veterans’ Museum and Trader Joe’s.[14]
- Media Theatre (1927) on State Street, designed by Louis Magziner as a Beaux-arts movie palace with Art Deco design elements. It now is home to the Media Theatre for the Performing Arts.[14]
- Jaisohn House, 100 East Lincoln Street Google Street View
Surrounding area
Since the borough of Media is only 0.8 sq mi (2.1 km2) and the "Media ZIP code" 19063 covers a much larger area,[15] the geographic term "Media" is often used in a sense that includes not only the borough of Media, but other contiguous areas that are part of other municipalities but that share the ZIP code. These include the entire Upper Providence Township, and in Nether Providence Township, the neighborhoods of South Media, Bowling Green, Pine Ridge, most of Middletown Township including the entire Elwyn, Bortondale, Riddlewood, Lima, Glen Riddle, and Lenni neighborhoods. Even some parts of Marple Township have the zip code 19063.
Geography
Media is located at 39°55′8″N 75°23′17″W / 39.91889°N 75.38806°W (39.918761, -75.388127).[16]
According to the United States Census Bureau, the borough has a total area of 0.8 square miles (2.1 km2), of which 0.8 square miles (2.1 km2) is land and 1.33% is water.
Demographics
Historical populations Census Pop. %± 1930 5,372 — 1940 5,351 −0.4% 1950 5,726 7.0% 1960 5,803 1.3% 1970 6,444 11.0% 1980 6,119 −5.0% 1990 5,957 −2.6% 2000 5,533 −7.1% www.dvrpc.org/data/databull/rdb/db82/appedixa.xls.</ref> As of the census[17] of 2000, there were 5,533 people, 2,782 households, and 1,112 families residing in the borough. The population density was 7,399.0 people per square mile (2,848.4/km²). There were 2,966 housing units at an average density of 3,966.3 per square mile (1,526.9/km²). The racial makeup of the borough was 81.02% White, 14.22% African American, 0.14% Native American, 2.01% Asian, 0.02% Pacific Islander, 0.65% from other races, and 1.93% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.88% of the population.
There were 2,782 households out of which 14.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 27.2% were married couples living together, 9.5% had a female householder with no husband present, and 60.0% were non-families. 49.2% of all households were made up of individuals and 11.7% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 1.85 and the average family size was 2.73.
In the borough the population was spread out with 13.7% under the age of 18, 8.3% from 18 to 24, 34.3% from 25 to 44, 23.0% from 45 to 64, and 20.6% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 41 years. For every 100 females there were 83.9 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 81.9 males.
The median income for a household in the borough was $42,703, and the median income for a family was $58,065. Males had a median income of $42,121 versus $31,904 for females. The per capita income for the borough was $28,188. About 6.1% of families and 7.9% of the population were below the poverty line, including 9.7% of those under age 18 and 11.2% of those age 65 or over.
The population in 1900 consisted of 3,075 people, whose numbers grew to 3,562 in 1910, and to 5,351 in 1940.
Religion
Media is home to many churches, including Cambell A.M.E, Christ Church (Episcopalian), First Baptist, First United Methodist, Media Presbyterian, Nativity B.V.M. (Roman Catholic), St. George (Greek Orthodox), the Unitarian Universalist Church of Delaware County and two Quaker meetinghouses, Media Friends Meeting and Providence Friends Meeting.[18] Congregation Beth Israel, a Reconstructionist synagogue formed in 1925, is west of town in Middletown Township and is the oldest Reconstructionist congregation in the Delaware Valley.[19]
Transportation
Media is connected to Upper Darby, Pennsylvania, by the 101 trolley and is the only suburban town in the United States to have a trolley run down the middle of its main street. The trolley terminates just after the Delaware County Courthouse, at a station known as Orange Street. Media also has a stop on the Media/Elwyn Regional Rail Line at the corner of Orange Street and Station Road.
U.S. 1 formerly ran through the borough until the "Media bypass" was completed in 1960.[20] The bypass has an unusual "volleyball" or three-level diamond interchange with Interstate 476. The road, formerly known as Route 1, is also known by its even older name, Baltimore Pike.[citation needed]
Philadelphia International Airport (PHL), the 11th busiest airport in the world in 2007, is 10.2 miles (16.4 km) driving distance (about 15 minutes) from downtown Media, following Baltimore Pike east, then Interstate 476 south and Interstate 95 northeast.[21][22]
Notable residents
- Jonathan Bixby, costume designer.
- John Martin Broomall, congressman.
- Edward Darlington, congressman.
- Paul DiMeo, actor, Extreme Makeover: Home Edition.[23]
- Philip Jaison, a Korean nationalist, lived in Media from 1925 to 1951.
- Harry Kalas, broadcaster for the Philadelphia Phillies.
- Lew Krausse, Sr., pitcher for the Philadelphia Athletics.
- Lew Krausse, Jr., pitcher for the Kansas City/Oakland Athletics, and other teams.
- Phil Martelli, Head Basketball Coach, Saint Joseph's University.
- Ida Saxton McKinley, First Lady.
- Dave Miller record producer for Bill Haley's "Rocket 88".[14]
- Michael A. O'Donnell, Ph.D., author, researcher, international lecturer, and Episcopal priest.
- Samuel D. Riddle, textile mill owner and race horse owner.
- John Buchanan Robinson, editor and congressman.
- Dean Sabatino, drummer for The Dead Milkmen.
References
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. http://www.naco.org/Counties/Pages/FindACounty.aspx. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- ^ Ashmead, Henry Graham (1884). History of Delaware County, Pennsylvania. Philadelphia: L. H. Everts & Co.. Chapters XVI and XLVI. http://www.delcohistory.org/ashmead/ashmead_pg587.htm#chapter46. Retrieved 2007-09-30.
- ^ First Free Trade Town
- ^ Media: A Walking Tour, Published by the Borough of Media, 1990
- ^ History of Delaware County
- ^ Nether Providence Through the Years (Delaware County Historical Society)
- ^ The City of Philadelphia two Miles in Length and one in Breadth (Lower Merion Historical Society)
- ^ Minshall House
- ^ The trackless train: Tracking Delco's role in the Underground Railroad, Feb. 27, 1989, LORETTA RODGERS, Delaware County Daily Times
- ^ Tyler Arboretum History
- ^ The Media Theatre for the Performing Arts - History
- ^ Media Borough Council Biographies
- ^ [1]
- ^ a b c Pennsylvania Veteran's Museum accessed October 28, 2009
- ^ Hipcode.com 19063
- ^ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. http://www.census.gov/geo/www/gazetteer/gazette.html. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- ^ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ "Religious Organizations in Media". Welcome to Media Borough. Borough of Media, Pennsylvania. http://mediaborough.com/about/religion.asp. Retrieved April 9, 2009.
- ^ History, Synagogue website. Accessed July 23, 2008.
- ^ US Expressway 1 South of Philadelphia - Historic Overview
- ^ Statistics: Top 30 World Airports
- ^ Google Map directions
- ^ Bio: Carpenter Paul Dimeo of ABC's Extreme Makeover: Home Edition
External links
 Providence Road (center of map) from Thomas Holme's 1687 map of Pennsylvania. Present day Media is located within the plots marked "P.Taylor" and "W.Taylor."
Providence Road (center of map) from Thomas Holme's 1687 map of Pennsylvania. Present day Media is located within the plots marked "P.Taylor" and "W.Taylor."
- Media PA Area Street Map
- Delaware County Community College
- Delaware County Institute of Science
- The Media Theatre
- Philip Jaisohn Memorial House
- Pennsylvania Veterans Museum
- Borough of Media
- Delaware County Youth Initiative
- Delaware County History
- Healthy Communities Initiative-Rose Tree Media
- Historical Photographs
- Media Arts Council
- Media Borough at DelawareCountyPA.com
- Media's Fair Trade Town Committee
- Nether Providence History
- Media, PA News
- All Things Media, PA
- Semi-centennial of the Borough of Media, Penna., May 19, 1900. Media, PA: T.V. Cooper. 1900. pp. 112. http://books.google.com/books?id=DhUVAAAAYAAJ.
- Lenny Campello (November 27, 2007). Sunday Evening Stroll through Media, PA. Media, PA. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7MKFjYrLHMc.
- Visit Media PA
County seats of Pennsylvania Cities Allentown | Butler | Easton | Erie | Franklin | Greensburg | Harrisburg | Lancaster | Lebanon | Lock Haven | Meadville | New Castle | Philadelphia | Pittsburgh | Pottsville | Reading | Scranton | Sunbury | Uniontown | Warren | Washington | Wilkes-Barre | Williamsport | York
Boroughs Beaver | Bedford | Bellefonte | Bloomfield | Brookville | Carlisle | Chambersburg | Clarion | Clearfield | Coudersport | Danville | Doylestown | Ebensburg | Emporium | Gettysburg | Hollidaysburg | Honesdale | Huntingdon | Indiana | Jim Thorpe | Kittanning | Laporte | Lewisburg | Lewistown | McConnellsburg | Media | Mercer | Middleburg | Mifflintown | Milford | Montrose | Norristown | Ridgway | Smethport | Somerset | Stroudsburg | Tionesta | Towanda | Tunkhannock | Waynesburg | Wellsboro | West Chester
Town Categories:- County seats in Pennsylvania
- Populated places established in 1682
- Boroughs in Delaware County, Pennsylvania
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.