- Xylulose
-
Xylulose[1][2] 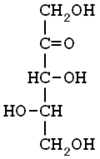
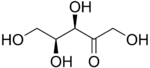 (3R,4S)-1,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxypentan-2-oneOther namesthreo-Pentulose
(3R,4S)-1,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxypentan-2-oneOther namesthreo-Pentulose
threo-2-PentuloseIdentifiers CAS number 5962-29-8 (D/L)  , 551-84-8 (D)
, 551-84-8 (D)  , 527-50-4 (L)
, 527-50-4 (L) 
PubChem 22253 ChemSpider 20892 
ChEBI CHEBI:17399 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C([C@@H]([C@H](C(=O)CO)O)O)O
Properties Molecular formula C5H10O5 Molar mass 150.13 g/mol Appearance Syrup  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Xylulose is a ketopentose, a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms, and including a ketone functional group. It has the chemical formula C5H10O5. In nature, it occurs in both the L- and D-enantiomers.
Contents
Pathology
L-Xylulose accumulates in the urine in patients with pentosuria, due to a deficiency in L-xylulose reductase. Since L-xylulose is a reducing sugar like D-glucose, pentosuria patients have been wrongly diagnosed in the past to be diabetic.
See also
References
External links
Types of carbohydrates General: Geometry Monosaccharides Aldodiose (Glycolaldehyde)Ketopentose (Ribulose, Xylulose)
Aldopentose (Ribose, Arabinose, Xylose, Lyxose)
Deoxy sugar (Deoxyribose)Ketoheptose (Sedoheptulose, Mannoheptulose)>7Multiple Other oligosaccharidesGlucose/Glucan: Glycogen · Starch (Amylose, Amylopectin) · Cellulose · Dextrin/Dextran · Beta-glucan (Zymosan, Lentinan, Sizofiran) · Maltodextrin
Fructose/Fructan: Inulin · Levan beta 2→6
N-Acetylglucosamine: Chitinbiochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/i
This article about a ketone is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
