- Mutarotation
-
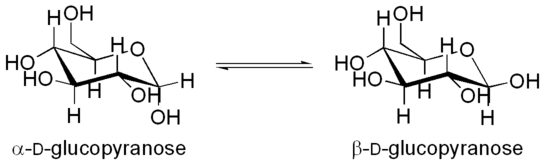
Mutarotation is the change in the optical rotation that occurs by epimerization (that is the change in the equilibrium between two epimers, when the corresponding stereocenters interconvert). Cyclic sugars show mutarotation as α and β anomeric forms interconvert.[1] The optical rotation of the solution depends on the optical rotation of each anomer and their ratio in the solution.
Mutarotation was discovered by French chemist Dubrunfaut in 1846, when he noticed that the specific rotation of aqueous sugar solution changes with time.[2][3]
Contents
Measurement
The α and β anomers are diastereomers of each other and usually have different specific rotations. A solution or liquid sample of a pure α anomer will rotate plane polarised light by a different amount and/or in the opposite direction than the pure β anomer of that compound. The optical rotation of the solution depends on the optical rotation of each anomer and their ratio in the solution.
For example if a solution of β-D-glucopyranose is dissolved in water, its specific optical rotation will be +18.7. Over time, some of the β-D-glucopyranose will undergo mutarotation to become α-D-glucopyranose, which has an optical rotation of +112.2. Thus the rotation of the solution will increase from +18.7 to an equilibrium value of +52.5 as some of the β form is converted to the α form. The equilibrium mixture is actually about 64% of β-D-glucopyranose and about 36% of α-D-glucopyranose, though there are also with traces of the other forms including furanoses and open chained form.[4]
The observed optical rotation of the sample is the weighted sum of the optical rotation of each anomer weighted by the amount of that anomer present. Therefore one can use a polarimeter to measure the rotation of a sample and then calculate the ratio of the two anomers present from the enantiomeric excess, as long as one knows the rotation of each pure anomer. One can monitor the mutarotation process over time or determine the equilibrium mixture by observing the optical rotation and how it changes.
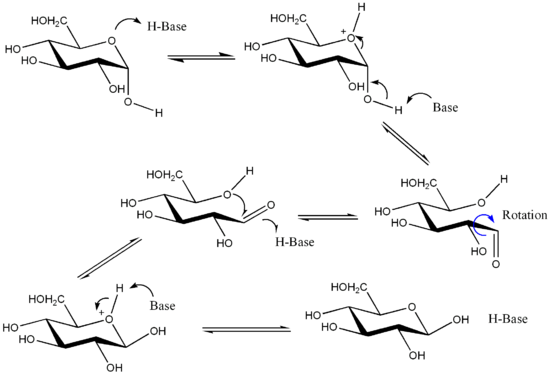
Reaction mechanism
See also
References
- ^ IUPAC Gold Book mutarotation
- ^ Derek Horton (2008). "The Development of Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biology". Carbohydrate Chemistry, Biology and Medical Applications: 1–28. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-054816-6.00001-X.
- ^ Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut—An early sugar chemist. Hewitt G. Fletcher, J. Chem. Educ., 1940, 17 (4), p 153, DOI: 10.1021/ed017p153
- ^ Francis Carey (2000). Organic Chemistry (4th, McGraw-Hill Higher Education Press ed.).
Types of carbohydrates General: Geometry Monosaccharides Aldodiose (Glycolaldehyde)Ketopentose (Ribulose, Xylulose)
Aldopentose (Ribose, Arabinose, Xylose, Lyxose)
Deoxy sugar (Deoxyribose)Ketoheptose (Sedoheptulose, Mannoheptulose)>7Multiple Other oligosaccharidesGlucose/Glucan: Glycogen · Starch (Amylose, Amylopectin) · Cellulose · Dextrin/Dextran · Beta-glucan (Zymosan, Lentinan, Sizofiran) · Maltodextrin
Fructose/Fructan: Inulin · Levan beta 2→6
N-Acetylglucosamine: Chitinbiochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iCategories:- Carbohydrate chemistry
- Organic chemistry
- Carbohydrates
- Stereochemistry
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.