- Oogenesis
-
Oogenesis Oogenesis, ovogenesis or oögenesis (
 /ˌoʊ.əˈdʒɛnɨsɪs/)[1] is the creation of an ovum (egg cell). It is the female form of gametogenesis. The male equivalent is spermatogenesis. It involves the development of the various stages of the immature ovum.
/ˌoʊ.əˈdʒɛnɨsɪs/)[1] is the creation of an ovum (egg cell). It is the female form of gametogenesis. The male equivalent is spermatogenesis. It involves the development of the various stages of the immature ovum.Contents
Oogenesis in mammals
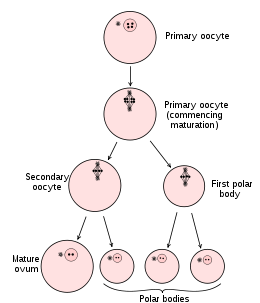 Diagram showing the reduction in number of the chromosomes in the process of maturation of the ovum.
Diagram showing the reduction in number of the chromosomes in the process of maturation of the ovum.
In mammals, the first part of oogenesis starts in the germinal epithelium, which gives rise to the development of ovarian follicles, the functional unit of the ovary.
Note that this process, important to all animal life cycles yet unlike all other instances of cell division, occurs completely without the aid of oo spindle-coordinating centrosomes.[citation needed]
Oogenesis consists of several sub-processes: oocytogenesis, ootidogenesis, and finally maturation to form an ovum (oogenesis proper). Folliculogenesis is a separate sub-process that accompanies and supports all three oogenetic sub-processes.
Cell type ploidy Process Process completion Oogonium diploid Oocytogenesis (mitosis) third trimester (forming oocytes) primary Oocyte diploid Ootidogenesis (meiosis 1) (Folliculogenesis) Dictyate in prophase I for up to 50 years secondary Oocyte haploid Ootidogenesis (meiosis 2) Halted in metaphase II until fertilization Ovum haploid Oogonium --(Oocytogenesis)--> Primary Oocyte --(Meiosis I)-->First Polar Body (Discarded afterward) + Secondary oocyte --(Meiosis II)--> Secondary Polar Body (Discarded afterward) + Ovum
The Creation of Oogonia
The creation of oogonia traditionally doesn't belong to oogenesis proper but, instead, to the common process of gametogenesis, which in the female human begins with the processes of folliculogenesis, oocytogenesis, and ootidogenesis.
Human Oogenesis
At the start of the menstrual cycle, some 12-20 primary follicles begin to develop under the influence of elevated FSH to form secondary follicles. The primary follicles have formed from primordial follicles, which developed in the ovary at around 10–30 weeks after conception. By around day 9 of the cycle, only one healthy secondary follicle remains, with the rest having undergone cellular atresia. The remaining follicle is called the dominant follicle and is responsible for producing large amounts of oestradiol during the late follicular phase. Oestradiol production depends upon co-operation between the theca and granulosa cells. On day 14 of the cycle, an LH surge occurs, which itself is triggered by the positive feedback of oestradiol. This causes the secondary follicle to develop into a tertiary follicle, which then ovulates some 24–36 hours later. An important event in the development of the tertiary follicle occurs when the primary oocyte completes the first meiotic division, resulting in the formation of a polar body and a secondary oocyte. The empty follicle then forms a corpus luteum.[citation needed]
Oocytogenesis
Oogenesis starts with the process of developing oogonia, which occurs via the transformation of primordial follicles into primary oocytes, a process called oocytogenesis.[2] Oocytogenesis is complete either before or shortly after birth.
Number of primary oocytes
It is commonly believed that, when oocytogenesis is complete, no additional primary oocytes are created, in contrast to the male process of spermatogenesis, where gametocytes are continuously created. In other words, primary oocytes reach their maximum development at ~20[3] weeks of gestational age, when approximately seven million primary oocytes have been created; however, at birth, this number has already been reduced to approximately 1-2 million.
Recently, however, two publications have challenged the belief that a finite number of oocytes are set around the time of birth.[4][5] The renewal of ovarian follicles from germline stem cells (originating from bone marrow and peripheral blood) has been reported in the postnatal mouse ovary.
Due to the revolutionary nature of these claims, further experiments are required to determine the true dynamics of small follicle formation.
Ootidogenesis
The succeeding phase of ootidogenesis occurs when the primary oocyte develops into an ootid. This is achieved by the process of meiosis. In fact, a primary oocyte is, by its biological definition, a cell whose primary function is to divide by the process of meiosis.[6]
However, although this process begins at prenatal age, it stops at prophase I. In late fetal life, all oocytes, still primary oocytes, have halted at this stage of development, called the dictyate. After menarche, these cells then continue to develop, although only a few do so every menstrual cycle.
Meiosis I
Meiosis I of ootidogenesis begins during embryonic development, but halts in the diplotene stage of prophase I until puberty. For those primary oocytes that continue to develop in each menstrual cycle, however, synapsis occurs and tetrads form, enabling Chromosomal crossover to occur. As a result of meiosis I, the primary oocyte has now developed into the secondary oocyte and the first polar body.
Meiosis II
Immediately after meiosis I, the haploid secondary oocyte initiates meiosis II. However, this process is also halted at the metaphase II stage until fertilization, if such should ever occur. When meiosis II has completed, an ootid and another polar body have now been created.
Folliculogenesis
Main article: FolliculogenesisSynchronously with ootidogenesis, the ovarian follicle surrounding the ootid has developed from a primordial follicle to a preovulatory one.
Maturation into ovum
Both polar bodies disintegrate at the end of Meiosis II, leaving only the ootid, which then eventually undergoes maturation into a mature ovum.
The function of forming polar bodies is to discard the extra haploid sets of chromosomes that have resulted as a consequence of meiosis.
In vitro maturation
Main article: In vitro maturationIn vitro maturation (IVM) is the technique of letting ovarian follicles mature in vitro. It can potentially be performed before an IVF. In such cases, ovarian hyperstimulation isn't essential. Rather, oocytes can mature outside the body prior to IVF. Hence, no (or at least a lower dose of) gonadotropins have to be injected in the body.[7] However, there still isn't enough evidence to prove the effectiveness and security of the technique.[7]
Oogenesis in non-mammals
Main article: Evolution of sexual reproductionMany protists produce egg cells in structures termed archegonia. Some algae and the oomycetes produce eggs in oogonia. In the brown alga Fucus, all four egg cells survive oogenesis, which is an exception to the rule that generally only one product of female meiosis survives to maturity.
In plants, oogenesis occurs inside the female gametophyte via mitosis. In many plants such as bryophytes, ferns, and gymnosperms, egg cells are formed in archegonia. In flowering plants, the female gametophyte has been reduced to an eight-celled embryo sac within the ovule inside the ovary of the flower. Oogenesis occurs within the embryo sac and leads to the formation of a single egg cell per ovule.
In ascaris, the oocyte does not even begin meiosis until the sperm touches it, in contrast to mammals, where meiosis is completed in the estrus cycle.
See also
References
- ^ Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary Definition: Oogenesis
- ^ NCBI - The saga of the germ line
- ^ Lobo RA (September 2003). "Early ovarian ageing: a hypothesis. What is early ovarian ageing?". Hum. Reprod. 18 (9): 1762–4. doi:10.1093/humrep/deg377. PMID 12923124. http://humrep.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12923124.
- ^ Johnson J, Bagley J, Skaznik-Wikiel M, et al. (July 2005). "Oocyte generation in adult mammalian ovaries by putative germ cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood". Cell 122 (2): 303–15. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.031. PMID 16051153.
- ^ Johnson J, Canning J, Kaneko T, Pru J, Tilly J (2004). "Germline stem cells and follicular renewal in the postnatal mammalian ovary". Nature 428 (6979): 145–50. doi:10.1038/nature02316. PMID 15014492.
- ^ Biochem
- ^ a b Vejledning om kunstig befrugtning 2006 (Danish)
External links
Female reproductive system (TA A09.1–2, TH H3.07.01, GA 11.1254) Internal Adnexacorpus (hemorrhagicum, luteum, albicans) · Theca of follicle (externa, interna) · Follicular antrum (Follicular fluid) · Corona radiata · Zona pellucida · Membrana granulosa · Perivitelline spaceOtherProper of ovary · Suspensory of ovarycorpus/body (Uterine cavity, Fundus) · cervix/neck (External orifice, Canal of the cervix, Internal orifice, Supravaginal portion of cervix, Vaginal portion of cervix, Cervical ectropion) · Uterine hornsGeneralExternal Mons pubis · Labia majora (Anterior commissure, Posterior commissure) · Pudendal cleft · Labia minora (Frenulum of labia minora, Frenulum of clitoris) · Vulval vestibule · Interlabial sulci · Bulb of vestibule · Vaginal orifice
vestibular glands/ducts (Bartholin's glands/Bartholin's ducts, Skene's glands/Skene's ducts)Other Human physiology and endocrinology of sexual reproduction Menstrual and estrous cycle Gametogenesis Spermatogenesis (spermatogonium, spermatocyte, spermatid, sperm) · Oogenesis (oogonium, oocyte, ootid, ovum) · Germ cell (gonocyte, gamete)Human sexual behavior Sexual intercourse · Masturbation · Erection · Orgasm · Ejaculation · Insemination · Fertilisation/Fertility · Implantation · Pregnancy · Postpartum period · Mechanics of sexLife span Egg (biology) Reproductive endocrinology
and infertilityBreast Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
