- Myometrium
-
Myometrium 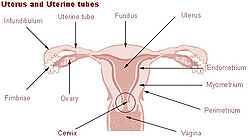
Uterus and uterine tubes (Myometrium labeled at center right) Microscopic slide of the myometrium. Latin tunica muscularis The myometrium is the middle layer of the uterine wall, consisting mainly of uterine smooth muscle cells (also called uterine myocytes[1]), but also of supporting stromal and vascular tissue. Its main function is to induce uterine contractions.
Contents
Macrostructure
The myometrium is located between the endometrium (the inner layer of the uterine wall), and the serosa or perimetrium (the outer uterine layer).
The inner one-third of the myometrium (termed the junctional or sub-endometrial layer) appears to be derived from the Müllerian duct, while the outer, more predominant layer myometrium appears to originate from non-Mullerian tissue, and is the major contractile tissue during parturition and abortion.[1] Also, the junctional layer appears to function like a circular muscle layer, capable of peristaltic and anti-peristaltic activity, equivalent to the muscular layer of the intestines.[1]
Molecular muscular structure
The smooth muscle of the myometrium is basically very similar in molecular structure to smooth muscle in other sites of the body, with myosin and actin being the predominant proteins expressed.[1] In uterine smooth muscle, there is approximately 6-fold more actin than myosin.[1] A shift in the myosin expression of the uterine smooth muscle has been hypothesized to avail for changes in the directions of uterine contractions that are seen during the menstrual cycle.[1]
Contractile patterns
Uterine smooth muscle has a phasic pattern, shifting between a contractile pattern and maintenance of a resting tone with discrete, intermittent contractions of varying frequency, amplitude and duration.[1]
Also, as noted for the macrostructure of uterine smooth muscle, the junctional layer appears be capable of both peristaltic and anti-peristaltic activity.[1]
Resting state
The resting membrane potential (Vrest) of uterine smooth muscle has been recorded to be between -35 and -80 mV.[1] As with the resting membrane potential of other cell types, it is basically maintained by a Na+/K+ pump that causes a higher concentration of Na+ ions in the extracellular space than in the intracellular space, and a higher concentration of K+ ions in the intracellular space than in the extracellular space. Subsequently, having K+ channels open to a higher degree than Na+ channels results in an overall efflux of positive ions, resulting in a negative potential.
This resting potential undergoes rhythmic oscillations, which have been termed slow waves, and reflect intrinsic activity of slow wave potentials.[1] These slow waves are caused by changes in the distribution of Ca2+, Na+, K+ and Cl- ions between the intracellular and extracellular spaces, which, in turn, reflects the permeability of the plasma membrane to each of those ions.[1] K+ is the major ion responsible for such changes in ion flux, reflecting changes in various K+ channels.[1]
Excitation-contraction
The excitation-contraction coupling of uterine smooth muscle is also basically very similar to smooth muscle in general, with intracellular increase in calcium (Ca2+) leading to contraction. However, the stimulating factors for uterine smooth muscle differs from other types of smooth muscle, availing for separate coordination of uterine smooth muscle.
Restoration to resting state
Removal of Ca2+ after contraction induces relaxation of the smooth muscle, and restores the molecular structure of the sarcoplasmic reticulum to avail for the next contractile stimulus.[1]
Functions
The myometrium stretches (the smooth muscle cells expand in both size and number[2]) during pregnancy to allow for the harboring of the pregnancy, and contracts in a coordinated fashion, via a positive feedback effect on the "Ferguson reflex"), during the process of labor. After delivery the myometrium contracts to expel the placenta and reduce blood loss. Thus a positive benefit to early breast feeding is a natural stimulation of this reflex to reduce blood loss and facilitate a swift return to prepregnancy uterine and abdominal muscle tone.
Pathology
Lack of contraction at this stage is termed uterine atony. After pregnancy the uterus returns to its nonpregnant size by a process of myometrial involution.
Neoplasms of the myometrium are very common, termed uterine leiomyomata or fibroids. Their malignant version, leiomyosarcoma, is rare.
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Aguilar, H. N.; Xiao, S.; Knoll, A. H.; Yuan, X. (2010). "Physiological pathways and molecular mechanisms regulating uterine contractility". Human Reproduction Update 16 (6): 725–744. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmq016. JSTOR 1306737. PMID 20551073.
- ^ Steven's and Lowe Histology p352
External links
Female reproductive system (TA A09.1–2, TH H3.07.01, GA 11.1254) Internal Adnexacorpus (hemorrhagicum, luteum, albicans) · Theca of follicle (externa, interna) · Follicular antrum (Follicular fluid) · Corona radiata · Zona pellucida · Membrana granulosa · Perivitelline spaceOthercorpus/body (Uterine cavity, Fundus) · cervix/neck (External orifice, Canal of the cervix, Internal orifice, Supravaginal portion of cervix, Vaginal portion of cervix, Cervical ectropion) · Uterine hornsGeneralExternal Mons pubis · Labia majora (Anterior commissure, Posterior commissure) · Pudendal cleft · Labia minora (Frenulum of labia minora, Frenulum of clitoris) · Vulval vestibule · Interlabial sulci · Bulb of vestibule · Vaginal orifice
vestibular glands/ducts (Bartholin's glands/Bartholin's ducts, Skene's glands/Skene's ducts)Other Categories:- Pelvis
- Female reproductive system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.