- Corona radiata (embryology)
-
Corona radiata (embryology) 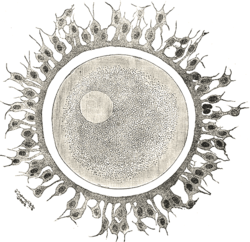
Human ovum examined fresh in the liquor folliculi. The zona pellucida is seen as a thick clear girdle surrounded by the cells of the corona radiata.
The egg itself shows a central granular deutoplasmic area and a peripheral clear layer, and encloses the germinal vesicle, in which is seen the germinal spot.Gray's subject #3 39 - For the structure in neuroanatomy, see Corona radiata.
The corona radiata surround an ovum or unfertilized egg cell, and consist of two or three strata (layers) of follicular cells. They are attached to the outer protective layer of the ovum, the zona pellucida, and their main purpose in many animals is to supply vital proteins to the cell.[citation needed] They are formed by follicle cells adhering to the oocyte before it leaves the ovarian follicle, and originate from the squamous granulosa cells present at the primordial stage of follicular development. The corona radiata is formed when the granulosa cells enlarge and become cuboidal, which occurs during the transition from the primordial to primary stage. These cuboidal granulosa cells, also know as the granulosa radiata, form more layers throughout the maturation process, and remain attached to the zona pellucida after the ovulation of the Graafian follicle. For fertilization to occur, sperm cells rely on hyaluronidase (an enzyme found in the acrosome of spermatozoa) to disperse the corona radiata from the zona pellucida of the secondary (ovulated) follicle, thus permitting entry into the perivitelline space and allowing contact between the sperm cell and the nucleus of the oocyte.
The corona radiata are layers of follicle cells, that protect the secondary oocyte as it passes through the ruptured follicular wall, on its way to the infundibulum of the uterine (AKA fallopian) tubes. In order for fertilization to occur, the sperm must break through this layer of follicular cells by secreting the enzyme hyaluronidase. It takes the secretions of dozens of sperm to weaken the layer enough for one sperm to penetrate.
External links
Female reproductive system (TA A09.1–2, TH H3.07.01, GA 11.1254) Internal Adnexacorpus (hemorrhagicum, luteum, albicans) · Theca of follicle (externa, interna) · Follicular antrum (Follicular fluid) · Corona radiata · Zona pellucida · Membrana granulosa · Perivitelline spaceOtherProper of ovary · Suspensory of ovarycorpus/body (Uterine cavity, Fundus) · cervix/neck (External orifice, Canal of the cervix, Internal orifice, Supravaginal portion of cervix, Vaginal portion of cervix, Cervical ectropion) · Uterine hornsGeneralExternal Mons pubis · Labia majora (Anterior commissure, Posterior commissure) · Pudendal cleft · Labia minora (Frenulum of labia minora, Frenulum of clitoris) · Vulval vestibule · Interlabial sulci · Bulb of vestibule · Vaginal orifice
vestibular glands/ducts (Bartholin's glands/Bartholin's ducts, Skene's glands/Skene's ducts)Other Categories:- Female reproductive system
- Developmental biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
