- Spermatogonium
Infobox Anatomy
Name = Spermatogonium
Latin =
GraySubject = 258
GrayPage = 1243
Caption = Germinal epithelium of the testicle. 1basal lamina , 2spermatogonia , 3spermatocyte 1st order, 4 spermatocyte 2nd order, 5spermatid , 6 mature spermatid, 7Sertoli cell , 8tight junction (blood testis barrier )
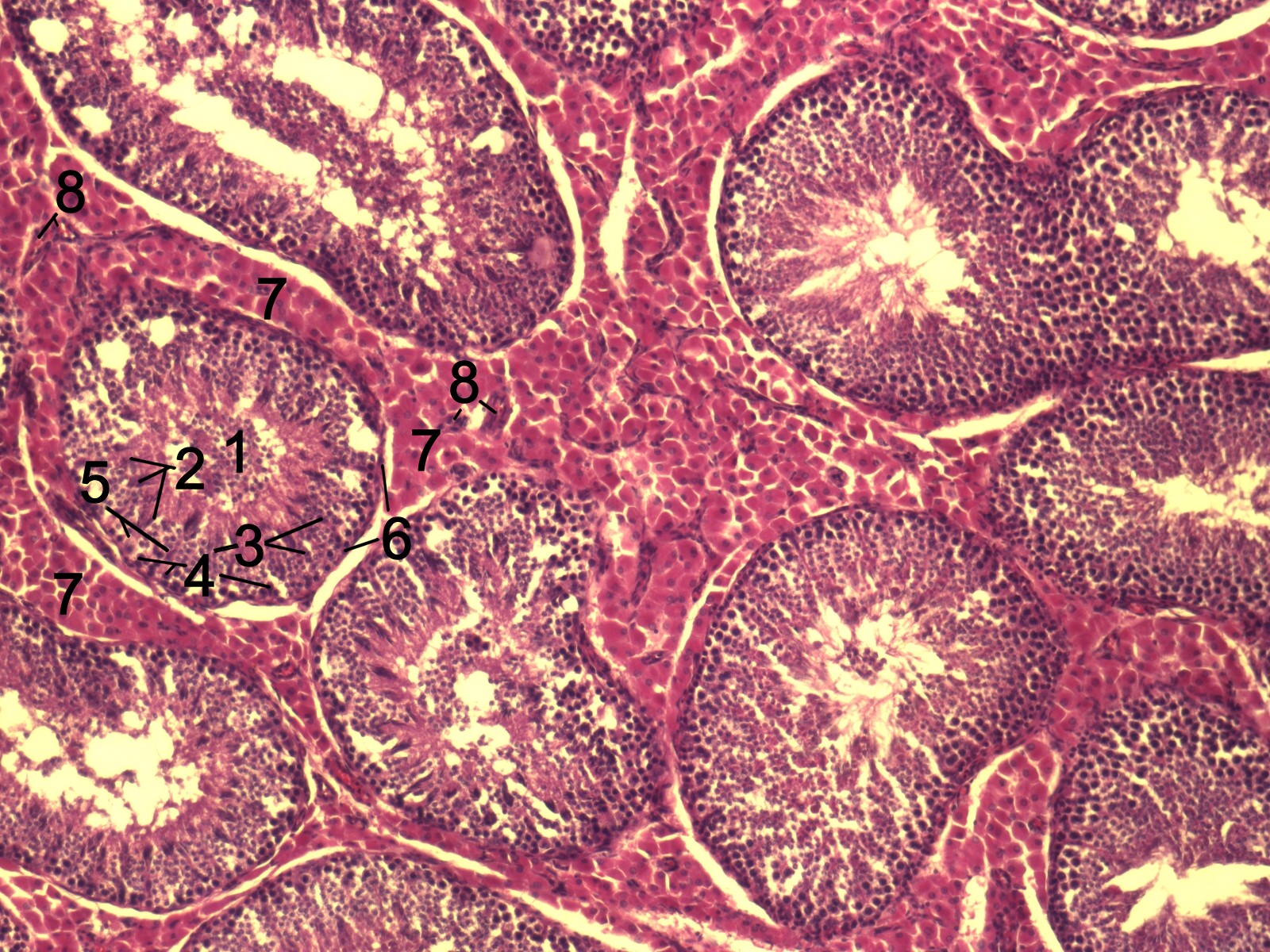
Caption2 = Histological section through testicular parenchyma of aboar . 1 Lumen ofTubulus seminiferus contortus , 2spermatids , 3spermatocytes , 4 spermatogonia, 5Sertoli cell , 6Myofibroblasts , 7Leydig cell s, 8capillaries
Width = 325
System =
MeshName = Spermatogonia
MeshNumber = A05.360.490.890.900
A spermatogonium (plural: "spermatogonia") is an intermediary malegametogonium (a kind ofgerm cell ) in the production ofspermatozoa .There are three subtypes:
*Type A(d) cells, with dark nuclei. These cells divide to produce copies of themselves, thereby ensuring a constant supply of spermatogonia to fuel spermatogenesis.
*Type A(p) cells, with pale nuclei. These cells divide by mitosis to produce Type B cells.
*Type B cells, which divide to give rise to "primary spermatocytes".Each primary spermatocyte duplicates its DNA and subsequently undergoes
meiosis I to produce two haploid secondary spermatocytes. Each of the two secondary spermatocytes further undergo meiosis II to produce two spermatids (haploid). (1 primary spermatocyte => 4 spermatids)The spermatids then undergo
spermiogenesis to producespermatozoa .
=Additionalource
This article includes material from [http://www.biology-online.org/ Biology Online] .
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

