- Parasitology
-
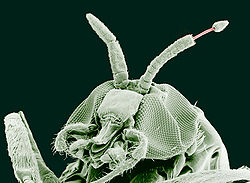 Adult black fly (Simulium yahense) with (Onchocerca volvulus) emerging from the insect's antenna. The parasite is responsible for the disease known as river blindness in Africa. Sample was chemically fixed and critical point dried, then observed using conventional scanning electron microscopy. Magnified 100×.
Adult black fly (Simulium yahense) with (Onchocerca volvulus) emerging from the insect's antenna. The parasite is responsible for the disease known as river blindness in Africa. Sample was chemically fixed and critical point dried, then observed using conventional scanning electron microscopy. Magnified 100×.
Parasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the relationship between them. As a biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question, but by their way of life. This means it forms a synthesis of other disciplines, and draws on techniques from fields such as cell biology, bioinformatics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, genetics, evolution and ecology.
Contents
Fields
The study of these diverse organisms means that the subject is often broken up into simpler, more focused units, which use common techniques, even if they are not studying the same organisms or diseases. Much research in parasitology falls somewhere between two or more of these definitions. In general, the study of prokaryotes falls under the field of bacteriology rather than parasitology.
Medical parasitology
See also: Human parasitesOne of the largest fields in parasitology, medical parasitology is the subject which deals with the parasites that infect man, the diseases caused by them, clinical picture and the response generated by man against them. It's also concerned with the various methods of their diagnosis, treatment and finally their prevention & control. A parasite is an organism that live on or within another organism called the host . These include organisms such as:
- Plasmodium spp., the protozoan parasite which causes malaria. The four species of malaria parasites infective to humans are Plasmodium falciparum,Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium vivax & Plasmodium ovale.
- Leishmania donovani, the unicellular organism which causes leishmaniasis
- Entamoeba and Giardia, which cause intestinal infections (dysentery and diarrhoea)
- Multicellular organisms and worms such as Schistosoma spp., Wuchereria bancrofti, Necator americanus (hookworm) and Taenia spp. (tapeworm)
- Ectoparasites such as ticks, scabies and lice
Medical parasitology can involve drug development, epidemiological studies and study of zoonoses.
Veterinary parasitology
The study of parasites that cause economic losses in agriculture or aquaculture operations, or which infect companion animals. Examples of species studied are:
- Lucilia sericata, a blowfly, which lays eggs on the skins of farm animals. The maggots hatch and burrow into the flesh, distressing the animal and causing economic loss to the farmer
- Otodectes cynotis, the cat ear mite, responsible for Canker.
- Gyrodactylus salaris, a monogenean parasite of salmon, which can wipe out populations which are not resistant.
Structural parasitology
This is the study of structures of proteins from parasites. Determination of parasitic protein structures may help to better understand how these proteins function differently from homologous proteins in humans. In addition, protein structures may inform the process of drug discovery.
Quantitative parasitology
Parasites exhibit an aggregated distribution among host individuals, thus the majority of parasites live in the minority of hosts. This feature forces parasitologists to use advanced biostatistical methodologies.
Parasite ecology
Parasites can provide information about host population ecology. In fisheries biology, for example, parasite communities can be used to distinguish distinct populations of the same fish species co-inhabiting a region. Additionally, parasites possess a variety of specialized traits and life-history strategies that enable them to colonize hosts. Understanding these aspects of parasite ecology, of interest in their own right, can illuminate parasite-avoidance strategies employed by hosts
Conservation biology of parasites
Conservation biology is concerned with the protection and preservation of vulnerable species, including parasites. A large proportion of parasite species are threatened by extinction, partly due to efforts to eradicate parasites which infect humans or domestic animals, or damage human economy, but also caused by the decline or fragmentation of host populations and the extinction of host species.
Taxonomy and phylogenetics
The huge diversity between parasitic organisms creates a challenge for biologists who wish to describe and catalogue them. Recent developments in using DNA to identify separate species and to investigate the relationship between groups at various taxonomic scales has been enormously useful to parasitologists, as many parasites are highly degenerate, disguising relationships between species.
See also
- List of publications in parasitology
- Parasitism
- Parasitologists
External links
- Online lectures in parasitology, University of South Carolina
- Companion Animal Parasite Council
- American Society of Parasitologists
- ARC-NHMRC Research Network for Parasitology
- Australian Society for Parasitology
- British Society for Parasitology
- Chinese Society of Parasitology
- Czech Society for Parasitology
- European Scientific Counsel Companion Animal Parasites
- Hungarian Society of Parasitologists
- Indian Society of Parasitology
- Israel Society for Parasitology, Protozoology and Tropical Diseases
- Japanese Society of Parasitology
- Korean Society for Parasitology
- Nederlandse Vereniging voor Parasitologie
- New Zealand Society for Parasitology
- Scandinavian and Baltic Societies for Parasitology
- Department of Parasitology, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
- An Introduction to Parasitology
- Parasites World
- Institute of Parasitology, McGill University
Branches of Biology Anatomy · Astrobiology · Biochemistry · Biogeography · Biomechanics · Biophysics · Bioinformatics · Biostatistics · Botany · Cell biology · Cellular microbiology · Chemical biology · Chronobiology · Conservation biology · Developmental biology · Ecology · Epidemiology · Epigenetics · Evolutionary biology · Genetics · Genomics · Histology · Human biology · Immunology · Marine biology · Mathematical biology · Microbiology · Molecular biology · Mycology · Neuroscience · Nutrition · Origin of life · Paleontology · Parasitology · Pathology · Pharmacology · Physiology · Quantum biology · Systematics · Systems biology · Taxonomy · Toxicology · ZoologyInfectious disease / Microbiology Disciplines/
pathogens/
major diseasesParasitologyPeople Special topics Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
