- Megabus (North America)
-
Megabus 
A Megabus Van Hool TD925 coach lays over by NY Penn Station.Slogan Low cost daily express bus service to and from (hub city) Parent Coach USA/Coach Canada
(some buses are owned by DATTCO)Founded 2006 Headquarters - USA: 349 1 Street
Elizabeth, NJ 07206[1] - Canada: 791 Webber Ave
Peterborough, ON K9J 8N3
Service area  USA
USA
 Canada
CanadaService type Intercity coach service Routes 30 Stops See list below Destinations See list below Hubs Fleet MCI single-deck coaches
Van Hool single- and double-deck coachesOperator - Academy Express LLC
- DATTCO, Inc.
- Megabus USA LLC
- Megabus Northeast LLC
- Trentway-Wagar, Inc.
- 3329003 Canada, Inc.
- Coach America
Chief executive Dale Moser Web site www.megabus.com/us Megabus, branded on buses as megabus.com, is an intercity bus service of Coach USA/Coach Canada and DATTCO (a non-Stagecoach company, under contract) providing discount travel services since 2006, operating throughout the Northeast, parts of the Southeast, and Midwestern United States, and in southern Canada. Initially operated as a spoke-and-hub model, Megabus now operates as a network of routes, with connections in each hub city to another hub or a route operating to another hub.
Contents
History
An established brand for no-frills service in the United Kingdom since 2003, Stagecoach Group, through subsidiary Coach USA, introduced the Megabus brand in March 2006. On March 22, 2006, Megabus started taking bookings for new routes in the United States (service began on April 10, 2006), with a network of services based in Chicago with daily routes to Milwaukee, Indianapolis, Cincinnati, Cleveland, St. Louis, Ann Arbor, Columbus, Louisville, Toledo, Detroit, Kansas City, Minneapolis, and State College, Pennsylvania .
On August 8, 2007, Megabus introduced service to the San Francisco Bay Area, Los Angeles, Las Vegas, San Diego, and Tempe, Arizona, using Coach America as a contractor.[2][3] However, service to the Phoenix area was discontinued in January 2008 due to low ridership and service to downtown San Diego and San Ysidro was discontinued on Sunday, March 23, 2008. In May 2008, as Megabus was about to be introduced from a hub in New York City, the company announced plans to shut down its Los Angeles hub and discontinue all related services stating “...in this case, the ridership trends aren't growing fast enough”; competition with California Shuttle Bus also caused Megabus' demise in the western United States. The last day for Megabus services from Los Angeles was June 22, 2008.[4]
While Megabus withdrew from California, it expanded in the Northeast in late May 2008, when Megabus began service from a hub in New York City, with service to Albany, Atlantic City, Baltimore, Boston, Buffalo , Philadelphia, Toronto, and Washington, D.C.. Further expansions included service to Syracuse, Rochester, Hartford, and Niagara Falls, Ontario (although Niagara Falls and Hartford were later withdrawn). In Spring 2009, while Eastern Shuttle was under Coach USA ownership, runs were added to Megabus under the Eastern Shuttle name, after Coach USA purchased two Chinatown bus companies in late 2008 and early 2009, significantly increasing capacity. Later in 2009, the Megabus concept was expanded to Toronto and Montreal, while the Chinatown bus companies acquired by Coach USA were sold to independent interests, as Megabus expanded deeper into Pennsylvania and the Southeast in 2009 and 2010, as the route system evolved from a spoke-and-hub model into a true network.
Service overview
Megabus fares start from 1.00 USD or CAD, with a booking fee of 0.50 USD or CAD on the internet. Megabus follows the yield management model, typically used by airlines, where the lowest fares are offered to those who book early (normally, only two seats are sold for 1.00 per schedule), so the less popular schedules tend to be less expensive. Also mirroring the low cost airline model, some locations of stops are on public streets, at park-and-ride lots, or shopping centers. Stops may also be outside railroad stations or transportation centers in major cities, or on college campuses in other cities.[5]
Tickets must be purchased in advance via the website or by telephone (in Canada, through the website only). Upon purchase, passengers are given a reservation number which they show the bus operator when they board. In the United States, tickets are normally not available from the bus operator, but can be purchased from ticket agents at the Penn Station stop in New York City.[6] In Canada, owing to franchise regulations, tickets are sold at stops at a fixed price (generally higher than purchasing the ticket through the website).
All Megabus coaches (except for M25 buses operated by Academy Bus) are equipped with Wi-Fi.
Fleet
The Megabus fleet is normally easily identifiable, with the megabus.com name on the front and sides in yellow against a blue base and the Megabus logo on the left side of the coach (facing forward) and rear of the bus. The slogans are also marked on the buses.
Upon its introduction, Megabus service began with used MCI 102EL3 Renaissance coaches, often transferred from other Coach USA operations, with some services utilizing Chicago- and Milwaukee-based Coach USA buses. In 2007, Coach USA updated its Chicago-based Megabus fleet with new MCI J4500 single-deck and Van Hool TD925 double-deck motorcoaches.
In May 2008, Megabus expanded to the Northeast market, with a fleet of mostly brand-new MCI D4505 coaches, a number of new Van Hool TD925-double decker buses, and some buses purchased secondhand or transferred from the Chicago fleet. This expansion came as Megabus exited from the West Coast market.[4] Further expansion in the Northeast came in the fall and winter of 2008-2009, when additional double-decker buses were delivered, resulting in much of the single-deck buses being transferred to sister operation Eastern Shuttle, pushing many of the EL3s to retirement. The fleet transferred to Eastern Shuttle was divested when Eastern Shuttle was sold in August 2009.
All Megabus coaches branded as such in the United States are equipped with Wi-Fi and electrical outlets.
In accordance with ADA regulations, wheelchair-accessible service is available on all lines with 48 hours advance notice (although most service is operated with true-low-floor double-deck coaches). Such service cannot be booked online, but must instead be booked by contacting Megabus.com's toll-free number.
The Canadian Megabus fleet consists of 15 2009 TD925 buses and are operated by Trentway-Wagar.[7] All of the Canada fleet is equipped with electrical outlets and Wi-Fi. The Canadian buses are pooled with the US fleet for NYC-Toronto or Philadelphia-Toronto runs, with drivers swapping at Buffalo to stay within their certified country. Note that on these runs the buses will typically only have WiFi service available in the home country for the bus being used; i.e. Canadian buses will turn off their WiFi at the US border and American buses will turn off WiFi upon entering Canada. This is to avoid incurring roaming charges from the cellular carriers that provide the internet service.
Hubs
Megabus service in the United States and Canada operates primarily as a hub and spoke model in the Midwest and as a network along the East Coast. Northeastern service uses New York City, Philadelphia, and Washington, D.C. as hub cities. There is a separate hub in Chicago, and a hub in Pittsburgh that allows connection from the Chicago routes to the east-coast routes by changing buses. A new hub will open in Atlanta in November 2011. Service was also operated from August 2007 until June 2008 from a hub in Los Angeles. As is the case with most Coach USA buses, all buses are licensed in Illinois, except for M22 Megabus units owned and operated by DATTCO, which are licensed in Connecticut (these units are identified with the DATTCO logo instead of the Coach USA logo).
Atlanta hub
Megabus announced the creation of their first southeastern United States hub, in Atlanta, on October 25, 2011. Commencing November 16, 2011, Megabus will begin operations out of its new Atlanta hub, located at the Civic Center MARTA Station in Downtown Atlanta.[8]
Initially, Megabus will begin service from Atlanta to: Chattanooga, Nashville, Knoxville, Montgomery, Jacksonville, Gainesville, Orlando, Memphis, Birmingham, Charlotte, Raleigh, Mobile, Richmond, and Washington, D.C. In addition, passengers will be able to link to northeastern US Megabus service through an extended M31 route. Connections to midwestern Megabus service will be available in Memphis.
Chicago hub
Megabus in the U.S. began operations on April 10, 2006 with routes between Chicago and Cincinnati, Cleveland, Columbus, Detroit, Indianapolis, Milwaukee, Minneapolis and St. Louis, from a hub at Chicago Union Station. Services also began between Indianapolis and Cincinnati. A service that was initially offered between Indianapolis and Columbus was later withdrawn due to low ridership, but has since been reinstated and currently operates.
On September 11, 2006, a stop in Toledo was added on the route operating between Chicago and Cleveland. Additional services were added on April 2, 2007: a stop in Ann Arbor along the Chicago-Detroit route for travel to and from Chicago, new service between Minneapolis and Milwaukee, an extension of the Chicago-Toledo-Cleveland route into Pittsburgh (since withdrawn on the Midwest network, but later re-entered on the Northeast network), an extension of the Chicago-St. Louis route into Kansas City, reactivation of the Chicago-Indianapolis-Columbus route, new service between Cincinnati and Columbus, and new service between Chicago and Louisville via Indianapolis (since withdrawn).
On March 13, 2008 a stop was added in Madison, Wisconsin on the twice daily Chicago-Minneapolis route. The Chicago-Minneapolis route operating via Milwaukee service gained a second daily bus. Also, Columbia, MO was added with one stop daily in each direction on the Chicago-St. Louis-Kansas City route. On March 27, 2008, a new route was added, Chicago-Champaign-Memphis, offering 2 daily trips in each direction. In early 2010, Champaign/Memphis route was cut to one daily round-trip due to poor ridership, but the second round trip has since been restored.
Later in 2008, Megabus expanded service to Minneapolis to 4 daily departures, but also announced the cancellation of overnight schedules mid-week on routes to Ohio and Memphis. Early in 2009, these midweek overnight schedules were restored, only to be pulled again in summer 2009.
On May 4, 2010, a new route from Chicago to Des Moines via Iowa City began operating.
On August 17, 2011, Megabus started service to Omaha via Des Moines and Iowa City; twice-daily departures and arrivals from Omaha and an increase to four daily departures and arrivals from Des Moines and Iowa City.
New York hub
On May 30, 2008 Megabus began East Coast operations with service to and from Atlantic City (operated by Academy Bus), Washington, D.C., Boston, Philadelphia, and Buffalo and Toronto. Service to Baltimore, MD was added after negotiations over the usage of the White Marsh Park & Ride were concluded. On June 6, a once-daily service was added to Binghamton for travel to and from Buffalo and Toronto.
On all routes except for the Atlantic City route, Megabus competes directly with various discount bus operators, including Greyhound and Peter Pan's BoltBus service, Washington Deluxe, Vamoose Bus, other Chinatown bus lines, and the NeOn service offered by Greyhound Canada and Adirondack Trailways.
During fall 2008, the New York City-Washington, DC line was expanded to 14 northbound and 13 southbound trips, with all service now stopping in Baltimore. Additional departures were also added on Fridays and Sundays to and from Boston.
In December 2008, service to Binghamton, which had been operating only to Buffalo and Toronto, was dropped in favor of service to Syracuse, Rochester, and Niagara Falls (Ontario). A new route also began service to and from Albany. Both revised services offer four trips daily (up from two on the Toronto line), with a fifth Buffalo-Toronto express overnight trip also offered. All services were moved from the Royal York Hotel to the Toronto Coach terminal. Hartford was also added on the M22 route in December 2008, with service to Boston or New York available.
In spring 2009, following the purchase of two Chinatown bus operators (Eastern Shuttle[9] and Today's Bus[10]) in late 2008 and early 2009 and subsequent merger of their operations (with the Eastern brand retained), the M21 route expanded to hourly (or less) departures during the day, with the M23 route expanding to over 20 departures in each direction on weekdays, and over 15 departures in each direction on weekends. As a result, Megabus would briefly enter the Chinatown bus market in the Northeast, a market that it would exit in August 2009.
For summer 2009, the Philadelphia schedule was streamlined to provide 18 daily trips in each direction (evenly split between Megabus and Eastern, but eventually transferred to Megabus when Eastern was sold), and the M24 route saw its two AM departures from either end of the route combined into a single departure. In addition, service to Rochester was reduced to once daily in each direction. Layover time at Syracuse was increased from 20 minutes to 30 minutes to account for the rest stop that used to occur between Syracuse and Rochester.
For winter 2009, service to and from Hartford, CT and to Niagara Falls, ON were dropped due to low ridership.
On May 4, 2010, a new route from New York to Pittsburgh via State College began operating; Pittsburgh had previously been served by a route to and from Chicago earlier.
In Spring 2010, Philadelphia was established as a second hub with originating buses to several additional destinations. In summer 2010, Providence to New York was added as an additional destination. On September 8, 2010, Service was stopped between Philadelphia and Atlantic City due to low ridership.
On 15 December 2010, Service was added to Hartford and Amherst due to public outcry in Greater Hartford.
At the Penn Station stop, there is a ticket window at the bus stop where walk-up ticket sales can be paid for with cash, debit card, or credit card. This is the only location in the United States where cash is accepted for travel on Megabus service. Megabus operators do not sell tickets- tickets must be purchased on the internet or by phone.
Toronto hub
Similar to the Megabus model in the United States, in June 2008, Coach Canada began offering tickets from C$1 on their route between Toronto and Montreal, using the same yield management model.[11] As of summer 2009, this route has been converted to a Megabus route as marketed on the Coach Canada website, with double-deckers branded for Megabus replacing single-deck Coach Canada buses on the route, except for over-booked trips in which case the Toronto-to-Kingston leg of the trip reverts to a single-deck Coach Canada bus and the Megabus does not stop in Kingston on route to Montreal. Like services in the United States, Wi-Fi is available on the Toronto-Montreal service. Unlike services in the USA, however, all service is normally accessible for those with mobility impairments; a 48-hour reservation in advance is still required because the number of seats per trip is affected.
Pittsburgh hub
On March 29, 2011, Megabus announced the Pittsburgh hub operating service out of the David L. Lawrence Convention Center underpass. In addition to serving the current Pittsburgh-State College-NYC, Pittsburgh-Washington, and Pittsburgh-Harrisburg-Philadelphia-Camden runs, Megabus is running four new routes: Pittsburgh-Erie-Buffalo-Toronto, Pittsburgh-Columbus-Cincinnati, Pittsburgh-Akron-Cleveland (a restoration of an earlier cut), and Pittsburgh-Toledo-Detroit.
Philadelphia hub
Starting July 21, 2010, Megabus began operating service out of a hub near 30th Street Station in Philadelphia. Service operates to the Pennsylvania cities of Harrisburg, State College and Pittsburgh, as well as to Baltimore, Boston, Buffalo, N.Y., Syracuse, N.Y., Toronto, and Washington, D.C..[12]
Washington D.C. hub
One of the original destinations from the New York City hub, Megabus began operating south of Washington D.C. on December 15th, 2010. In November 2011, Megabus began operating from the bus deck above the top level of the Amtrak station at Washington's Union Station.[13]
Los Angeles hub
Megabus operated briefly from Los Angeles, opening for business on August 8, 2007 at Los Angeles Union Station, with services operated by unaffiliated Coach America under contract from facilities in Oxnard and Bakersfield. Initially services were offered to Phoenix, Tempe, Las Vegas, San Diego, and San Francisco via either San Jose and Millbrae, or Oakland. However, with ridership not meeting expectations, service to Arizona was withdrawn after only five months, and by late March 2008, service to San Diego was also canceled. After June 8, 2008, only the Los Angeles-Oakland-San Francisco service remained. After June 22, 2008, Megabus service originating from Los Angeles ended altogether.[4] Megabus, however, has explored re-entry into this market, along with an expansion into Texas.
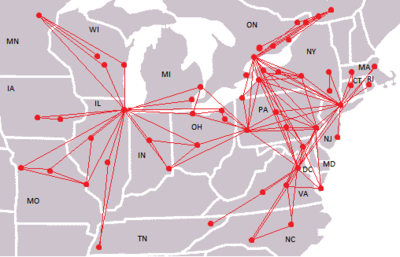
Routes
All Megabus-branded buses are normally equipped with Wi-Fi.
Route Terminal A Serves Terminal B Notes and history M1 Chicago, IL Ann Arbor, MI or
Detroit, MI- Service began on April 10, 2006.
- Ann Arbor added on April 2, 2007.
- Passengers are carried to and from Chicago only.
M3 Chicago, IL Toledo, OH Cleveland, OH - Service began on April 10, 2006.
- Toledo, OH added on September 11, 2006.
- Pittsburgh, PA added April 2, 2007; initially withdrawn on September 16, 2007 due to insufficient ridership.
Restored on route M45 in 2011.
M4 Chicago, IL Milwaukee or
MadisonMinneapolis, MN - Service began on April 10, 2006.
- Minneapolis, MN added on April 2, 2007. Madison, WI added on March 13, 2008.
- Service is not available wholly within Wisconsin.
M5 Chicago, IL Kansas City, MO - Service began on April 10, 2006
- Kansas City, MO added on April 2, 2007.
- Columbia added on March 13, 2008.
- Columbia and Normal are not served on the same trip.
M6 Chicago, IL Indianapolis, IN Columbus, OH or
Cincinnati, OH- Service began on April 10, 2006. Overnight trips serve both terminals.
- Columbus, OH withdrawn June 4, 2006 due to low ridership. Reinstated on April 2, 2007.
- Louisville, Kentucky withdrawn September 16, 2007 due to low ridership.
M7 Chicago, IL Champaign, IL Memphis, TN - Service began on March 27, 2008.
M8 Chicago, IL Iowa City, IA Des Moines, IA or
Omaha, NE- Service began on May 4, 2010
- Service with two of four continuing to Omaha, began August 17, 2011.
M20 New York, NY Providence, RI Hyannis, MA - Providence added in 2010. Providence is a standalone line. NY-Boston runs do not stop in Providence.
M21 New York, NY Baltimore, MD Washington, D.C. - Service began on May 30, 2008.
- Passengers are carried to and from New York City only.
- Early morning AM trip from New York are interlined with the M31 service.
- Customers traveling between Baltimore and Washington D.C. must use the M31.
M22 New York, NY Boston, MA - Operated by DATTCO under contract to Coach USA (using both Coach USA-owned and DATTCO-owned equipment).
- Service began on May 30, 2008.
- Hartford added December 4, 2008, but withdrawn on September 14, 2009.[14]
- NY-Boston runs do not stop in Providence. NY-PROV runs are designated as M20.
M23 New York, NY Philadelphia, PA - Service began on May 30, 2008.
M24 New York, NY Toronto, ON - Service began on May 30, 2008. Syracuse and Rochester local service began on December 4, 2008.
- Binghamton was added on June 6, 2008, but withdrawn on December 3, 2008 because of low ridership.
- Niagara Falls, Ontario was added on December 4, 2008, but withdrawn on June 28, 2009 due to low ridership.
M25 New York, NY Atlantic City, NJ - Operated by Academy Bus. Wi-Fi is not available on this route.
- Only round-trip fares are sold.
M27 New York, NY Ridgewood, NJ Rensselaer (Albany, NY) - Service began on December 4, 2008.
- Passengers are carried to and from Albany-Rensselaer only.
M28 New York, NY State College, PA Pittsburgh, PA - Service began on May 4, 2010.
M29 Pittsburgh, PA Philadelphia, PA - Service began on July 21, 2010
M30 (Camden, NJ) Harrisburg, PA State College, PA - Two daily round trips
- Buses terminate at Camden, NJ as of July 24, 2010.
- No local passengers carried between Camden and Philadelphia.
M31 Philadelphia Baltimore, MD
Washington, D.C.
Richmond, VA
Durham, NC
Charlotte, NC'Hampton, VA or Atlanta, GA - Eight weekday round trips.
- Local passengers may be carried between Washington and Baltimore on the M31 line.
- Some trips are interlined with M21 trips.
- Route was extended to North Carolina and Georgia on November 16, 2011
M32 Philadelphia Secaucus, NJ Boston, MA - Four daily round trips.
M34 Philadelphia Toronto, ON - Two round trips, only one of which serves the airport in Buffalo
M35 New York, NY Hartford, CT Amherst, MA - Service began on December 15, 2010.
M36 Pittsburgh, PA Washington, D.C. - Service began on December 15, 2010
- Frederick added May 11, 2011
M38 Washington, DC Christiansburg, VA
Knoxville, TN M42 Washington D.C. Baltimore, MD
Secaucus, NJ
Boston, MA - Two daily round-trips.
M44 Washington D.C. Baltimore, MD
Harrisburg, PA
Buffalo, NYToronto, ON - Two daily round-trips.
M45 Pittsburgh, PA Cleveland, OH - Service began May 11, 2011
M46 Pittsburgh, PA Detroit, MI - Service began May 11, 2011
M47 Pittsburgh, PA Cincinnati, OH - Service began May 11, 2011.
M51 Boston Hartford, CT New Haven, CT - Service began August 17, 2011.
M53 Boston Burlington, VT - Service began August 17, 2011.
M64 Pittsburgh, PA Toronto, ON - Service began May 11, 2011
M80 Atlanta, GA Chattanooga, TN Knoxville, TN
or
Nashville, TN- Service began November 16, 2011
M75 Atlanta, GA Birmingham, AL Memphis, TN - Service began November 16, 2011
M19 Atlanta, GA Montgomery, AL Mobile, AL - Service began November 16, 2011
M96 Atlanta, GA Jacksonville, FL
or
Gainesville, FLOrlando, FL - Service began November 16, 2011
TOR-
MTLToronto Kingston, ON Montreal - Various pickup points within the Greater Toronto Area and on the Island of Montreal only for travel to Kingston and beyond.
Discontinued services
Route Terminal A Served Terminal B Begun Withdrawn Notes M10 Los Angeles, CA Phoenix, AZ Tempe, AZ August 7, 2007 January 7, 2008 - Withdrawn because of poor ridership.
M11 Los Angeles, CA Las Vegas, NV August 7, 2007 June 8, 2008 - Withdrawn because of poor ridership.
M12 Los Angeles, CA Oakland, CA San Francisco, CA August 7, 2007 June 22, 2008 - Withdrawn because of poor ridership.
M14 Los Angeles, CA San Jose, CA
Millbrae, CASan Francisco, CA August 7, 2007 June 8, 2008 - Withdrawn because of poor ridership.
M15 Los Angeles, CA San Diego, CA August 7, 2007 March 2008 - Withdrawn because of poor ridership.
M33 Philadelphia, PA Atlantic City, NJ July 21, 2010 September 8, 2010 - Withdrawn because of poor ridership.
Incidents and accidents
Below is a list of notable incidents and accidents involving Megabus vehicles (not counting Megabus vehicles operated by DATTCO or Concord Coach Lines on services to and from Boston, and services on the M25, which are operated separately).
- On September 1, 2008, a Detroit-bound M1 coach was pulled over by Michigan State police after officers noticed the bus swaying and speeding outside Benton Township, MI. Megabus driver Kenneth Lewis failed sobriety tests administered at the scene and was arrested. Lewis was found to have a blood alcohol level of .07, well above the .0015 limit for commercial bus operators. A replacement driver was brought in to bring the 30 passengers to their final destination. It was the first drunk driving incident in Coach USA history. Lewis was suspended from Coach USA.[15]
- On December 10, 2009 at 3:20 a.m., a Toronto-bound M24 coach slid off the New York State Thruway, 3 miles past exit 49 in Lancaster, New York, just east of Buffalo. Eight passengers and the driver were taken to nearby hospitals with minor injuries. Poor visibility, blowing snow, high winds combined with an unsafe lane change contributed to the accident.[16][17][18]
- On September 11, 2010, around 2:30 a.m., a Toronto-bound M34 double-decker coach missed an exit to the William F. Walsh Regional Transportation Center, slammed into a railway overpass carrying the St. Lawrence Subdivision along NY Route 370 two miles farther away. Four passengers were killed---all in the front of the upper deck, which was crushed into the lower deck in the crash---and 17 others were injured.[19][20][21]
- On October 21, 2011, at 10:08 p.m., a A Megabus driver from Chicago, Carl H. Smiley, was arrested by an Iowa state trooper for drunk driving while transporting passengers from Chicago to Iowa City and Des Moines. The trooper pulled the driver over for failing to maintain a lane. Police records stated the driver “smelled strongly of an alcoholic beverage and admitted he had been drinking.” The driver also failed a field sobriety test.[22]
According to federal records, since August 2007, Chicago hub drivers have been cited 54 times by police: 21 times for not maintaining driver logs, 20 times for speeding, 3 times for following too closely, 2 times for improper lane changes, and 2 for windshield violations. There were 6 other violations of local laws.[23] Also, New York hub drivers have been cited 29 times by police: 14 times for speeding, 5 times for not maintaining driver logs, 2 times for failing to obey a traffic control device, 2 times for defects (windshield cracked and other), and 1 time for falsifying a log book. There were 5 other violations of local laws.[23] There have also been four other accidents involving Megabus vehicles.[23]
See also
- BoltBus - a competing curbside bus carrier owned by Greyhound and Peter Pan Bus Lines
- Chinatown bus lines
- BusJunction - ticket search engine that includes Megabus tickets
References
- ^ Megabus US HQ
- ^ George Raine (2007-08-02). "Bargain bus company riding into Bay Area next week". San Francisco Chronicle. http://www.sfgate.com/cgi-bin/article.cgi?f=/c/a/2007/08/02/BU8GRBEPS2.DTL. Retrieved 2007-08-02.
- ^ Kerry Fehr-Snyder (August 2, 2007). "Phoenix-LA bus service for as low as $1.50". The Arizona Republic. http://www.azcentral.com/business/articles/0802megabus0802.html. Retrieved 2007-08-02.[dead link]
- ^ a b c Chang, Andrea (2008), "Megabus to halt service in L.A.", Los Angeles Times: C3, 2008-05-17, http://www.latimes.com/business/la-fi-megabus17-2008may17,0,2008552.story, retrieved 2008-05-18[dead link]
- ^ [1] Buying tickets on Megabus.com, retrieve data on 23 October 2008
- ^ [2] Reservation seats, retrieve data on 23 October 2008
- ^ Canadian Public Transit Discussion Board thread (must be logged in to view), cptdb.ca, retrieved on 2009-08-18
- ^ "Megabus to open Atlanta Hub". Atlanta Business Chronicle. 24. http://www.bizjournals.com/atlanta/news/2011/10/24/megabus-to-open-atlanta-hub.html. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- ^ Coach USA acquires Eastern Travel & Tour
- ^ Todays Bus Now Part of Eastern Coach/Coach USA
- ^ Coach Canada begins offering $1 fares from Toronto to Montreal
- ^ [3]
- ^ "Bus Stops". megabus.com. http://us.megabus.com/busStops.aspx. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ http://www.facebook.com/note.php?note_id=124415988282&ref=mf
- ^ http://www.michigandaily.com/content/megabus-driver-arrested-dui-charges-southwest-mich
- ^ The Globe and Mail (Toronto). http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/national/toronto/toronto-bound-bus-tips-in-ny-storm/article1396507/.
- ^ http://www.wgrz.com/news/local/story.aspx?storyid=72691&catid=13
- ^ "Toronto-bound bus accident injures 12". CBC News. December 10, 2009. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/toronto/story/2009/12/10/megasbus-accident.html.
- ^ http://www.9wsyr.com/news/local/story/Four-dead-after-Megabus-hits-Parkway-bridge/LiNwgSPQkkyL0gzAwfLlJg.cspx
- ^ http://www.syracuse.com/news/index.ssf/2010/09/sleeping_passengers_awake_to_c.html
- ^ The Globe and Mail (Toronto). http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/national/toronto/canadians-not-among-4-killed-in-megabus-crash/article1703804/.
- ^ http://www.desmoinesregister.com/apps/pbcs.dll/article?AID=2011111022013
- ^ a b c http://ai.fmcsa.dot.gov/SafeStat/safestatmain.asp
External links
Key personnel United Kingdom
bus companiesStagecoach London (East London, Selkent, Thameside) · Stagecoach West Scotland (Western, A1 Service, Arran, Glasgow) · Stagecoach Highlands (Caithness, Inverness, Lochaber, Skye, Orkney) · Stagecoach East Scotland (Fife, Bluebird, Perth, Strathtay, JW Coaches, Rennies) · Stagecoach North East (Newcastle, South Shields, Sunderland, Hartlepool, Teesside) · Stagecoach North West (Cumbria, Lancaster, Lancashire, Preston, Network Chorley) · Stagecoach Manchester (Manchester, Magic Bus) · Stagecoach Merseyside (Merseyside) · Stagecoach Yorkshire (Yorkshire, Chesterfield, Sheffield) · Stagecoach East Midlands (Bassetlaw, Mansfield, Grimsby-Cleethorpes, Hull, Lincolnshire) · Stagecoach Midlands (Northants, Warwickshire) · Stagecoach Oxfordshire (Oxfordshire, Oxford Tube) · Stagecoach East (Stagecoach Cambridgeshire (Cambridge, Peterborough. The Fens), Bedford) · Stagecoach West (Cheltenham, Swindon, Gloucester, Cotswolds, Wye and Dean) · Stagecoach Wales (Stagecoach in South Wales) · Stagecoach South East (East Kent, East Sussex, Eastbourne, Hastings) · Stagecoach South (Hants & Surrey, Hampshire, Portsmouth, South Downs) · Stagecoach South West (Devon) · Stagecoach Express · Scottish Citylink (35% with ComfortDelGro) · Megabus (United Kingdom) · Stagecoach Gold/Citylink GoldUnited Kingdom
railway companiesEast Midlands Trains · South West Trains (Island Line Trains) · Virgin Trains (49% with Virgin Group) · MegatrainUnited Kingdom
tram operationsStagecoach Sheffield SupertramNorth American
bus companiesUnited States: Coach USA (Northeast: Community Coach, Gray Line New York (50% with New York Airport Service), Olympia Trails, Red & Tan Tours, Rockland Coaches, Short Line Bus, Suburban Trails) · (North Central: Butler Motor Transit, Central Cab Company, Coach USA Chicago, Lenzner Coach Lines, Tri-State/United Limo, Wisconsin Coach Lines, Van Galder) · Megabus (North America)
Canada: Coach Canada: Erie Coach Lines, Trentway-Wagar, Gray Line MontrealAnnual revenue: £2,176 million GBP (  8.9% FY 2007) · Employees: 27,000 · Stock symbol: LSE: SGC · Website: stagecoachgroup.comCategories:
8.9% FY 2007) · Employees: 27,000 · Stock symbol: LSE: SGC · Website: stagecoachgroup.comCategories:- No frills
- Intercity bus companies of the United States
- 2006 introductions
- Stagecoach Group bus operators in the United States and Canada
- Intercity bus companies of Canada
- Scottish brands
- USA: 349 1 Street
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.