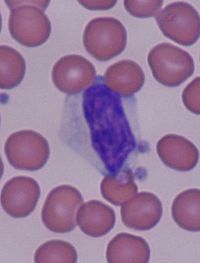
- Reactive lymphocyte
-
Reactive lymphocytes are lymphocytes that become large as a result of antigen stimulation. Typically they can be more than 30 µm in diameter with varying size and shape.
The nucleus of a reactive lymphocyte can be round, elliptic, indented, cleft or folded. The cytoplasm is often abundant and can be basophilic. Vacuoles and/or azurophilic granules are also sometimes present. Most often the cytoplasm is gray, pale blue or deep blue in colour.
The distinctive cell associated with EBV or CMV is known as a "Downey cell", after Hal Downey, who contributed to the characterization of it in 1923.[1][2] It is sometimes erroneously called a "Downy cell".[3]
Causes
Reactive lymphocytes are usually associated with viral illnesses, however, they can also be present as a result of drug reactions (such as phenytoin), immunisations, radiation, hormonal causes (such as stress and Addison's disease) as well as some auto-immune disorders (such as rheumatoid arthritis).
Some pathogen-related causes include:
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Cytomegalovirus
- Toxoplasma
- Treponema pallidum (Syphilis)
- Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Streptococci),
- Hepatitis C
- Hantavirus[4]
External links
- Review Article: The Atypical Lymphocyte- International Pediatrics Volume 18, No. 1; Michael W. Simon.
- Educational Commentary: Blood Cell Identification - American Society for Clinical Pathology article.
References
- ^ Cabot, Richard C.; Scully, Robert E.; Mark, Eugene J.; McNeely, William F.; McNeely, Betty U.; Rosenfield, Cathy G.; Kaplan, Mark A. (June 1994). "Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 24-1994. A two-year-old boy with thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, and hepatosplenomegaly". N. Engl. J. Med. 330 (24): 1739–46. doi:10.1056/NEJM199406163302408. PMID 8190136. http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=8190136&promo=ONFLNS19.
- ^ Downey H, McKinlay CA. Acute Lymphadenosis Compared with Acute Lymphatic Leukemia. Arch Intern Med. 1923;32:82-112
- ^ "MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia: Mononucleosis, photomicrograph of cells". http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/imagepages/1456.htm. Retrieved 2009-03-07.
- ^ Peters CJ, Khan AS (2002). "Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome: the new American hemorrhagic fever". Clin Infect Dis 34 (9): 1224–31. doi:10.1086/339864. PMID 11941549.
Lymphoid system (TA A13.1–2, TH H3.10, GA 8 and 9) Primary lymphoid organs Secondary lymphoid organs structural: Hilum · Trabeculae · Diaphragmatic surface of spleen · Visceral surface of spleen
Red pulp (Cords of Billroth, Marginal zone)
White pulp (Periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths, Germinal center)
blood flow: Trabecular arteries · Trabecular veinslymph flow: Afferent lymph vessels · Cortical sinuses · Medullary sinuses · Efferent lymph vessels
T cells: High endothelial venules
B cells: Primary follicle/Germinal center · Mantle zone · Marginal zone
layers: Capsule/Trabeculae · Subcapsular sinus · Cortex · Paracortex · Medulla (Medullary cord) · HilumM: LMO
anat(h, u, t, a, l)/phys/depv
noco/cong/tumr
proc
Abnormal clinical and laboratory findings for blood tests (R70–R79, 790) Red blood cells SizeShape (Poikilocyte)developmental organelles (Howell-Jolly body, Basophilic stippling, Pappenheimer bodies, Cabot rings)OtherLymphocytes Smudge cell · Downey cellSmall molecules NitrogenousProteins OtherMinerals Pathogens/sepsis Categories:- Medicine stubs
- Cell biology stubs
- Lymphocytes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.