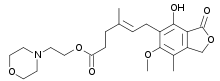
- Mycophenolic acid
-
Mycophenolic acid 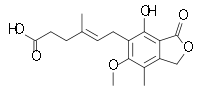
Systematic (IUPAC) name (4E)-6-(4-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-7-methyl-3-oxo-1,3-dihydro-2-benzofuran-5-yl)-4-methylhex-4-enoic acid Clinical data Licence data EMA:Link, US FDA:link Pregnancy cat. D (Au), D (U.S.) Legal status S4 (Au), POM (UK), ℞-only (U.S.) Routes Oral, IV Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 94% (mofetil), 72% (sodium) Protein binding 97% Metabolism Hepatic Half-life 16–18 hours Excretion Renal 93% Identifiers CAS number 24280-93-1 
ATC code L04AA06 PubChem CID 446541 DrugBank DB01024 ChemSpider 393865 
UNII HU9DX48N0T 
KEGG D05096 
ChEBI CHEBI:168396 
ChEMBL CHEMBL866 
Chemical data Formula C17H20O6 Mol. mass 320.34 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) acid (verify)
(what is this?) acid (verify)Mycophenolic acid INN (
 /ˌmaɪkoʊfɨˈnɒlɪk/) or mycophenolate is an immunosuppressant drug used to prevent rejection in organ transplantation. It inhibits an enzyme needed for the growth of T cells and B cells. It was initially marketed as the prodrug mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) to improve oral bioavailability. More recently, the salt mycophenolate sodium has also been introduced. Mycophenolic acid is commonly marketed under the trade names CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil; Roche) and Myfortic (mycophenolate sodium; Novartis).
/ˌmaɪkoʊfɨˈnɒlɪk/) or mycophenolate is an immunosuppressant drug used to prevent rejection in organ transplantation. It inhibits an enzyme needed for the growth of T cells and B cells. It was initially marketed as the prodrug mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) to improve oral bioavailability. More recently, the salt mycophenolate sodium has also been introduced. Mycophenolic acid is commonly marketed under the trade names CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil; Roche) and Myfortic (mycophenolate sodium; Novartis).Contents
Clinical use
Indications
In general, mycophenolate is used for the prevention of organ transplant rejection. Mycophenolate mofetil is indicated for the prevention of organ transplant rejection in adults and renal transplant rejection in children over 2 years; whereas mycophenolate sodium is indicated for the prevention of renal transplant rejection in adults. Mycophenolate sodium has also been used for the prevention of rejection in liver, heart, and/or lung transplants in children older than two years.[1]
An immunosuppressant that has drastically decreased the incidence of acute rejection in solid transplant recipients, mycophenolate is increasingly utilized as a steroid sparing treatment in immune-mediated disorders including immunoglobulin A nephropathy, small vessel vasculitides, and psoriasis.[2]
Its increasing application in treating lupus nephritis has demonstrated more frequent complete response and less frequent complications [2] compared to cyclophosphamide bolus therapy, a regimen with risk of bone marrow suppression, infertility, and malignancy.[3] Further work addressing maintenance therapy demonstrated mycophenolate superior to cyclophosphamide, again in terms of response and side-effects.[3] Walsh et al. even propose that mycophenolate should be considered as a first-line induction therapy for treatment of lupus nephritis in patients without renal dysfunction,[4] suggesting that mycophenolate will be encountered more frequently in medical practice.
Comparison to other agents
Compared with azathioprine it has significantly higher incidence of diarrhoea, and no difference in risk of any of the other side effects.[5] Mycophenolic acid is 15 times more expensive than azathioprine[6] The exact role of mycophenolate vs azathioprine has yet to be conclusively established. In long-term immunosuppression, it may be used to avoid calcineurin inhibitors or steroids.
Potential future uses
Mycophenolate mofetil is beginning to be used in the management of auto-immune disorders such as idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), scleroderma (systemic sclerosis or SSc) and pemphigus vulgaris (PV) with success for some patients.[7]
It is also currently being used as a long-term therapy for maintaining remission of C-ANCA positive (Wegener's) granulomatosis. A combination of mycophenolate and ribavirin has been found to stop infection by and replication of dengue virus in vitro.[8][9]
Adverse effects
Common adverse drug reactions (≥1% of patients) associated with mycophenolate therapy include diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, infections, leukopenia, and/or anemia. Mycophenolate sodium is also commonly associated with fatigue, headache, and/or cough. Intravenous (IV) administration of mycophenolate mofetil is also commonly associated with thrombophlebitis and thrombosis. Infrequent adverse effects (0.1–1% of patients) include esophagitis, gastritis, gastrointestinal tract hemorrhage, and/or invasive cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection.[1] Several cases of pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) have also been reported.[10]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued an alert that patients on mycophenolate mofetil and mycophenolic acid are at increased risk of opportunistic infections, such as activation of latent viral infections, including shingles, other herpes infections, cytomegalovirus, and BK virus associated nephropathy. In addition the FDA is investigating 16 patients that developed a rare neurological disease while taking the drug. The neurological condition known as progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy attacks the brain and central nervous system and is usually fatal.[11]
Mycophenolic acid is associated with miscarriage and congenital malformations when used during pregnancy, and should be avoided whenever possible by women trying to conceive.[12][13]
Pharmacology
Mycophenolate is derived from the fungus Penicillium stoloniferum or in P. echinulatum.[14]. Mycophenolate mofetil is metabolised in the liver to the active moiety mycophenolic acid. It inhibits inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, the enzyme that controls the rate of synthesis of guanine monophosphate in the de novo pathway of purine synthesis used in the proliferation of B and T lymphocytes.[15]
Mycophenolate is potent and can be used in place of the older anti-proliferative azathioprine. It is usually used as part of a three-compound regimen of immunosuppressants, also including a calcineurin inhibitor (ciclosporin or tacrolimus) and prednisolone.
References
- ^ a b Rossi S, editor. Australian Medicines Handbook 2006. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook; 2006. ISBN 0-9757919-2-3[page needed]
- ^ a b Moore RA, Derry S (2006). "Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials and cohort studies of mycophenolate mofetil in lupus nephritis". Arthritis Research & Therapy 8 (6): R182. doi:10.1186/ar2093. PMC 1794528. PMID 17163990. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1794528.
- ^ a b D'Cruz DP, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR (February 2007). "Systemic lupus erythematosus". Lancet 369 (9561): 587–96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60279-7. PMID 17307106.
- ^ Walsh M, James M, Jayne D, Tonelli M, Manns BJ, Hemmelgarn BR (September 2007). "Mycophenolate mofetil for induction therapy of lupus nephritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2 (5): 968–75. doi:10.2215/CJN.01200307. PMID 17702723.
- ^ Knight SR, Russell NK, Barcena L, Morris PJ (March 2009). "Mycophenolate mofetil decreases acute rejection and may improve graft survival in renal transplant recipients when compared with azathioprine: a systematic review". Transplantation 87 (6): 785–94. doi:10.1097/TP.0b013e3181952623. PMID 19300178.
- ^ Remuzzi G, Lesti M, Gotti E, et al. (2004). "Mycophenolate mofetil versus azathioprine for prevention of acute rejection in renal transplantation (MYSS): a randomised trial". Lancet 364 (9433): 503–12. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16808-6. PMID 15302193.
- ^ Mimouni D, Anhalt GJ, Cummins DL, Kouba DJ, Thorne JE, Nousari HC (June 2003). "Treatment of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus with mycophenolate mofetil". Archives of Dermatology 139 (6): 739–42. doi:10.1001/archderm.139.6.739. PMID 12810504.
- ^ Diamond MS, Zachariah M, Harris E (2002). "Mycophenolic acid inhibits dengue virus infection by preventing replication of viral RNA". Virology 304 (2): 211–21. doi:10.1006/viro.2002.1685. PMID 12504563.
- ^ Takhampunya R, Ubol S, Houng HS, Cameron CE, Padmanabhan R (July 2006). "Inhibition of dengue virus replication by mycophenolic acid and ribavirin". The Journal of General Virology 87 (Pt 7): 1947–52. doi:10.1099/vir.0.81655-0. PMID 16760396.
- ^ "CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil) August 2009". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. August 14, 2009. http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm177397.htm. Retrieved 2009-08-21.
- ^ "CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil) August 2009". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. August 14, 2009. http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm177397.htm. Retrieved 2009-08-21.
- ^ "FDA Issues Second CellCept Warning". newsinferno.com. 2008-05-18. http://www.newsinferno.com/archive/fda-issues-second-cellcept-warning/. Retrieved 2010-10-26.
- ^ "MedWatch Safety Alerts for Human Medical Products". fda.gov. 2008-05. http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm092157.htm. Retrieved 2010-10-26.
- ^ 5-Hydroxymaltol and mycophenolic acid, secondary metabolites from Penicillium echinulatum. H.A. Anderson, J.M. Bracewell, A.R. Fraser, D. Jones, G.W. Robertson and J.D. Russell, Transactions of the British Mycological Society, Volume 91, Issue 4, December 1988, pp. 649-651, doi:10.1016/S0007-1536(88)80040-8
- ^ Ransom JT (December 1995). "Mechanism of action of mycophenolate mofetil". Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 17 (6): 681–4. doi:10.1097/00007691-199512000-00023. PMID 8588241.
External links
- MedlinePlus drug information: mycophenolate (systemic) – information from USP DI Advice for the Patient
Categories:- Lactones
- Immunosuppressants
- Phenols
- Isobenzofurans
- Phenol ethers
- Carboxylic acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.