- Ciclacillin
-
Cyclacillin 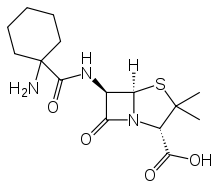
Systematic (IUPAC) name (2S,5R,6R)-6-{[(1-aminocyclohexyl)carbonyl]amino}- 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane- 2-carboxylic acid Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com International Drug Names Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability Moderate Protein binding <25% Identifiers CAS number 3485-14-1 
ATC code None PubChem CID 19003 DrugBank DB01000 ChemSpider 17941 
UNII 72ZJ154X86 
KEGG D01334 
ChEBI CHEBI:31444 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1200356 
Chemical data Formula C15H23N3O4S Mol. mass 341.425 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Ciclacillin (INN) or cyclacillin (USAN), trade names Cyclapen, Cyclapen-W, Vastcillin, and others, is an aminopenicillin antibiotic. Its spectrum of activity is similar to that of ampicillin, although it is less susceptible to beta-lactamases than ampicillin and has much higher bioavailability.[1] A large randomized, double-blind clinical trial published in 1978 also showed that ciclacillin is associated with significantly fewer and milder adverse effects than ampicillin;[2] later studies seemed to confirm this improved tolerability, at least in children.[3][4]
Ciclacillin has been superseded by newer antibiotics and is no longer in clinical use, at least in the United States.[5]
References
- ^ Warren GH (1976). "Cyclacillin: microbiological and pharmacological properties and use in chemotherapy of infection - a critical appraisal". Chemotherapy 22 (3-4): 154–82. doi:10.1159/000221924. PMID 773605.
- ^ Gold JA, Hegarty CP, Deitch MW, Walker BR (January 1979). "Double-blind clinical trials of oral cyclacillin and ampicillin". Antimicrob Agents Chemother 15 (1): 55–8. PMC 352600. PMID 371540. http://aac.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=371540.
- ^ McLinn SE, Goldberg F, Kramer R, Saltstein E, Bomze JP, Deitch MW (October 1982). "Double-blind multicenter comparison of cyclacillin and amoxicillin for the treatment of acute otitis media". J Pediatr 101 (4): 617–21. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(82)80724-5. PMID 6750067.
- ^ McLinn SE, Kaplan J, West N (1983). "Multicenter comparison of cyclacillin and amoxicillin in the treatment of acute streptococcal pharyngitis". Clin Ther 5 (3): 299–304. PMID 6342785.
- ^ Gorbach SL, Bartlett JG, Blacklow NR (2004). Infectious diseases (3rd ed.). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. p. 186. ISBN 0-7817-3371-5. http://books.google.com/?id=_eHyE9lRw7oC. Retrieved on September 7, 2008 through Google Book Search.
Further reading
- Scheld WM, Sydnor A, Farr B, Gratz JC, Gwaltney JM (September 1986). "Comparison of cyclacillin and amoxicillin for therapy for acute maxillary sinusitis". Antimicrob Agents Chemother 30 (3): 350–3. PMC 180557. PMID 3535660. http://aac.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=3535660.
PenemsCefazolin# • Cefacetrile • Cefadroxil • Cefalexin • Cefaloglycin • Cefalonium • Cefaloridine • Cefalotin • Cefapirin • Cefatrizine • Cefazedone • Cefazaflur • Cefradine • Cefroxadine • CeftezoleCefaclor • Cefamandole • Cefminox • Cefonicid • Ceforanide • Cefotiam • Cefprozil • Cefbuperazone • Cefuroxime • Cefuzonam • cephamycin (Cefoxitin, Cefotetan, Cefmetazole) • carbacephem (Loracarbef)Cefixime# • Ceftriaxone# • antipseudomonal (Ceftazidime# • Cefoperazone) • Cefcapene • Cefdaloxime • Cefdinir • Cefditoren • Cefetamet • Cefmenoxime • Cefodizime • Cefotaxime • Cefpimizole • Cefpiramide • Cefpodoxime • Cefsulodin • Cefteram • Ceftibuten • Ceftiolene • Ceftizoxime • oxacephem (Flomoxef, Latamoxef ‡)4th (antips-)CombinationsAmoxicillin/clavulanic acid# • Imipenem/cilastatin# • Ampicillin/flucloxacillin • Ampicillin/sulbactam (Sultamicillin) • Piperacillin/tazobactamOtherpolymyxins/detergent (Colistin, Polymyxin B) • depolarizing (Daptomycin) • hydrolyze NAM-NAG (Lysozyme) • GramicidinCategories:- Antibiotic stubs
- Beta-lactam antibiotics
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
