- History of ancient Israel and Judah
-
Further information: History of Palestine, Pre-history of the Southern Levant, History of the Southern Levant, and History of the Levant
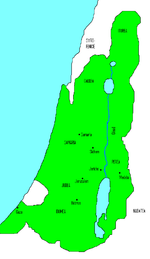
 The Iron Age kingdom of Israel (blue) and kingdom of Judah (tan), with their neighbours (8th century BC)
The Iron Age kingdom of Israel (blue) and kingdom of Judah (tan), with their neighbours (8th century BC)
Israel and Judah were related Iron Age kingdoms of ancient Palestine. The earliest known reference to the name Israel in archaeological records is in the Merneptah stele, an Egyptian record of c. 1209 BCE. By the 9th century BCE the Kingdom of Israel had emerged as an important local power before falling to the Neo-Assyrian Empire in 722 BCE. Israel's southern neighbor, the Kingdom of Judah, enjoyed a period of prosperity as a client-state of the greater empires of the region before a revolt against the Neo-Babylonian Empire led to its destruction in 586 BCE and the deportation of the elite. There is no definite answer to the question of when Judah emerged,[1] although it seems to have occurred no earlier than the 9th century BCE.[2][3] In the 7th century BCE Jerusalem became a city with a population many times greater than before and clear dominance over its neighbours, probably as the result of a cooperative arrangement with the Assyrians, who wished to establish Judah as a pro-Assyrian vassal state controlling the valuable olive industry.[4] Following the fall of the Neo-Babylonian Empire to the Persian Cyrus the Great, 539 BC, some Judean exiles returned to Jerusalem during the Persian period, inaugurating the formative period in the development of a distinctive Judahite identity in the Persian province of Yehud. Yehud was absorbed into the subsequent Hellenistic kingdoms that followed the conquests of Alexander the Great, but in the 2nd century BCE the Judaeans revolted against the Hellenist Seleucid Empire and created the Hasmonean kingdom. This, the last nominally independent Judean kingdom, came to an end in 63 BCE with its conquest by Pompey of the Roman Republic.
Contents
Periods
- Late Bronze: 1300-1200
- Iron Age I: 1200–1000
- Iron Age II:1000-586
- Neo-Babylonian: 586–539
- Persian: 539–332
- Hellenistic: 332–53[5]
Sources
The sources for the history of ancient Israel and Judah can be broadly divided into the biblical narrative (essentially the Hebrew Bible, but also Deuterocanonical and non-biblical works for the later period) and the archaeological record. The latter can again be divided between epigraphy (written inscriptions, both from Israel and other lands including Mesopotamia and Egypt) and the material record (everything else).
The biblical history
The Hebrew Bible contains "sagas, heroic epics, oral traditions, annals, biographies, narrative histories, novellae, belles lettres, proverbs and wisdom-sayings, poetry, prophecy, apocalyptic, and much more ... the whole finally woven into a composite, highly complex literary fabric sometime in the Hellenistic era."[6] Although tradition ascribes them to times and authors contemporaneous with events, they were in fact written in many cases considerably after the times they describe and by authors with a clear religious and nationalist agenda, and it is therefore critical to treat them with circumspection.[7]
By the 1920s, it was clear that the idea of an Israelite conquest of Canaan - the story of the book of Joshua - was not supported by the archaeological record. The response of the time was to propose that the main biblical idea was still correct, but that the Israelites entered Canaan peacefully instead of through conquest. Later, even this compromise was abandoned, and the Israelites were interpreted to be indigenous Canaanites. The revision of Israelite origins has implications for Israelite religion: whereas the bible had depicted them as monotheists from the beginning, the new understanding is that they were polytheists who harboured a small and ultimately successful group of monotheistic revolutionaries.[8]
The new understanding, even if it recognised the Israelites as Canaanites by origin, still treated post-Conquest biblical story as real history. But eventually this also came under challenge: if, after 200 years of archaeology, there is still no direct evidence of the existence of David and Solomon, then they too must be fiction, the product of Jews of the 6th and 5th century Persian empire. The most radical reconstruction goes even further, alleging that the Jews originated as a "mixed multitude" of settlers sent to Jerusalem by the Persians, where they concocted a past for themselves. There are few scholars who believe this, but it demonstrates how the paradigm (the argument) has shifted.[9]
The archaeological record
Dating of remains to the biblical history is made difficult by the bible's lack of datable events and its unreliable internal chronology; the interpretation of remains has been influenced by religious and nationalistic arguments, as evidenced by arguments over burials from the highland settlement phase; and no material remains have been found which can reliably separate Israelite from non-Israelite (Canaanite) sites in the earliest period.[10]
Late Bronze Age
 The Canaanite god Ba'al, 14th–12th century BC (Louvre museum, Paris)
The Canaanite god Ba'al, 14th–12th century BC (Louvre museum, Paris)
The eastern Mediterranean seaboard – the Levant – stretches 400 miles north to south from the Taurus Mountains to the Sinai desert, and 70 to 100 miles east to west between the sea and the Arabian desert.[11] The coastal plain of the southern Levant, broad in the south and narrowing to the north, is backed in its southernmost portion by a zone of foothills, the Shephalah; like the plain this narrows as it goes northwards, ending in the promontory of Mount Carmel. East of the plain and the Shephalah is a mountainous ridge, the "hill country of Judah" in the south, the "hill country of Ephraim" north of that, then Galilee and the Lebanon mountains. To the east again lie the steep-sided valley occupied by the Jordan River, the Dead Sea, and the wadi of the Arabah, which continues down to the eastern arm of the Red Sea. Beyond the plateau is the Syrian desert, separating the Levant from Mesopotamia. To the southwest is Egypt, to the northeast Mesopotamia. "The Levant thus constitutes a narrow corridor whose geographical setting made it a constant area of contention between more powerful entities".[12]
Canaan in the Late Bronze Age was a shadow of what it had been centuries earlier: many cities were abandoned, others shrank in size, and the total settled population was probably not much more than a hundred thousand.[13] Settlement was concentrated in cities along the coastal plain and along major communication routes; the central and northern hill country which would later become the biblical kingdom of Israel was only sparsely inhabited[14] although letters from the Egyptian archives indicate that Jerusalem was already a Canaanite city-state recognising Egyptian overlordship.[15] Politically and culturally it was dominated by Egypt,[16] each city under its own ruler, constantly at odds with its neighbours, and appealing to the Egyptians to adjudicate their differences.[14]
The Canaanite city-state system broke down at the end of the Late Bronze period,[17] and Canaanite culture was then gradually absorbed into that of the Philistines, Phoenicians and Israelites.[18] The process was gradual rather than swift:[19] a strong Egyptian presence continued into the 12th century BC, and, while some Canaanite cities were destroyed, others continued to exist in Iron I.[20]
Iron Age I
The Merneptah stele (JE 31408), bearing the first record of the name Israel (Cairo Museum)
The name Israel first appears in the stele of the Egyptian pharaoh Merneptah c. 1209 BC, "Israel is laid waste and his seed is not."[21] This "Israel" was a cultural and probably political entity of the central highlands, well enough established to be perceived by the Egyptians as a possible challenge to their hegemony, but an ethnic group rather than an organised state;[22] Archaeologist Paula McNutt says: "It is probably ... during Iron Age I [that] a population began to identify itself as 'Israelite'," differentiating itself from its neighbours via prohibitions on intermarriage, an emphasis on family history and genealogy, and religion.[23]
In the Late Bronze Age there were no more than about 25 villages in the highlands, but this increased to over 300 by the end of Iron I, while the settled population doubled from 20,000 to 40,000.[24] The villages were more numerous and larger in the north, and probably shared the highlands with pastoral nomads who left no remains.[25] Archaeologists and historians attempting to trace the origins of these villagers have found it impossible to identify any distinctive features that could definine them as specifically Israelite – collared-rim jars and four-room houses have been identified outside the highlands and thus cannot be used to distinguish Israelite sites,[26] and while the pottery of the highland villages is far more limited than that of lowland Canaanite sites, it develops typologically out of Canaanite pottery that came before.[27] Israel Finkelstein proposed that the oval or circular layout that distinguishes some of the earliest highland sites, and the notable absence of pig bones from hill sites, could be taken as a marker of ethnicity, but others have cautioned that these can be a "common-sense" adaptation to highland life and not necessarily revelatory of origins.[28] Modern scholars therefore see Israel arising peacefully and internally in the highlands.[29]
Iron Age II
 A reconstructed Israelite house, 10th–7th century BC. Eretz Israel Museum, Tel Aviv.
A reconstructed Israelite house, 10th–7th century BC. Eretz Israel Museum, Tel Aviv.
Unusually favourable climatic conditions in the first two centuries of Iron Age II brought about an expansion of population, settlements and trade throughout the region.[30] In the central highlands this resulted in unification in a kingdom with the city of Samaria as its capital,[30] possibly by the second half of the 10th century BCE when an inscription of the Egyptian pharaoh Shoshenq I, the biblical Shishak, records a series of campaigns directed at the area.[31] Israel had clearly emerged by the middle of the 9th century BCE, when the Assyrian king Shalmaneser III names "Ahab the Israelite" among his enemies at the battle of Qarqar (853), and the Mesha stele (c. 830) left by a king of Moab celebrates his success in throwing off the oppression of the "House of Omri" (i.e. Israel).[31]It bears what is generally thought to be the earliest extra-biblical Semitic reference to the name Yahweh (YHWH), whose temple goods were plundered by Mesha and brought before his own god Kemosh.[32] French scholar André Lemaire has reconstructed a portion of line 31 of the stele as mentioning the "House of David".[33] Tel Dan stele tells of the death of a king of Israel, probably Jehoram, at the hands of an Aramean king (c. 841).[31] In the earlier part of this period Israel was apparently engaged in a three-way contest with Damascus and Tyre for control of the Jezreel Valley and Galilee in the north, and with Moab, Ammon and Damascus in the east for control of Gilead;[30] During the reign of Hezekiah, between c. 715 and 686 BCE, a notable increase in the power of the Judean state can be observed.[34] This is reflected by archaeological sites and findings such as the Broad Wall, defensive city wall in Jerusalem, Hezekiah's Tunnel, an aqueduct designed to provide Jerusalem with water during an impending siege by the Assyrians, led by Sennacherib. Siloam Inscription, lintel inscription, found over the doorway of a tomb, has been ascribed to his comptroller Shebna. LMLK seals on storage jar handles, excavated from strata formed by Sennacherib's destruction as well as immediately above that layer suggesting they were used throughout his 29-year reign, and Bullae from sealed documents, some that belonged to Hezekiah himself, while others name his servants.[35] King Ahaz's Seal is a well-preserved piece of reddish-brown clay that belonged to King Ahaz of Judah, who ruled from 732 to 716 BCE. The seal contains not only the name of the king, but the name of his father, King Yehotam. In addition, Ahaz is specifically identified as "king of Judah." The Hebrew inscription, which is set on three lines, reads as follows: "l'hz*y/hwtm*mlk*/yhdh", which translates as "belonging to Ahaz (son of) Yehotam, King of Judah.[36]
In the earlier part of its history Israel was apparently engaged in a three-way contest with Damascus and Tyre for control of the Jezreel Valley and Galilee in the north, and with Moab, Ammon and Damascus in the east for control of Gilead.[30] From the middle of the 8th century BCE it came into increasing conflict with the expanding neo-Assyrian empire, which first split its territory into several smaller units and then destroyed its capital, Samaria (722). Both the biblical and Assyrian sources speak of a massive deportation of the people of Israel and their replacement with an equally large number of forced settlers from other parts of the empire – such population exchanges were an established part of Assyrian imperial policy, a means of breaking the old power structure - and the former Israel never again became an independent political entity.[37]
Judah emerged somewhat later than Israel, probably no earlier than the 9th century BCE, but the subject is one of considerable controversy and there is no definite answer to the question.[38] Surface surveys indicate that during the 10th and 9th centuries BCE the southern highlands were divided between a number of centres, none with clear primacy.[39] In the 7th century, probably in a cooperative arrangement with the Assyrians to establish Judah as an Assyrian vassal controlling the valuable olive industry, Jerusalem grew to contain a population many times greater than before and achieved clear dominance over its neighbours.[4] Judah prospered under Assyrian vassalage (despite a disastrous rebellion against the Assyrian king Sennacherib), but in the last half of the 7th century BCE Assyria suddenly collapsed, and the ensuing competition between the Egyptian and Neo-Babylonian empires for control of Palestine led to the destruction of Judah in a series of campaigns between 597 and 582.[4]
Babylonian period
Babylonian Judah suffered a steep decline in both economy and population[40] and lost the Negev, the Shephelah, and part of the Judean hill country, including Hebron, to encroachments from Edom and other neighbours.[41] Jerusalem, while probably not totally abandoned, was much smaller than previously, and the town of Mizpah in Benjamin in the relatively unscathed northern section of the kingdom became the capital of the new Babylonian province of Yehud Medinata.[42] (This was standard Babylonian practice: when the Philistine city of Ashkalon was conquered in 604, the political, religious and economic elite (but not the bulk of the population) was banished and the administrative centre shifted to a new location).[43] There is also a strong probability that for most or all of the period the temple at Bethel in Benjamin replaced that at Jerusalem, boosting the prestige of Bethel's priests (the Aaronites) against those of Jerusalem (the Zadokites), now in exile in Babylon.[44]
The Babylonian conquest entailed not just the destruction of Jerusalem and its temple, but the liquidation of the entire infrastructure which had sustained Judah for centuries.[45] The most significant casualty was the State ideology of "Zion theology,"[46] the idea that the God of Israel had chosen Jerusalem for his dwelling-place and that the Davidic dynasty would reign there forever.[47] The fall of the city and the end of Davidic kingship forced the leaders of the exile community – kings, priests, scribes and prophets – to reformulate the concepts of community, faith and politics.[48] The exile community in Babylon thus became the source of significant portions of the Hebrew Bible: Isaiah 40–55, Ezekiel, the final version of Jeremiah, the work of the Priestly source in the Pentateuch, and the final form of the history of Israel from Deuteronomy to 2 Kings[49] Theologically, they were responsible for the doctrines of individual responsibility and universalism (the concept that one god controls the entire world), and for the increased emphasis on purity and holiness.[49] Most significantly, the trauma of the exile experience led to the development of a strong sense of identity as a people distinct from other peoples,[50] and increased emphasis on symbols such as circumcision and Sabbath-observance to maintain that separation.[51]
The concentration of the biblical literature on the experience of the exiles in Babylon disguises the fact that the great majority of the population remained in Judah, and for them life after the fall of Jerusalem probably went on much as it had before.[52] It may even have improved, as they were rewarded with the land and property of the deportees, much to the anger of the exile community in Babylon.[53] The assassination of the Babylonian governor around 582 by a disaffected member of the former royal house of David provoked a Babylonian crackdown, possibly reflected in the Book of Lamentations, but the situation seems to have soon stabilised again.[54] Nevertheless, the unwalled cities and towns that remained were subject to slave raids by the Phoenicians and intervention in their internal affairs from Samaritans, Arabs and Ammonites.[55]
Persian period
Main article: Yehud MedinataWhen Babylon fell to the Persian Cyrus the Great in 539 BC, Judah (or Yehud medinata, the "province of Yehud") became an administrative division within the Persian empire. Cyrus was succeeded as king by Cambyses, who added Egypt to the empire, incidentally transforming Yehud and the Philistine plain into an important frontier zone. His death in 522 was followed by a period of turmoil until Darius the Great seized the throne in about 521. Darius introduced a reform of the administrative arrangements of the empire including the collection, codification and administration of local law codes, and it is reasonable to suppose that this policy lay behind the redaction of the Jewish Torah.[56] After 404 the Persians lost control of Egypt, which became Persia's main rival outside Europe, causing the Persian authorities to tighten their administrative control over Yehud and the rest of the Levant.[57] Egypt was eventually reconquered, but soon afterward Persia fell to Alexander the Great, ushering in the Hellenistic period in the Levant.
Yehud's population over the entire period was probably never more than about 30,000, and that of Jerusalem no more than about 1,500, most of them connected in some way to the Temple.[58] According to the biblical history, one of the first acts of Cyrus, the Persian conqueror of Babylon, was to commission the Jewish exiles to return to Jerusalem and rebuild the Temple, a task which they are said to have completed c. 515.[59] Yet it was probably only in the middle of the next century, at the earliest, that Jerusalem again became the capital of Judah.[60] The Persians may have experimented initially with ruling Yehud as a Dividic client-kingdom under descendants of Jehoiachin,[61] but by the mid–5th century BC Yehud had become in practice a theocracy, ruled by hereditary High Priests[62] and a Persian-appointed governor, frequently Jewish, charged with keeping order and seeing that tribute was paid.[63] According to the biblical history Ezra and Nehemiah arrived in Jerusalem in the middle of the 5th century BC, the first empowered by the Persian king to enforce the Torah, the second with the status of governor and a royal mission to restore the walls of the city.[64] The biblical history mentions tension between the returnees and those who had remained in Yehud, the former rebuffing the attempt of the "peoples of the land" to participate in the rebuilding of the Temple; this attitude was based partly on the exclusivism which the exiles had developed while in Babylon and, probably, partly on disputes over property.[65] The careers of Ezra and Nehemiah in the 5th century BC were thus a kind of religious colonisation in reverse, an attempt by one of the many Jewish factions in Babylon to create a self-segregated, ritually pure society inspired by the prophesies of Ezekiel and his followers.[66]
The Persian era, and especially the period 538–400, laid the foundations of later Jewish and Christian religion and the beginnings of a scriptural canon.[67] Other important landmarks include the replacement of Hebrew by Aramaic as the everyday language of Judah (although it continued to be used for religious and literary purposes),[68] and Darius's reform of the administrative arrangements of the empire, which may lie behind the redaction of the Jewish Torah.[56] The Israel of the Persian period included descendants of the inhabitants of the old kingdom of Judah, returnees from the Babylonian exile community, Mesopotamians who had joined them or had been exiled themselves to Samaria at a far earlier period, Samaritans and others.[69]
Hellenistic period
The Hasmonean kingdom at its largest extent
On the death of Alexander the Great (322) his generals divided the empire between them. Ptolemy I, the ruler of Egypt, seized Palestine, but his successors lost it to the Seleucids of Syria in 198. At first relations between the Seleucids and the Jews were cordial, but the attempt of Antiochus IV Epiphanes (174–163) to impose Hellenic culture sparked a national rebellion, which ended in the expulsion of the Syrians and the establishment of an independent Jewish kingdom under the Hasmonean dynasty. The Hasmonean kingdom was a conscious attempt to revive the Judah described in the Bible: a Jewish monarchy ruled from Jerusalem and stretching over all the territories once ruled by David and Solomon. In order to carry out this project the Hasmoneans forcibly converted to Judaism the one-time Moabites, Edomites and Ammonites, as well as the lost kingdom of Israel.[70] Some scholars argue that the "Jewish biblical canon" was fixed by the Hasmonean dynasty.[71]
In 63 BC the Roman general Pompey conquered Jerusalem and made the Jewish kingdom a client of Rome. In 40–39, Herod the Great was appointed King of the Jews by the Roman Senate, and in 6 AD the last ethnarch of Judea was deposed by the emperor Augustus and his territories were combined with Idumea and Samaria and annexed as Iudaea Province under direct Roman administration.[72] The name Judea (Iudaea) was removed after the revolt of Simon Bar Kochba in 135 AD, after which the area was called Syria Palaestina, (Greek: Παλαιστίνη, Palaistinē; Latin: Palaestina.)
Religion
Iron Age Yahwism
Further information: Yahweh (Canaanite deity) and El (god)Current models among scholars see the emergence of Israelite monotheism as a gradual process which began with the normal beliefs and practices of the ancient world.[73]
The religion of the Israelites of Iron Age I, like many Ancient Near Eastern religions, was based on the cult of the ancestors and the worship of family gods (the "gods of the fathers").[74] The major deities were not numerous – El, Asherah, and Yahweh, with Baal as a fourth god in the early period.[75] By the early monarchy El and Yahweh had become identified and Asherah did not continue as a separate state cult,[75] although she continued to be popular at a community level until Persian times.[76] Yahweh, later the national god of both Israel and Judah seems to have originated in Edom and Midian in southern Canaan, and may have been brought north to Israel by the Kenites and Midianites at an early stage.[77] With the emergence of monarchy at the beginning of Iron Age II the king promoted his own family god, Yahweh, as the god of the kingdom, but beyond the royal court religion continued to be both polytheistic and family-centered, as it was also for other societies in the Ancient Near East.[78]
There is a general consensus among scholars that the first formative event in the emergence of the distinctive religion described in the bible was triggered by the destruction of Israel by Assyria in c.722 BC. Refugees came south to Judah, bringing with them laws and a Prophetic tradition that Yahweh was the only god who should be served. These beliefs were adopted by the "people of the land", meaning the landed families who provided the administrative class of the kingdom, and in 640 BC these circles were decisive in placing on the throne the eight-year-old Josiah. Judah at this time was a vassal of Assyria, but Assyrian power collapsed in the 630s, and in around 622 Josiah and the Deuteronomists, as the circle around him are called by modern scholars, launched a bid for independence expressed as loyalty to "Yahweh alone" and the law-code in the book of Deuteronomy, written in the form of a treaty between Judah and Yahweh to replace the vassal-treaty with Assyria.[79]
According to the theology of the Deuteronomists the terms of the treaty with Yahweh were that he would preserve both the city and the king in return for their worship and obedience to the law-code. The destruction of Jerusalem, the Temple, and the Davidic dynasty by Babylon in 587/586 BC was therefore a deeply traumatic event, and led to much theological reflection on the meaning of the national tragedy. The solution, set out in the series of history books from Joshua and Judges to Samuel and Kings, was to interpret the Babylonian destruction as divinely-ordained punishment for the failure of the kings to worship Yahweh alone.[79]
Second Temple Judaism
Main article: Second Temple JudaismThe Second Temple period (520BC-70AD) differed in significant ways from what had gone before.[80] Monotheism emerged among the priests and the Temple establishment probably by the beginning of the Persian period, and beliefs regarding angels and demons were developing rapidly by its end.[81] It was at this time that the Torah was written, circumcision and Sabbath-observance became symbols of Jewish identity, and the institution of the synagogue became increasingly important.[82] By the end of the Second Temple period the Jewish canon was becoming fixed, and, since there was still no monarchy and the reality of life did not match the expectations created by the religious traditions, messianic expectation began to surface.[82]
See also
- Biblical archaeology
- Chronology of the Bible
- History of the Southern Levant
- History of Israel
- Jew
- Jewish diaspora
- Old Testament
- Tanakh
- United Monarchy
- History of the Jews in Iran
- History of the Jews in the Roman Empire
- History of the Jews in Egypt
Kings of Israel
Saul, Ish-bosheth, David, Solomon, Jeroboam, Nadab, Baasha, Elah, Zimri, Omri, Ahab Ahaziah, Jehoram, Jehu, Jehoahaz, Jehoash, Jeroboam II, Zachariah, Shallum, Menahem, Pekahiah, Pekah, Hoshea
Main: List of the Kings of IsraelKings of Judah
Rehoboam, Abijam, Asa, Jehoshaphat, Jehoram, Ahaziah, Athaliah, Jehoash, Amaziah, Uzziah, Jotham, Ahaz, Hezekiah, Manasseh, Amon, Josiah, Jehoahaz, Jehoiakim, Jeconiah, Zedekiah
Main: List of the Kings of JudahReferences
- ^ Grabbe 2008, pp. 225–6.
- ^ Grabbe 2008, pp. 225–6.
- ^ Lehman in Vaughn 1992, p. 149.
- ^ a b c Thompson 1992, pp. 410–1.
- ^ King 2001, p. xxiii.
- ^ Dever 2001, p. 2.
- ^ Golden 2004b, pp. 62–3.
- ^ Rendsberg, pp.3-5
- ^ Rendsberg, pp.5-6
- ^ Bloch-Smith, pp.27,29,30
- ^ Miller 1986, p. 36.
- ^ Coogan 1998, pp. 4–7.
- ^ Finkelstein 2001, p. 78.
- ^ a b Killebrew 2005, pp. 38–9.
- ^ Cahill in Vaughn 1992, pp. 27–33.
- ^ Kuhrt 1995, p. 317.
- ^ Killebrew 2005, pp. 10–6.
- ^ Golden 2004b, pp. 61–2.
- ^ McNutt 1999, p. 47.
- ^ Golden 2004a, p. 155.
- ^ Stager in Coogan 1998, p. 91.
- ^ Dever 2003, p. 206.
- ^ McNutt 1999, pp. 35.
- ^ McNutt 1999, pp.46-47.
- ^ McNutt 1999, p. 69.
- ^ Miller 1986, p. 72.
- ^ Killebrew 2005, p. 13.
- ^ Edelman in Brett 2002, p. 46-47.
- ^ Gnuse 1997, pp.28,31
- ^ a b c d Thompson 1992, p. 408.
- ^ a b c Mazar in Finkelstein 2007, p. 163.
- ^ http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Moab#The_Mesha_stele
- ^ Biblical Archaeology Review [May/June 1994], pp. 30–37
- ^ David M. Carr, Writing on the Tablet of the Heart: Origins of Scripture and Literature, Oxford University Press, 2005, p. 164.
- ^ Seal of Amariah Hananiah--Servant of Hezekiah
- ^ First Impression: What We Learn from King Ahaz’s Seal (#m1), by Robert Deutsch, Archaeological Center
- ^ Lemche 1998, p. 85.
- ^ Grabbe 2008, pp. 225–6.
- ^ Lehman in Vaughn 1992, p. 149.
- ^ Grabbe 2004, p. 28.
- ^ Lemaire in Blenkinsopp 2003, p. 291.
- ^ Davies 2009.
- ^ Lipschits 2005, p. 48.
- ^ Blenkinsopp in Blenkinsopp 2003, pp. 103–5.
- ^ Blenkinsopp 2009, p. 228.
- ^ Middlemas 2005, pp. 1–2.
- ^ Miller 1986, p. 203.
- ^ Middlemas 2005, p. 2.
- ^ a b Middlemas 2005, p. 10.
- ^ Middlemas 2005, p. 17.
- ^ Bedford 2001, p. 48.
- ^ Barstad 2008, p. 109.
- ^ Albertz 2003a, p. 92.
- ^ Albertz 2003a, pp. 95–6.
- ^ Albertz 2003a, p. 96.
- ^ a b Blenkinsopp 1988, p. 64.
- ^ Lipschits in Lipschits 2006, pp. 86–9.
- ^ Grabbe 2004, pp. 29–30.
- ^ Nodet 1999, p. 25.
- ^ Davies in Amit 2006, p. 141.
- ^ Niehr in Becking 1999, p. 231.
- ^ Wylen 1996, p. 25.
- ^ Grabbe 2004, pp. 154–5.
- ^ Soggin 1998, p. 311.
- ^ Miller 1986, p. 458.
- ^ Blenkinsopp 2009, p. 229.
- ^ Albertz 1994, pp. 437–8.
- ^ Kottsieper in Lipschits 2006, pp. 109–10.
- ^ Becking in Albertz 2003b, p. 19.
- ^ Davies 1992, pp. 149–50.
- ^ Philip R. Davies in The Canon Debate, page 50: "With many other scholars, I conclude that the fixing of a canonical list was almost certainly the achievement of the Hasmonean dynasty."
- ^ Ben-Sasson 1976, p. 246.
- ^ Gnuse 1997, pp. 62–3.
- ^ Van der Toorn 1996, p.4.
- ^ a b Smith 2002, p. 57.
- ^ Dever (2005), p.
- ^ Van der Toorn 1999, p. 911–3.
- ^ Van der Toorn 1996, p. 181–2.
- ^ a b Dunn and Rogerson, pp.153–154
- ^ Avery Peck, p.58
- ^ Grabbe (2004), pp. 243-244
- ^ a b Avery Peck, p.59
Bibliography
- Albertz, Rainer (1994) [Vanderhoek & Ruprecht 1992]. A History of Israelite Religion, Volume I: From the Beginnings to the End of the Monarchy. Westminster John Knox Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=yvZUWbTftSgC&pg=RA1-PA145&lpg=RA1-PA145&dq=History+of+Israelite+Religion,+Volume+1++Albertz#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Albertz, Rainer (1994) [Vanderhoek & Ruprecht 1992]. A History of Israelite Religion, Volume II: From the Exile to the Maccabees. Westminster John Knox Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=exjyhvRy7YUC&dq=Albertz+a+history+of+israelite+religion&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Albertz, Rainer (2003a). Israel in Exile: The History and Literature of the Sixth Century B.C.E.. Society of Biblical Literature. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=Xx9YzJq2B9wC&dq=Rainer+Albertz,+%22Israel+in+exile%22&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Albertz, Rainer; Becking, Bob, eds. (2003b). Yahwism After the Exile: Perspectives on Israelite Religion in the Persian Era. Koninklijke Van Gorcum. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=hwExATCqwvwC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Yahwism+after+the+exile:+perspectives+on+Israelite+religion+in+the+Persian+era#v=onepage&q&f=false. Becking, Bob. "Law as Expression of Religion (Ezra 7–10)".
- Amit, Yaira, et al., eds. (2006). Essays on Ancient Israel in its Near Eastern Context: A Tribute to Nadav Na'aman. Eisenbrauns. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=Ku4OKVrEd4MC&pg=PA467&lpg=PA467&dq=Essays+on+Ancient+Israel+in+its+Near+Eastern+Context:+A+Tribute+to+Nadav+Na%27aman#v=onepage&q=Essays%20on%20Ancient%20Israel%20in%20its%20Near%20Eastern%20Context%3A%20A%20Tribute%20to%20Nadav%20Na%27aman&f=false. Davies, Philip R. "The Origin of Biblical Israel".
- Avery-Peck, Alan, et al., eds. (2003). The Blackwell Companion to Judaism. Blackwell. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=asYoIwz9z2UC&pg=PA230&lpg=PA230&dq=The+Blackwell+Companion+to+Judaism++By+Jacob+Neusner,+Alan+Avery-Peck#v=onepage&q=&f=false. Murphy, Frederick J. R. "Second Temple Judaism".
- Barstad, Hans M. (2008). History and the Hebrew Bible. Mohr Siebeck. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=zqJxkKy-cMMC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Barstad+History+and+the+Hebrew+Bible:+studies+in+ancient+Israelite+and+ancient+Near#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Becking, Bob, ed. (2001). Only One God? Monotheism in Ancient Israel and the Veneration of the Goddess Asherah. Sheffield Academic Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=z72KmReV-bIC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Only+One+God%3F+Monotheism+in+Ancient+Israel+and+the+Veneration+of+the+Goddess+Asherah#v=onepage&q&f=false. Dijkstra, Meindert. "El the God of Israel, Israel the People of YHWH: On the Origins of Ancient Israelite Yahwism". Dijkstra, Meindert. "I Have Blessed You by Yahweh of Samaria and His Asherah: Texts with Religious Elements from the Soil Archive of Ancient Israel".
- Becking, Bob; Korpel, Marjo Christina Annette, eds. (1999). The Crisis of Israelite Religion: Transformation of Religious Tradition in Exilic and Post-Exilic Times. Brill. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=lak_YWjCjDMC&printsec=frontcover&dq=The+crisis+of+Israelite+religion:+transformation+of+religious+tradition#v=onepage&q&f=false. Niehr, Herbert. Religio-Historical Aspects of the Early Post-Exilic Period.
- Bedford, Peter Ross (2001). Temple Restoration in Early Achaemenid Judah. Brill. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=MOd320e710IC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Osarsiph&cad=1#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Ben-Sasson, H.H. (1976). A History of the Jewish People. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0674397312.
- Blenkinsopp, Joseph (1988). Ezra-Nehemiah: A Commentary. Eerdmans. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=3PvirfZkfvQC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Ezra-Nehemiah:+A+Commentary++By+Joseph+Blenkinsopp#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Blenkinsopp, Joseph; Lipschits, Oded, eds. (2003). Judah and the Judeans in the Neo-Babylonian Period. Eisenbrauns. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=R65fhpcUFcgC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Judah+and+the+Judeans+in+the+neo-Babylonian+period#v=onepage&q&f=false. Blenkinsopp, Joseph. "Bethel in the Neo-Babylonian Period". Lemaire, Andre. "Nabonidus in Arabia and Judea During the Neo-Babylonian Period".
- Blenkinsopp, Joseph (2009). Judaism, the First Phase: The Place of Ezra and Nehemiah in the Origins of Judaism. Eerdmans. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=m1V1DeBS6P0C&printsec=frontcover&dq=Judaism,+the+first+phase:+the+place+of+Ezra+and+Nehemiah#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Bloch-Smith, Elizabeth (2008). "Bible, Archaeology, and the Social Sciences". In Frederick E. Greenspahn. The Hebrew Bible: new insights and scholarship. NYU Press. http://books.google.com/books?id=Z0wawEnu0UkC&pg=PA43&dq=Hebrew+Bible&cad=3#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Brett, Mark G. (2002). Ethnicity and the Bible. Brill. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=RfFRhC4FpZkC&pg=PA45&lpg=PA45&dq=Finkelstein+haser-style+layout#v=onepage&q=Finkelstein%20haser-style%20layout&f=false. Edelman, Diana. "Ethnicity and Early Israel".
- Bright, John (2000; 4th ed., 1st ed. 1959). A History of Israel. Westminster John Knox Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=0VG67yLs-LAC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Bright+History+of+Israel#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Coogan, Michael D., ed. (1998). The Oxford History of the Biblical World. Oxford University Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=zFhvECwNQD0C&dq=The+Oxford+History+of+the+Biblical+World&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q&f=false. Stager, Lawrence E. "Forging an Identity: The Emergence of Ancient Israel".
- Coogan, Michael D. (2009). A Brief Introduction to the Old Testament. Oxford University Press. http://books.google.com/books?id=nlb1PQAACAAJ&dq=A+brief+introduction+to+the+old+testament+coogan.
- Coote, Robert B.; Whitelam, Keith W. (1986). "The Emergence of Israel: Social Transformation and State Formation Following the Decline in Late Bronze Age Trade". Semeia (37): 107–47.
- Davies, Philip R. (1992). In Search of Ancient Israel. Sheffield. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=pMcM8GGO_n8C&printsec=frontcover&dq=Philip+Davies+In+search+of+Ancient+Israel#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- Davies, Philip R. (2009). "The Origin of Biblical Israel". Journal of Hebrew Scriptures 9 (47). http://www.arts.ualberta.ca/JHS/Articles/article_47.htm.
- Day, John (2002). Yahweh and the Gods and Goddesses of Canaan. Sheffield Academic Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=y-gfwlltlRwC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Yahweh+and+the+gods+and+goddesses+of+Canaan#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Dever, William (2001). What Did the Biblical Writers Know, and When Did They Know It?. Eerdmans. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=6-VxwC5rQtwC&printsec=frontcover&dq=What+did+the+biblical+writers+know,+and+when+did+they+know+it#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Dever, William (2003). Who Were the Early Israelites and Where Did They Come From?. Eerdmans. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=8WkbUkKeqcoC&dq=Who+were+the+early+Israelites,+and+where+did+they+come+from%3F&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- Dever, William (2005). Did God Have a Wife?: Archaeology and Folk Religion in Ancient Israel. Eerdmans. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=6AOE9sxg3bMC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Did+God+have+a+wife%3F:+archaeology+and+folk+religion+in+ancient+Israel#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Dunn, James D.G; Rogerson, John William, eds. (2003). Eerdmans commentary on the Bible. Eerdmans. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=2Vo-11umIZQC&pg=PA153&lpg=PA153&dq=John+W.+Rogerson+Deuteronomy#v=onepage&q=John%20W.%20Rogerson%20Deuteronomy&f=false. Rogerson, John William. "Deuteronomy".
- Edelman, Diana, ed. (1995). The Triumph of Elohim: From Yahwisms to Judaisms. Kok Pharos. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=bua2dMa9fJ4C&printsec=frontcover&dq=The+crisis+of+Israelite+religion:+transformation+of+religious+tradition&cad=1#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Finkelstein, Neil Asher; Silberman (2001). The Bible Unearthed. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=lu6ywyJr0CMC&printsec=frontcover&dq=The+Bible+Unearthed:+Archaeology%27s+New+Vision+of+Ancient+Israel#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Finkelstein, Israel; Mazar, Amihay; Schmidt, Brian B. (2007). The Quest for the Historical Israel. Society of Biblical Literature. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=jpbngoKHg8gC&dq=The+quest+for+the+historical+Israel:&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q=&f=false. Mazar, Amihay. "The Divided Monarchy: Comments on Some Archaeological Issues".
- Gnuse, Robert Karl (1997). No Other Gods: Emergent Monotheism in Israel. Sheffield Academic Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=0Kf1ZwDifdAC&dq=Robert+Karl+Gnuse,+%22No+Other+Gods:+Emergent+Monotheism+in+Israel%22&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Golden, Jonathan Michael (2004a). Ancient Canaan and Israel: An Introduction. Oxford University Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=EResmS5wOnkC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Ancient+Canaan+and+Israel:+An+Introduction++By+Jonathan+M+Golden#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Golden, Jonathan Michael (2004b). Ancient Canaan and Israel: New Perspectives. ABC-CLIO. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=yTMzJAKowyEC&pg=PA62&lpg=PA62&dq=Late+Bronze+collapse+in+Canaan#v=onepage&q=Late%20Bronze%20collapse%20in%20Canaan&f=false.
- Goodison, Lucy; Morris, Christine (1998). Goddesses in Early Israelite Religion in Ancient Goddesses: The Myths and the Evidence. University of Wisconsin Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=VSJWkrXfbLQC&dq=Family+religion+in+Babylonia,+Syria,+and+Israel&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Grabbe, Lester L. (2004). A History of the Jews and Judaism in the Second Temple Period. T&T Clark International. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=VK2fEzruIn0C&printsec=frontcover&dq=A+history+of+the+Jews+and+Judaism+in+the+Second+Temple+Period#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Grabbe, Lester L., ed. (2008). Israel in Transition: From Late Bronze II to Iron IIa (c. 1250–850 B.C.E.). T&T Clark International. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=tR0Qpz2zRogC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Israel+in+transition:+from+late+Bronze+II+to+Iron+IIa+%28c.+1250-850+B.C.E.%29#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Killebrew, Ann E. (2005). Biblical Peoples and Ethnicity: An Archaeological Study of Egyptians, Canaanites, and Early Israel, 1300–1100 B.C.E.. Society of Biblical Literature. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=VtAmmwapfVAC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Biblical+peoples+and+ethnicity:+an+archaeological#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- King, Philip J.; Stager, Lawrence E. (2001). Life in Biblical Israel. Westminster John Knox Press. ISBN 0664221483. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=OtOhypZz_pEC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Life+in+biblical+Israel++By+Philip+J.+King,+Lawrence+E.+Stager#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Kuhrt, Amélie (1995). The Ancient Near East c. 3000–330 BC. Routledge. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=V_sfMzRPTgoC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Am%C3%A9lie+Kuhrt+The+ancient+Near+East#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Lemche, Niels Peter (1998). The Israelites in History and Tradition. Westminster John Knox Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=JIoY7PagAOAC&dq=lemche+the+israelites+in+history+and+tradition&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- Levy, Thomas E. (1998). The Archaeology of Society in the Holy Land. Continuum International Publishing. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=-etsKv-4V2oC&printsec=frontcover&dq=The+archaeology+of+society+in+the+Holy+Land++Thomas+E.+Levy#v=onepage&q&f=false. LaBianca, Øystein S.; Younker, Randall W. "The Kingdoms of Ammon, Moab and Edom: The Archaeology of Society in Late Bronze/Iron Age Transjordan (c. 1400–500 CE)".
- Lipschits, Oded (2005). The Fall and Rise of Jerusalem. Eisenbrauns. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=78nRWgb-rp8C&printsec=frontcover&dq=Lipschitz,+Oded+fall+and+rise#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Lipschits, Oded, et al., eds. (2006). Judah and the Judeans in the Fourth Century B.C.E.. Eisenbrauns. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=6NsxZRnxE70C&pg=PA75&lpg=PA75&dq=Lipschits+Yehud#v=onepage&q=Lipschits%20Yehud&f=false. Kottsieper, Ingo. "And They Did Not Care to Speak Yehudit". Lipschits, Oded; Vanderhooft, David. "Yehud Stamp Impressions in the Fourth Century B.C.E.".
- Liverani, Mario (2005). Israel's History and the History of Israel, London, Equinox.
- Markoe, Glenn (2000). Phoenicians. University of California Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=smPZ-ou74EwC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Phoenicians++Glenn+Markoe#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Mays, James Luther, et al., eds. (1995). Old Testament Interpretation. T&T Clarke. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=SNLN1nEEys0C&printsec=frontcover&dq=Old+Testament+Interpretation+James+Luther+Mays,+David+L.+Petersen,+Kent+Harold+Richards#v=onepage&q&f=false. Miller, J. Maxwell. "The Middle East and Archaeology".
- McNutt, Paula (1999). Reconstructing the Society of Ancient Israel. Westminster John Knox Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=hd28MdGNyTYC&pg=PA33&lpg=PA33&dq=Reconstructing+the+Society+of+Ancient+Israel++By+Paula+M.+McNutt#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- Merrill, Eugene H. (1995). "The Late Bronze/Early Iron Age Transition and the Emergence of Israel". Bibliotheca Sacra 152 (606): 145–62.
- Middlemas, Jill Anne (2005). The Troubles of Templeless Judah. Oxford University Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=Jrpx-op_-XkC&printsec=frontcover&dq=lester+grabbe+1995&cad=1#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Miller, James Maxwell; Hayes, John Haralson (1986). A History of Ancient Israel and Judah. Westminster John Knox Press. ISBN 066421262X. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=uDijjc_D5P0C&dq=A+history+of+ancient+Israel+and+Judah++By+James+Maxwell+Miller,+John+Haralson+Hayes&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- Miller, Robert D. (2005). Chieftains of the Highland Clans: A History of Israel in the 12th and 11th Centuries B.C.. Eerdmans. http://books.google.com.kh/books?id=Gtm7NtK87poC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Chieftains+of+the+highland+clans#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- Nodet, Étienne (1999) [Editions du Cerf 1997]. A Search for the Origins of Judaism: From Joshua to the Mishnah. Sheffield Academic Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=rE49wYHz5YUC&printsec=frontcover&dq=A+search+for+the+origins+of+Judaism:+from+Joshua+to+the+Mishnah#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Pitkänen, Pekka (2004). "Ethnicity, Assimilation and the Israelite Settlement". Tyndale Bulletin 55 (2): 161–82. http://www.tyndalehouse.com/tynbul/library/TynBull_2004_55_2_01_Pitkanen_EthnicityIsraelSettlement.pdf.
- Silberman, Neil Asher; Small, David B., eds. (1997). The Archaeology of Israel: Constructing the Past, Interpreting the Present. Sheffield Academic Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=qX7r2lAQdFkC&pg=PA238&lpg=PA238&dq=hesse+wapnish#v=onepage&q=hesse%20wapnish&f=false. Hesse, Brian; Wapnish, Paula. "Can Pig Remains Be Used for Ethnic Diagnosis in the Ancient Near East?".
- Smith, Mark S. (2001). Untold Stories: The Bible and Ugaritic Studies in the Twentieth Century. Hendrickson Publishers.
- Smith, Mark S.; Miller, Patrick D. (2002) [Harper & Row 1990]. The Early History of God. Eerdmans. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=1yM3AuBh4AsC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Smith+Early+History+of+God#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Rendsberg, Gary (2008). "Israel without the Bible". In Frederick E. Greenspahn. The Hebrew Bible: new insights and scholarship. NYU Press. http://books.google.com/books?id=Z0wawEnu0UkC&pg=PA43&dq=Hebrew+Bible&cad=3#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Soggin, Michael J. (1998). An Introduction to the History of Israel and Judah. Paideia. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=Dzw_H5GhkfYC&printsec=frontcover&dq=An+introduction+to+the+history+of+Israel+and+Judah++By+J.+Alberto+Soggin#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- Thompson, Thomas L. (1992). Early History of the Israelite People. Brill. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=XqoMRPJca-wC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Early+history+of+the+Israelite+people:+from+the+written+and+archaeological+...++By+Thomas+L.+Thompson#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- Van der Toorn, Karel (1996). Family Religion in Babylonia, Syria, and Israel. Brill. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=VSJWkrXfbLQC&dq=Family+religion+in+Babylonia,+Syria,+and+Israel&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Van der Toorn, Karel; Becking, Bob; Van der Horst, Pieter Willem (1999). Dictionary of Deities and Demons in the Bible (2d ed.). Koninklijke Brill. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=yCkRz5pfxz0C&printsec=frontcover&dq=Dictionary+of+Deities#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Vaughn, Andrew G.; Killebrew, Ann E., eds. (1992). Jerusalem in Bible and Archaeology: The First Temple Period. Sheffield. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=yYS4VEu08h4C&dq=Jerusalem+in+Bible+and+archaeology:+the+First+Temple+period++By+Andrew+G.+Vaughn,+Ann+E.+Killebrew&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q=&f=false. Cahill, Jane M. "Jerusalem at the Time of the United Monarchy". Lehman, Gunnar. "The United Monarchy in the Countryside".
- Wylen, Stephen M. (1996). The Jews in the Time of Jesus: An Introduction. Paulist Press. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=SHgiy-k_wsUC&printsec=frontcover&dq=An+introduction+to+early+Judaism++By+James+C.+VanderKam&cad=1#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Zevit, Ziony (2001). The Religions of Ancient Israel: A Synthesis of Parallactic Approaches. Continuum. http://books.google.com.au/books?id=db4hr55j0yYC&pg=PA1&dq=The+religion+of+ancient+Israel++By+Patrick+D.+Miller&cad=4#v=onepage&q&f=false.
Further reading
- Avery-Peck, Alan, and Neusner, Jacob, (eds), "The Blackwell Companion to Judaism (Blackwell, 2003)
- Boadt, Lawrence, "Reading the Old Testament: An Introduction" (Paulist Press, 1984)
- Brettler, Marc Zvi, "The Creation of History in Ancient Israel" (Routledge, 1995), and also review at Dannyreviews.com
- Cook, Stephen L., "The social roots of biblical Yahwism" (Society of Biblical Literature, 2004)
- Day, John (ed), "In search of pre-exilic Israel: proceedings of the Oxford Old Testament Seminar" (T&T Clark International, 2004)
- Gravett, Sandra L., "An Introduction to the Hebrew Bible: A Thematic Approach" (Westminster John Knox Press, 2008)
- Grisanti, Michael A., and Howard, David M., (eds), "Giving the Sense:Understanding and Using Old Testament Historical Texts" (Kregel Publications, 2003)
- Hess, Richard S., "Israelite religions: an archaeological and biblical survey" Baker, 2007)
- Kavon, Eli, "Did the Maccabees Betray the Hanukka Revolution?" (The Jerusalem Post, 26 December 2005)
- Lemche, Neils Peter, "The Old Testament between theology and history: a critical survey" (Westminster John Knox Press, 2008)
- Levine, Lee I., "Jerusalem: portrait of the city in the second Temple period (538 B.C.E.–70 C.E.)" (Jewish Publication Society, 2002)
- Na'aman, Nadav, "Ancient Israel and its neighbours" (Eisenbrauns, 2005)
- Penchansky, David, "Twilight of the gods: polytheism in the Hebrew Bible" (Westminster John Knox Press, 2005)
- Provan, Iain William, Long, V. Philips, Longman, Tremper, "A Biblical History of Israel" (Westminster John Knox Press, 2003)
- Russell, Stephen C., "Images of Egypt in early biblical literature" (Walter de Gruyter, 2009)
- Sparks, Kenton L., "Ethnicity and identity in ancient Israel" (Eisenbrauns, 1998)
- Stackert, Jeffrey, "Rewriting the Torah: literary revision in Deuteronomy and the holiness code" (Mohr Siebeck, 2007)
- Vanderkam, James, "An introduction to early Judaism" (Eerdmans, 2001)
- Velazquez, Efrain, "The Persian Period and the Origins of 'Israel': Beyond the Myths", (Bible and Interpretation, July 2009)
- Library of latest modern books of biblical studies and biblical criticism
Categories:- Jewish history
- Ancient Levant
- Ancient Israel and Judah
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.