- Lenape
-
Lenape people Total population Estimated 16,000[2] Regions with significant populations  United States (
United States ( Oklahoma)
Oklahoma)11,1951 (2010) [3]  United States (
United States ( Wisconsin)
Wisconsin) Canada (
Canada ( Ontario)
Ontario)Languages Religion Christianity, Native American Church,
traditional tribal religionRelated ethnic groups Other Lenape and Algonquian peoples
The Lenape (
 /ˈlɛnəpiː/ or /ləˈnɑːpi/) are an Algonquian group of Native Americans of the Northeastern Woodlands. They are also called Delaware Indians. As a result of the American Revolutionary War and later Indian removals from eastern United States territories, today the main groups live in Canada, where they are enrolled in the 'Munsee-Delaware Nation 1, Moravian of the Thames First Nation, and the Delaware of Six Nations; and the United States, where they are enrolled in three federally recognized tribes, the Delaware Nation and the Delaware Tribe of Indians, both located in Oklahoma, and the Stockbridge-Munsee Community, located in Wisconsin. Groups of self-identified Lenape also live in places where they are not officially recognized by the subsequent settler nation-state, such as the Lenape Nation of Pennsylvania.
/ˈlɛnəpiː/ or /ləˈnɑːpi/) are an Algonquian group of Native Americans of the Northeastern Woodlands. They are also called Delaware Indians. As a result of the American Revolutionary War and later Indian removals from eastern United States territories, today the main groups live in Canada, where they are enrolled in the 'Munsee-Delaware Nation 1, Moravian of the Thames First Nation, and the Delaware of Six Nations; and the United States, where they are enrolled in three federally recognized tribes, the Delaware Nation and the Delaware Tribe of Indians, both located in Oklahoma, and the Stockbridge-Munsee Community, located in Wisconsin. Groups of self-identified Lenape also live in places where they are not officially recognized by the subsequent settler nation-state, such as the Lenape Nation of Pennsylvania.At the time of European contact in the 16th and 17th centuries, the Lenape lived in the area they called Lenapehoking, roughly the area around and between the Delaware and lower Hudson rivers. This encompassed what are now known as the U.S. state of New Jersey; eastern Pennsylvania around the Delaware and Lehigh valleys; the north shore of Delaware; and much of southeastern New York, particularly the lower Hudson Valley, Upper New York Bay, Staten Island and western Long Island. They spoke two related languages in the Algonquian subfamily, collectively known as the Delaware languages: Unami and Munsee.[4]
Lenape society is organized into clans determined by matrilineal descent. Territory was collective, but divided by clan, with women having rights to property. Other aspects of the matrilineal culture were that a young married couple would live with the woman's family, where her mother and sisters could assist her with her growing family. Hereditary leadership passed through the maternal line, and women elders could remove leaders of whom they disapproved. Children belonged to the mother's clan, where they gained their status and identity. The mother's eldest brother was more significant as a mentor to the boy children than was their father, who was of another clan.
At the time of European contact, the Lenape practiced large-scale agriculture, mostly companion planting; the women cultivated many varieties of the "Three Sisters:" corn, beans and squash. The men also practiced hunting and the harvesting of seafood. They were primarily sedentary, moving to different established campsites by season.
After the arrival of settlers and traders to the 17th-century colony of New Netherland, the Lenape and other native peoples became extensively involved in the North American fur trade. Their trapping depleted the beaver population in the region, proving disastrous for both the Lenape and the Dutch settlers. The Lenape were further weakened by newly introduced infectious diseases, and by conflict with both Europeans and the traditional Lenape enemies, the Iroquoian-speaking Susquehannock. Over the next centuries, they were pushed out of their lands by Iroquoian enemies, treaties and overcrowding by European settlers; the Lenape moved west into the Ohio River valley. In the 1860s, most Lenape remaining in the Eastern United States were sent to the Oklahoma Territory under Indian removal policy. In the 21st century, most Lenape now reside in the U.S. state of Oklahoma, with some communities living also in Kansas, Wisconsin, Ontario, Canada, and in their traditional homelands.
Contents
Name
Leni Lenape means "Human Beings" or the "Real People" in the Unami language.[2] Their (autonym) is also spelled Lennape or Lenapi, meaning "the people." The term "Delaware" was used by the English, who named the people for their territory by the Delaware River. They named the river in honor of Lord De La Warr, the governor of the colony at Jamestown, Virginia.[2] The English colonists used the exonym "Delaware" for almost all the Lenape people living along this river and its tributaries.
Society
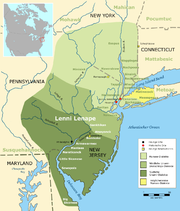 Map depicting Lenapehoking the historic homeland of the Lenape. In the north were the Munsee, the center the Unami and in the south the Unalichtigo a subdivision of the Unami[5][unreliable source?]
Map depicting Lenapehoking the historic homeland of the Lenape. In the north were the Munsee, the center the Unami and in the south the Unalichtigo a subdivision of the Unami[5][unreliable source?]
Early Indian "tribes" are perhaps better understood as language groups, rather than as "nations". At the time of first European contact, a Lenape individual would likely have identified primarily with his or her immediate family and friends, the clan, and/or village unit; then with surrounding and familiar village units; next with more distant neighbors who spoke the same dialect; and ultimately, while often fitfully, with all those in the surrounding area who spoke mutually comprehensible languages, including the Mahican. Among other Algonquian peoples, the Lenape were considered the "grandfathers" from whom all the other Algonquian peoples originated. Consequently, in inter-tribal councils, the Lenape were given respect as one would to elders.
Those of a different language stock – such as the Iroquois (or, in the Lenape language, the Minqua) – were regarded as foreigners. As in the case of the Iroquois, the animosity of difference and competition spanned many generations, and tribes became traditional enemies. Ethnicity seems to have mattered little to the Lenape and many other "tribes". Archaeological excavations have found Munsee-speaking Lenape burials that included identifiably ethnic Iroquois remains interred along with those of Lenape. The two groups were bitter enemies since before recorded history but intermarriage occurred. In addition, both tribes practiced adopting young captives from warfare into their tribes and assimilating them as full tribal members.
Overlaying these relationships was a phratry system, a division into clans. Clan membership was matrilineal; children inherited membership in a clan from their mother. On reaching adulthood, a Lenape traditionally married outside the clan, a practice known by ethnographers as, "exogamy". The practice effectively prevented inbreeding, even among individuals whose kinship was obscure or unknown.
Early Europeans who first wrote about Indians found matrilineal social organization to be unfamiliar and perplexing. Because of this, Europeans often tried to interpret Lenape society through more familiar European arrangements. As a result, the early records are full of clues about early Lenape society, but were usually written by observers who did not fully understand what they were seeing. For example, a man's maternal uncle (his mother's brother), and not his father, was usually considered to be his closest male ancestor, since his father belonged to a different clan. The maternal uncle played a more prominent role in the lives of his sister's children than did the father. Early European chroniclers did not understand this concept.
Land was assigned to a particular clan for hunting, fishing, and cultivation. Individual private ownership of land was unknown, as the land belonged to the clan collectively while they inhabited it, but women often had rights to traditional areas for cultivation.[6] Clans lived in fixed settlements, using the surrounding areas for communal hunting and planting until the land was exhausted. In a common practice known as "agricultural shifting", the group then moved to found a new settlement within their territory.
The Lenape practiced large-scale agriculture to augment a mobile hunter-gatherer society in the region around the Delaware River, the lower Hudson River, and western Long Island Sound. The Lenape were largely a sedentary people who occupied campsites seasonally, which gave them relatively easy access to the small game that inhabited the region: fish, birds, shellfish and deer. They developed sophisticated techniques of hunting and managing their resources.
By the time of the arrival of Europeans, the Lenape were cultivating fields of vegetation through the slash and burn technique. This extended the productive life of planted fields.[7][8][9][10][11][12] They also harvested vast quantities of fish and shellfish from the bays of the area,[13] and, in southern New Jersey, harvested clams year-round.[14] The success of these methods allowed the tribe to maintain a larger population than nomadic hunter-gatherers could support. Scholars have estimated that at the time of European settlement, there may have been about 15,000 Lenape total in approximately 80 settlement sites around much of the New York City area, alone.[15] In 1524 Lenape in canoes met Giovanni da Verrazzano, the first European explorer to enter New York Harbor.
The early European settlers, especially the Dutch and Swedes, were surprised at the Lenape's skill in fashioning beautiful articles of clothing from natural materials.[citation needed] In hot weather both men and women wore only loin cloth and skirt respectively, while they used beaver pelts or bear skins to serve as winter mantles. Additionally, both sexes might wear buckskin leggings and moccasins in cold weather.[16] Deer hair, dyed a deep scarlet, was a favorite component of headdresses and breast ornaments for males.[17] The Lenape also adorned themselves with various ornaments made of stone, shell, animal teeth, and claws. The women often wore headbands of dyed deer hair or wampum. They painted their skin skirts or decorated them with porcupine quills. These skirts were so elaborately appointed that, when seen from a distance, they reminded Dutch settlers of fine European lace.[18]The winter cloaks of the women were striking, fashioned entirely from the iridescent body feathers of wild turkeys.[19]
History
European contact
The first recorded contact with Europeans and people presumed to have been the Lenape was in 1524. The explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano was greeted by local Lenape who came by canoe, after his ship entered what is now called Lower New York Bay. The Lenape occupied coastal areas throughout the mid-Atlantic and New York.
The early interaction between the Lenape and Dutch traders in the 17th century was primarily through the fur trade, specifically, the Lenape trapped and traded beaver pelts for European-made goods. According to Dutch settler Isaac de Rasieres, who observed the Lenape in 1628, the Lenape's primary crop was maize, which they planted in March. They quickly adopted European metal tools for this task.
In May, the Lenape planted kidney beans near the maize plants; the latter served as props for the climbing bean vines. They also planted squash, whose broad leaves cut down on weeds and conserved moisture in the soil. The women devoted their summers to field work and harvested the crops in August. Women cultivated varieties of maize, squash and beans, and did most of the field work, processing and cooking of food.
The men limited their agricultural labor to clearing the field and breaking the soil. They primarily hunted and fished during the rest of the year. Dutch settler David de Vries, who stayed in the area from 1634 to 1644, described a Lenape hunt in the valley of the Achinigeu-hach (or "Ackingsah-sack," the Hackensack River), in which one hundred or more men stood in a line many paces from each other, beating thigh bones on their palms to drive animals to the river, where they could be killed easily. Other methods of hunting included lassoing and drowning deer, as well as forming a circle around prey and setting the brush on fire.
17th century
New Amsterdam was founded by the Dutch in what would later become New York City in 1624. Dutch settlers founded a colony at present-day Lewes, Delaware on June 3, 1631 and named it Zwaanendael (Swan Valley).[20] The colony had a short life, as in 1632 a local band of Lenape killed the 32 Dutch settlers after a misunderstanding escalated over Lenape defacement of the insignia of the Dutch West India Company.[21] In 1634, the Iroquoian-speaking Susquehannock went to war with the Lenape over access to trade with the Dutch at New Amsterdam. They defeated the Lenape, and some scholars believe that the Lenape may have become tributaries to the Susquehannock.[22] After the warfare, the Lenape referred to the Susquehannock as "uncles." The Lenape were added to the Covenant Chain by the Iroquois in 1676, remaining tributary to the Five (later Six) Nations until 1753.
The Lenape's quick adoption of trade goods, and their need to trap furs to meet high European demand, resulted in their disastrous over-harvesting of the beaver population in the lower Hudson Valley. With the fur sources exhausted, the Dutch shifted their operations to present-day upstate New York. The Lenape who produced wampum in the vicinity of Manhattan Island temporarily forestalled the negative effects of this decline in trade.[23] Lenape population fell sharply during this period, due to high fatalities from epidemics of infectious diseases carried by Europeans, such as measles and smallpox, to which they had no natural immunity.
The Lenape had a culture in which the clan and family controlled property. Europeans often tried to contract for land with the tribal chiefs, confusing their culture with that of neighboring tribes such as the Iroquois. The Lenape would petition for grievances on the basis that not all their families had been recognized in the transaction (not that they wanted to "share" the land).[24] After the Dutch arrival in the 1620s, the Lenape were successful in restricting Dutch settlement until the 1660s to Pavonia in present-day Jersey City along the Hudson. The Dutch finally established a garrison at Bergen, which allowed settlement west of the Hudson within the province of New Netherland. This land was purchased from the Lenape after the fact.[24]
In the early 1680s, William Penn and Quaker colonists created the English colony of Pennsylvania beginning at the lower Delaware River. In the decades immediately following, some 20,000 new colonists arrived in the region, putting pressure on Lenape settlements and hunting grounds. Although Penn endeavored to live peaceably with the Lenape and to create a colony that would do the same, he also expected his authority and that of the colonial government to take precedence. His new colony effectively displaced the Lenape and forced others to adapt to new cultural demands. Penn gained a reputation for benevolence and tolerance, but his efforts resulted in more effective colonization of the ancestral Lenape homeland than previous ones.[25]
18th century
William Penn died in 1718. His heirs, John Penn and Thomas Penn, and their agents were running the colony, and had abandoned many of the elder Penn's practices. In 1737, the colonial administrators claimed that they had a deed dating to the 1680s in which the Lenape-Delaware had promised to sell a portion of land beginning between the junction of the Delaware River and Lehigh River and extending "as far west as a man could walk in a day and a half."[citation needed] They contrived to have runners travel west, and thus claim huge swaths of land in the eastern portion of the state. Although reluctant to agree to the dubious claim, after years of fighting protest, the Lenape acquiesced to the Walking Purchase.[citation needed]
Beginning in the 18th century, the Moravian Church established missions among the Lenape.[26] The Moravians required the Christian converts to share their pacifism, as well as to live in a structured and European-style mission village.[27] Moravian pacifism and unwillingness to take loyalty oaths caused conflicts with British authorities, who were seeking aid against the French and their Native American allies during the French and Indian War (Seven Years War). The Moravians' insistence on Christian Lenapes' abandoning traditional warfare practices also alienated mission populations from other Lenape and Native American groups. The Moravians accompanied Lenape relocations to Ohio and Canada, continuing their missionary work. The Moravian Lenape who settled permanently in Ontario after the American Revolutionary War were sometimes referred to as "Christian Munsee", as they mostly spoke the Munsee branch of the Delaware language.
The Treaty of Easton, signed in 1758 between the Lenape and the Anglo-American colonists, required the Lenape to move westward, out of present-day New York and New Jersey and into Pennsylvania, then Ohio and beyond. Sporadically they continued to raid European-American settlers from far outside the area.
During the French and Indian War, the Lenape initially sided with the French. But, such leaders as Teedyuscung in the east and Tamaqua in the vicinity of modern Pittsburgh shifted to building alliances with the English. After the end of the war, however, Anglo-American settlers continued to kill Lenape, often to such an extent that the historian Amy Schutt writes the dead since the wars outnumbered those killed during the war.[28]
In 1763 Bill Hickman, Lenape, warned English colonists in the Juniata River region of an impending attack. Many Lenape joined in Pontiac's War, and were numerous among those Native Americans who besieged Pittsburgh.[29] In April 1763 Teedyuscung was killed when his home was burned. His son Captain Bull responded by attacking settlers from New England who had migrated to the Wyoming Valley of Pennsylvania. The settlers had been sponsored by the Susquehanna Company.[30]
The Lenape were the first Indian tribe to enter into a treaty with the new United States government, with the Treaty of Fort Pitt signed in 1778 during the American Revolutionary War. By then living mostly in the Ohio Country, the Lenape supplied the Continental Army with warriors and scouts in exchange for food supplies and security.
Ohio: 1750s to 1812 (American Revolution and War of 1812)
Further information: Lenape settlementsAfter the signing of the Treaty of Easton in 1758, the Lenape were forced to move west out of their native lands into what is today known as Ohio.[31]
During the American Revolution, the Munsee-speaking Lenape (then called Delaware) bands of the Ohio Country were deeply divided over which side, if any, to take in the conflict. Years earlier, many Lenape had migrated west to Ohio from their territory on the mid-Atlantic coast to try to escape colonial encroachment, as well as pressure from Iroquois tribes from the north. They resettled, with bands in numerous villages around their main village of Coshocton.[32] By the time of the Revolutionary War, the Lenape found their villages lay between the western frontier strongholds of the war's opponents: the American colonists' military outpost at Fort Pitt (present-day Pittsburgh) and the British with Indian allies around Fort Detroit (in present-day Michigan).
Some Lenape decided to take up arms against the American colonials and moved to the west, closer to Detroit, where they settled on the Scioto and Sandusky rivers. Those Lenape sympathetic to the United States remained at Coshocton, and leaders signed the Treaty of Fort Pitt (1778) with the Americans. Through this, the Lenape hoped to establish the Ohio Country as a state inhabited exclusively by Native Americans, as part of the new United States. A third group of Lenape, many of them converted Christian Munsees, lived in several mission villages run by Moravians. (They spoke the Munsee branch of Delaware, an Algonquian language.)
White Eyes, the Lenape chief who had negotiated the treaty, died in 1778. Many Lenape at Coshocton eventually joined the war against the Americans. In response, Colonel Daniel Brodhead led an expedition out of Fort Pitt and on 19 April 1781 destroyed Coshocton. Surviving residents fled to the north. Colonel Brodhead convinced the militia to leave the Lenape at the Moravian mission villages unmolested, since they were unarmed non-combatants.
Brodhead's having to restrain the militia from attacking the Moravian villages was a reflection of the brutal nature of frontier warfare. Violence had escalated on both sides. Relations between regular Continental Army officers from the East (such as Brodhead) and western militia were frequently strained. The tensions were worsened by the American government's policy of recruiting some Indian tribes as allies in the war. Western militiamen, many of whom had lost friends and family in Indian raids against settlers' encroachment, blamed all Indians for the acts of some.
During the early 1770s, missionaries, including David Zeisberger and John Heckewelder, arrived in the Ohio Country near the Delaware villages. The Moravian Church sent these men to convert the natives to Christianity. The missionaries established several missions, including Gnadenhutten, Lichtenau, and Schoenbrunn. The missionaries asked that the natives forsake all of their traditional customs and ways of life. Many Delaware did adopt Christianity, but others refused to do so. The Delaware became a divided people during the 1770s, including in Killbuck's family. Killbuck resented his grandfather for allowing the Moravians to remain in the Ohio Country. The Moravians believed in pacifism, and Killbuck believed that every convert to the Moravians deprived the Delaware of a warrior to stop further white settlement of their land.
During the French and Indian War, Killbuck assisted the English against their French enemy. In 1761, Killbuck led an English supply train from Fort Pitt to Fort Sandusky. The British paid him one dollar per day. Later Killbuck became a leader in a very dangerous time for the Delaware. The American Revolution had just begun, and Killbuck found his people caught between the English in the West and the Americans in the East. At the war's beginning, Killbuck and many Delaware claimed to be neutral. In 1778, Killbuck permitted American soldiers to traverse Delaware territory so that the soldiers could attack Fort Detroit. In return, Killbuck requested that the Americans build a fort near the natives' major village of Coshocton to provide the Delaware with protection from English attacks. The Americans agreed and built Fort Laurens, which they garrisoned.
Other Indian groups, especially the Wyandot, the Mingo, the Munsee, the Shawnee, and the Wolf Clan of the Delaware, favored the British. They believed that by their proclamation of 1763, restricting Anglo-American settlement to east of the Appalachian Mountains, that the British would help them preserve a Native American territory. The British planned to attack Fort Laurens in early 1779 and demanded that the neutral Delawares formally side with the British. Killbuck warned the Americans of the planned attack. His actions helped save the fort, but the Americans abandoned it in August 1779. The Delaware had lost their protectors and, in theory, faced attacks from the British, their native allies, and the American settlers who flooded into the area in the late 1770s and early 1780s after the war. Most Delaware formally joined the British after the American withdrawal from Fort Laurens.
Facing pressure from the British, the Americans, and even his fellow natives, Killbuck hoped a policy of neutrality would save his people from destruction. It did not.
19th century
The amateur anthropologist Silas Wood published a book claiming that there were several American Indian tribes that were distinct to Long Island, New York. He collectively called them the Metoac. Modern scientific scholarship has shown that two linguistic groups represented two Algonquian cultural identities on the island, not "13 individual tribes" as asserted by Wood. The bands to the west were Lenape. Those to the east were more related culturally to the Algonquian tribes of New England across Long Island Sound, such as the Pequot.[33][34] Wood (and earlier settlers) often misinterpreted the Indian use of place names for identity as indicating their names for "tribes."
Over a period of 176 years, European settlers progressively crowded the Lenape out of the East Coast and Ohio, and pressed them to move further west. Most members of the Munsee-language branch of the Lenape left the United States after the British were defeated in the American Revolutionary War, and their descendants live on three Indian reserves in Western Ontario, Canada. They are descendants of those Lenape of Ohio Country who sided with the British during the Revolutionary War. The largest reserve is at Moraviantown, Ontario, where the Turtle Clan settled in 1792 following the war.
Indiana to Missouri
By the Treaty of St. Mary’s, signed October 3, 1818 in St. Mary's Ohio, the Delaware ceded their lands in Indiana for lands west of the Mississippi and an annuity of $4,000. Over the next few years, the Delaware settled on the James River near its confluence with Wilson Creek, occupying eventually about 40,000 acres (160 km2) of the approximately 2,000,000 acres (8,100 km2) allotted to them.[35] Anderson, Indiana is named after Chief William Anderson, whose father was Swedish. The Delaware Village in Indiana was called Anderson's Town while the Delaware Village in Missouri on the James River was often called Anderson’s Village. The tribes' cabins and cornfields were spread out along the James River and Wilson Creek.[36]
Role in western history
Many Delaware participated in exploration of the western United States, working as trappers with the mountain men, and as guides and hunters for wagon trains. They served as army guides and scouts in events such as the Second Seminole War, Frémont's expeditions, and the conquest of California during the Mexican-American War.[37][38][39] Occasionally, they played surprising roles as Indian allies.[40]
Sagundai accompanied one of Frémont's expeditions as one of his Delaware guides. From California, Fremont needed to communicate with Senator Benton. Sagundai volunteered to carry the message, through some 2,200 kilometres of hostile territory. He took many scalps in this adventure, including that of a Comanche with a particularly fine horse, who had outrun both Sagundai and the other Comanches. Sagundai was thrown when his horse stepped into a prairie-dog hole, avoided the Comanche's lance, shot him dead, and caught his horse by the trailing lariat to make good his own escape. Upon his arrival among his own people, the Delaware held the last war and scalp dances in their history. These were held "where Edwin Taylor now (in 1918) lives, on the hill", at Edwardsville, Kansas.[41]
Kansas reservation
By the terms of the "Treaty of the James Fork" made September 24, 1829 and ratified by the US Senate in 1830, the Delaware were granted lands west of the Missouri River in Indian Territory in exchange for lands on the James Fork on the White River in Missouri. These lands, in what is now Kansas, were west of the Missouri and north of the Kansas River. The main reserve consisted of about 1,000,000 acres (4,000 km2) with an additional "outlet" strip 10 miles (16 km) wide extending to the west.[42][43][44] About 1,000 Delaware lived on the Delaware Reservation in Kansas, many in log cabins, but some in substantial farm houses with outbuildings.[45] The center of activity was in what is now Muncie, Kansas, a neighborhood of Kansas City, Kansas north of Delaware Crossing on the Kansas River. The Delaware Indian agency, the blacksmith, and the Baptist and Methodist missions were located there.
White encroachment
In 1854 Congress passed the Kansas-Nebraska Act, which created the Territory of Kansas and opened the area for white settlement. It also authorized negotiation with Indian tribes regarding removal. The Delaware were reluctant to negotiate for another relocation, but they feared serious trouble with white settlers, which developed.
As the Delaware were not considered citizens, they had no access to the courts, and no way to enforce their property rights. That was, theoretically, done by the United States Army after the Indian Agent had followed onerous procedures requiring both posting a public notice warning trespassers and serving written notice on them. Major B.F. Robinson, the Indian Agent appointed in 1855, did his best, but could not control the hundreds of white trespassers who stole stock, cut timber, and built houses and squatted on Delaware lands. By 1860 the Delaware had reached consensus to leave Kansas, which was in accord with the government's Indian removal policy.[46]
Oklahoma
The main body of Lenape arrived in the northeast region of Oklahoma in the 1860s.[citation needed] Along the way many smaller groups left, or were told to stay where they were.[citation needed] As a result of the multiple removals, each leavign some Delaware who chose to stay in place, today, from New Jersey to Wisconsin to southwest Oklahoma, there are groups who retain a sense of connection with ancestors who lived in the Delaware Valley in the 17th century and with cousins in the Lenape diaspora.
The two largest groups are the Delaware Nation (Anadarko, Oklahoma), and the Delaware Tribe of Indians (Bartlesville, Oklahoma), the only two federally recognized Lenape (Delaware) tribes in the United States.[47] The Oklahoma branches were established in 1867. The Delaware were required to purchase land from the reservation of the Cherokee Nation; they made two payments totaling $438,000. A court dispute followed over whether the sale included rights for the Delaware as citizens within the Cherokee Nation.
While the dispute was unsettled, the Curtis Act of 1898 dissolved tribal governments and ordered the allotment of tribal lands to individual members of tribes. After the lands were allotted in 160 acre (650,000 m²) lots to tribal members in 1907, the government sold "surplus" land to non-Indians. The relatively arid land was not suitable for subsistence farming on such small plots.[citation needed]
20th century
In 1979, the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs revoked the tribal status of the Delaware living among Cherokee in Oklahoma. They began to count the Delaware as Cherokee. The Delaware had this decision overturned in 1996, when they were recognized by the federal government as a separate tribal nation.[citation needed]
21st century
The Cherokee Nation filed suit to overturn the independent federal recognition of the Delaware. The tribe lost federal recognition in a 2004 court ruling in favor of the Cherokee Nation, but regained it on 28 July 2009.[48] After recognition, the tribe reorganized under the Oklahoma Indian Welfare Act. Members approved a constitution and bylaws in a May 26, 2009 vote. Jerry Douglas was elected as tribal chief.[47]
In 2004 the Delaware of Oklahoma sued the state of Pennsylvania over land lost in 1800. This was related to the Walking Purchase of 1737, an agreement of doubtful legal standing.[49][50]
Today
Lenape communities today include the following:
Oklahoma:
- Delaware Tribe of Indians (Bartlesville, Oklahoma), US federally recognized.
- Delaware Nation (Anadarko, Oklahoma), US federally recognized.
Ontario, Canada:
- Munsee-Delaware Nation 1, Ontario, Canadian reserve.
- Moravian of the Thames First Nation, Canadian reserve.
- Delaware of Six Nations (at Six Nations of the Grand River), two Canadian reserves.
Wisconsin:
- Stockbridge-Munsee Community, US federally recognized.
Four or five claiming to be of Lenape descent are trying to achieve federal recognition as organized tribes. They are the Munsee-Delaware/Lenape bands of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Missouri, Ohio and New York state. In addition, a Lenape group in Pennslyvania is pursuing a land claim against the state government.[citation needed]
Lenape or Delaware live in communities known as Urban Indians in their historic homeland in a number of states such as Delaware, Maryland, New Jersey and Virginia. They also live in the New England States; within the city of Tulsa, Oklahoma. New York City and Philadelphia are known to have some Lenape residents; and others live in diaspora across the country.
Literature
The Delaware feature prominently in The Last of the Mohicans and the other Leatherstocking Tales of James Fenimore Cooper. The Delaware are the subject of a legend which inspired the Boy Scouts of America honor society known as the Order of the Arrow.
The Walam Olum, which purported to be an account of the Delaware's migration to the lands around the Delaware River, emerged through the works of Constantine Samuel Rafinesque in the nineteenth century. For many decades, scholars believed it was genuine. In the 1980s and 1990s, newer textual analysis suggested it was a hoax. Some Delaware, upon hearing of it for the first time, found the account to be plausible.
In Cormac McCarthy's Blood Meridian, the group of American scalphunters are aided by an unspecified number of Delaware, who serve as scouts and guides through the western deserts. In The Light in the Forest, True Son is adopted by a band of Lenape.
In Mark Raymond Harrington's 1938 novel, The Indians of New Jersey: Dickon among the Lenapes, a group of Lenape find a shipwrecked English boy. His gradual integration into the tribe provides a study of Lenape life, society, weaponry, and beliefs. The book includes a glossary for Lenape terms. Trouble's Daughter: The Story of Susanna Hutchinson, Indian Captive is a young adult novel of a fictional kidnapping by the Lenape Turtle Clan of a daughter of Anne Hutchinson, the religious reformer and founder of the Rhode Island colony. Moon of Two Dark Horses is a novel of the friendship between a white settler and a Lenape boy at the time of the Revolutionary War. Standing in the Light: The Captive Diary of Catharine Carey Logan, part of the Dear America series of fictional diaries, is a novel by Mary Pope Osborne. It tells the story of the capture of a teenage girl and her brother by a band of Lenape, and the youths' assimilation into Lenape culture.
Peter Lindestrom's Geographia America with an Account of the Delaware Indians is one of the few sympathetic contemporary accounts of Lenape life in the lower Delaware River valley during the 17th century.
Moravian missionary John Heckewelder published a sympathetic account of the Lenape in exile in the Ohio Valley. His account, published in 1818, provides some alternate Lenape tribal history disputing the tributary relationship with the Susquehannock. "Scouts of '76: a tale of the revolutionary war", a 1924 book by Charles E. Willis, contains an account of the contributions of the Lenni Lenape to the American Revolution when they lived in the area of Lake Wawayanda.
Notable Lenape people
- Dan Barker, founder of the Freedom From Religion Foundation
- Black Beaver (1806-1880), Trapper, trader and scout; first inductee into the American Indian Hall of Fame.
- Buckongahelas, Wolf clan war leader
- Charles Journeycake, Chief of the Wolf Clan from 1855 and principal chief from 1861. Visited Washington, D.C. 24 times on his tribe's behalf.[51]
- Killbuck (Gelelemend), Turtle clan leader[52]
- Captain Jacobs, War Chief
- Oratam, sachem of the Hackensack
- Neolin, the Delaware Prophet
- Captain Pipe (Hopocan), (ca. 1725—ca. 1818), 18th Century chief and member of the Wolf Clan.
- Shingas, Turkey clan war leader
- Tamanend, leader who, according to tradition, negotiated treaty with William Penn, and who Tammany Hall was named for
- Tamaqua (King Bear), Turkey clan civil leader
- Teedyuscung, "King" of the eastern Delawares
- White Eyes, Turtle clan civil leader
- Chief Newcomer, founder the village of Gekelmukpechunk (Newcomerstown), Ohio in the 1760s
- White Eyes (d. 1778), chief who negotiated the Treaty of Fort Pitt
See also
- Lenape settlements
- Burial Ridge
- Ramapough Mountain Indians
- Walking Purchase
- Unalachtigo Lenape
- Museum of Indian Culture
- Hell Town, Ohio (Lenape settlement in Ohio)
- Economy of the Iroquois
Notes
- ^ "Art on the Prairies: Delaware", All About the Shoes, (retrieved 19 July 2011)
- ^ a b c d Pritzker 422
- ^ "Pocket Pictorial." Oklahoma Indian Affairs Commission. 2010: 13. (retrieved 10 June 2010)
- ^ Paul Otto, 179 "Intercultural Relations Between Native Americans and Europeans in New Netherland and New York" in Four Centuries of Dutch-American Relations,SUNY Press, 2009
- ^ Fariello, Leonardo A. "A Place Called Whippany." Whippanong Library. 2000 (retrieved 19 July 2011)
- ^ see New Amsterdam for discussion of the Dutch "purchase" of Manhattan
- ^ Stevenson W. Fletcher, Pennsylvania Agriculture and Country Life 1640-1840 (Harrisburg: Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission, 1950), 2, 35-37, 63-65, 124.
- ^ Day, Gordon M. “The Indian as an Ecological Factor in the Northeastern Forests.” Ecology, Vol. 34, #2 (April): 329-346. New England and New York areas 1580-1800. Notes that the Lenni Lenape (Delaware) tribe in New Jersey and the Massachuset tribe in Massachusetts used fire in ecosystems.1953
- ^ Russell, Emily W.B. Vegetational Change in Northern New Jersey Since 1500 A.D.: A Palynological, Vegetational and Historical Synthesis Ph.D. dissertation. New Brunswick, PA: Rutgers University. Author notes on page 8 that Indians often augmented lightning fires. 1979
- ^ Russell, Emily W.B. "Indian Set Fires in the Forests of the Northeastern United States." Ecology, Vol. 64, #1 (Feb): 78 88. 1983a Author found no strong evidence that Indians purposely burned large areas, but they did burn small areas near their habitation sites. Noted that the Lenna Lenape Tribe used fire.
- ^ A Brief Description of New York, Formerly Called New Netherlands with the Places Thereunto Adjoining, Likewise a Brief Relation of the Customs of the Indians There, New York, NY: William Gowans. 1670. Reprinted in 1937 by the Facsimile Text Society, Columbia University Press, New York. Notes that the Lenni Lenape (Delaware) tribe in New Jersey used fire in ecosystems.
- ^ Smithsonian Institution - Handbook of North American Indians series: Handbook of North American Indians, Volume 15 - Northeast. Bruce G. Trigger (volume editor). Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution. 1978 References to Indian burning for the Eastern Algonquians, Virginia Algonquians, Northern Iroquois, Huron, Mahican, and Delaware Tribes and peoples.
- ^ Mark Kurlansky, 2006.
- ^ D. Dreibelbis, 1978.
- ^ Edwin G. Burrows and Mike Wallace, 1999.
- ^ Weslager, C. A.., The Delaware Indians: A History, Rutgers University Press, 2000, p. 54.
- ^ Kraft, Herbert C., The Lenape-Delaware Indian Heritage: 10,000 BC to AD 2000, Lenape Books, 2001, pp. 237-240.
- ^ Ibid., p. 239.
- ^ Weslager, p. 54.
- ^ Munroe, John A.: Colonial Delaware: A History: Millwood, New York: KTO Press; 1978; pp. 9-12
- ^ Cook, Albert Myers. Narratives of Early Pennsylvania, West New Jersey and Delaware 1630-1707. Charles Scribner's Sons, 1912, p. 9
- ^ Jennings (2000), p. 117
- ^ Otto, Paul, 91 The Dutch-Munsee Encounter in America: The Struggle for Sovereignty in the Hudson Valley. New York: Berghahn Press, 2006.
- ^ a b William Christie MacLeod. "The Family Hunting Territory and Lenape Political Organization," American Anthropologist 24.
- ^ Spady (2004), pp. 18-40
- ^ Gray, Elma. Wilderness Christians: Moravian Missions to the Delaware Indians. Ithaca. 1956
- ^ Olmstead, Earl P. Blackcoats among the Delaware: David Zeisberger on the Ohio frontier. Kent, Ohio. 1991
- ^ Amy C. Schutt. Peoples of the Rivers. p. 118
- ^ Schutt. People of the River, p. 118
- ^ Schutt. People of the River, p. 119
- ^ Keenan, Encyclopedia of American Indian Wars, 1492-1890, 1999, p. 234; Moore, The Northwest Under Three Flags, 1635-1796, 1900, p. 151.
- ^
 William Dean Howells, “Gnadenhütten,” Three Villages, Boston: James R. Osgood and Co., 1884., accessed 19 Mar 2010
William Dean Howells, “Gnadenhütten,” Three Villages, Boston: James R. Osgood and Co., 1884., accessed 19 Mar 2010 - ^ Strong, John A. Algonquian Peoples of Long Island Heart of the Lakes Publishing (March 1997). ISBN 978-1-55787-148-0
- ^ Bragdon, Kathleen. The Columbia Guide to American Indians of the Northeast,Columbia University Press (2002). ISBN 978-0-231-11452-3.
- ^ "Removal Era", accessed September 8, 2010
- ^ "Delaware Town", Missouri State University, accessed September 8, 2010
- ^ Weslager, The Delaware Indians, pp. 375, 378-380
- ^ Sides, Hampton, Blood and Thunder: An Epic of the American West, Doubleday (2006), pp. 77-80, 94, 101, hardcover, 462 pages, ISBN 978-0-385-50777-6
- ^ Page lv of the introduction by Frank McNitt, Simpson, James H, edited and annotated by Frank McNitt, forward by Durwood Ball, Navaho Expedition: Journal of a Military Reconnaissance from Santa Fe, New Mexico, to the Navaho Country, Made in 1849, University of Oklahoma Press (1964), trade paperback (2003), 296 pages, ISBN 0.8061-3570-0
- ^ Sides, Blood and Thunder, p. 181
- ^ http://skyways.lib.ks.us/genweb/archives/1918ks/v1/ch10p8.html William E. Connelley, A Standard History of Kansas and Kansans, transcribed by Carolyn Ward, Kansas State Library, Genweb, 1998, accessed 12 March 2011.
- ^ "BIBLIOGRAPHY DELAWARE INDIANS IN KANSAS 1829-1867. Kansas State Historical Society,Accessed September 2, 2010
- ^ 9 Indian Claims Commission 346
- ^ 12 Indian Claims Commission 404
- ^ Weslager, The Delaware Indians, pp. 373-374,
- ^ Pages 401 to 409. Weslager, The Delaware Indians
- ^ a b "Delaware Tribe regains federal recognition" NewsOk. 4 Aug 2009 (retrieved 5 August 2009)
- ^ "Delaware Tribe of Indians’ federal recognition restored", Indian Country Today. 7 Aug 2009 (retrieved 11 August 2009)
- ^ http://www.law.com/jsp/article.jsp?id=1074259221938 Law.com, subscription required for access
- ^ "Walking Purchase", Delaware Tribe of Indians
- ^ S. H. Mitchell (1895)
- ^ Killbuck, Ohio History Central. July 1, 2005
References
- Burrows, Edward G. and Wallace, Mike, Gotham: A History of New York City to 1989 Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1999. ISBN 0-19-514049-4.
- Dreibelbis, Dana E., "The Use of Microstructural Growth Patterns of Mercenaria Mercenaria to Determine the Prehistoric Seasons of Harvest at Tuckerton Midden, Tuckerton, New Jersey," thesis, Princeton University, 1978.
- Jennings, Francis, The Ambiguous Iroquois Empire, 2000. ISBN 0-393-01719-2
- Kurlansky, Mark. The Big Oyster: History on the Half Shell. Random House Trade Paperbacks, 2007. ISBN 978-0-345-47639-5
- Mitchell, S. H. Internet Archive The Indian Chief, Journeycake. Philadelphia: American Baptist Publication Society, 1895.
- Pritzker, Barry M. A Native American Encyclopedia: History, Culture, and Peoples. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000. ISBN 978-0195138771.
- Spady, James. "Colonialism and the Discursive Antecedents of Penn's Treaty with the Indians". Daniel K. Richter and William A. Pencak, eds. Friends and Enemies in Penn's Woods: Indians, Colonists, and the Racial Construction of Pennsylvania. University Park, PA: PSU Press, 2004: 18-40.
- Weslager, C.A. The Delaware Indians: A History. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 1972. ISBN 0-8135-0702-2.
Further reading
- Adams, Richard Calmit, The Delaware Indians, a brief history, Hope Farm Press (Saugerties, NY 1995) [originally published by Government Printing Office, (Washington, DC 1909)]
- Bierhorst, John. The White Deer and Other Stories Told by the Lenape. New York: W. Morrow, 1995. ISBN 0-688-12900-5
- Brown, James W. and Rita T. Kohn, eds. Long Journey Home ISBN 978-0-253-34968-2. Indiana University Press (2007).
- Grumet, Robert Steven (2009). The Munsee Indians: a history. Civilization of the American Indian. 262. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 9780806140629. OCLC 317361732.
- Kraft, Herbert C., The Lenape: archaeology, history and ethnography, New Jersey Historical Society, (Newark, NJ 1986)
- Kraft, Herbert C. The Lenape-Delaware Indian Heritage: 10,000 B.C. to A.D. 2000. Stanhope, NJ: Lenape Books, 2001.
- O'Meara, John, Delaware-English / English-Delaware dictionary, University of Toronto Press (Toronto, 1996) ISBN 0-8020-0670-1.
- Otto, Paul, The Dutch-Munsee Encounter in America: The Struggle for Sovereignty in the Hudson Valley (New York: Berghahn Books, 2006). ISBN 1-57181-672-0
- Pritchard, Evan T., Native New Yorkers: The Legacy of the Algonquin People of New York. Council Oak Books: San Francisco, 2002, 2007. ISBN 1-57178-107-2.
- Richter, Conrad, The Light In The Forest, (New York, NY 1953).
External links
- Delaware Nation (Anadarko, Oklahoma)
- Delaware Tribe of Indians (Bartlesville, OK)
- Lenape/English dictionary
- Lenni Lenape Historical Society
- Lenape (Southern Unami) Talking Dictionary
Categories:- Lenape people
- Native American tribes in Oklahoma
- Native American tribes in New Jersey
- Native American tribes in Pennsylvania
- Native American tribes in New York
- Native American tribes in Delaware
- Native American tribes in Ohio
- First Nations in Ontario
- Native American history of New York
- Native American history of Pennsylvania
- Native American history of Ohio
- Native American history of New Jersey
- Native American history of Delaware
- First Nations history
- Algonquian ethnonyms
- People of New Netherland
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.