- Outline of Guam
-
 The location of Guam
The location of Guam
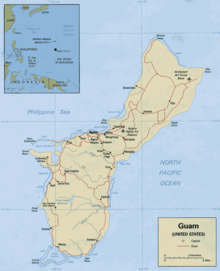 An enlargeable map of the United States Territory of Guam
An enlargeable map of the United States Territory of Guam See also: Index of Guam-related articles
See also: Index of Guam-related articlesThe United States Territory of Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States of America that comprises the Island of Guam in the western North Pacific Ocean.[1] It is one of five U.S. territories with an established civilian government.[2] The island's capital is Hagåtña (formerly Agana). Guam is the largest and southernmost of the Mariana Islands.
The Chamorros, Guam's indigenous inhabitants, first populated the island approximately 4,000 years ago.[citation needed] The island has a long history of European colonialism beginning in 1668 with the arrival of Spanish settlers including Padre San Vitores, a Catholic missionary. The island was taken over from Spain by the United States during the Spanish American War in 1898. As the largest island in Micronesia and the only American-held island in the region before World War II, Guam was occupied by the Japanese between December 1941 and July 1944. Today, Guam's economy is mainly supported by tourism (primarily from Japan) and U.S. military bases.[3]
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Guam:
General reference
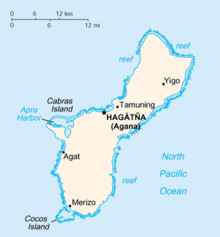 An enlargeable basic map of Guam
An enlargeable basic map of Guam
- Pronunciation: /ˈɡwɑːm/
- Common English country name: Guam
- Official English country name: The United States Territory of Guam
- Common endonym(s): List of countries and capitals in native languages
- Official endonym(s): List of official endonyms of present-day nations and states
- Adjectival(s): Guamanian
- Demonym(s):
- Etymology: Name of Guam
- ISO country codes: GU, GUM, 316
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:GU
- Internet country code top-level domain: .gu
Geography of Guam
Main article: Geography of Guam- Guam is: a United States territory
- Location:
- Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
- Pacific Ocean
- North Pacific
- Time zone: Chamorro Standard Time (UTC+10)
- Extreme points of Guam
- High: Mount Lamlam 406 m (1,332 ft) – 11,377 meters above Challenger Deep
- Low: North Pacific Ocean 0 m
- Land boundaries: none
- Coastline: 125.5 km
- Population of Guam: 173,000 - 179th most populous country
- Area of Guam: 541 km2
- Atlas of Guam
Environment of Guam
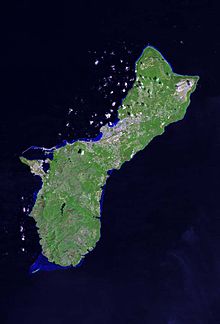 An enlargeable satellite image of Guam
An enlargeable satellite image of Guam Main article: Environment of Guam
Main article: Environment of Guam- Climate of Guam
- Environmental issues in Guam
- Ecoregions in Guam
- Renewable energy in Guam
- Geology of Guam
- Protected areas of Guam
- Biosphere reserves in Guam
- National parks of Guam
- Superfund sites in Guam
- Wildlife of Guam
- Flora of Guam
- Fauna of Guam
- Birds of Guam
- Mammals of Guam
Natural geographic features of Guam
Main article: Landforms of Guam- Fjords of Guam
- Glaciers of Guam
- Islands of Guam
- Lakes of Guam
- Mountains of Guam
- Volcanoes in Guam
- Rivers of Guam
- Waterfalls of Guam
- Valleys of Guam
- World Heritage Sites in Guam: None
Regions of Guam
- Main article: Regions of Guam
Ecoregions of Guam
- Main article: Ecoregions in Guam
Administrative divisions of Guam
None
Municipalities of Guam
- Capital of Guam: Hagåtña
- Cities of Guam
Demography of Guam
- Main article: Demographics of Guam
Government and politics of Guam
- Main article: Government of Guam and Politics of Guam
- Form of government: presidential representative democracy
- Capital of Guam: Hagåtña
- Elections in Guam
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Guam
- Political scandals of Guam
- Taxation in Guam
Branches of the government of Guam
Main article: Government of GuamExecutive branch of the government of Guam
- Head of state: President of United States
- Head of government: Governor of Guam
- Cabinet of Guam
Legislative branch of the government of Guam
- Parliament of Guam (bicameral)
- Upper house: Senate of Guam
- Lower house: House of Commons of Guam
Judicial branch of the government of Guam
Main article: Court system of GuamForeign relations of Guam
Main article: Foreign relations of Guam- Diplomatic missions in Guam
- Diplomatic missions of Guam
International organization membership
The United States Territory of Guam is a member of:[1]
- International Olympic Committee (IOC)
- Secretariat of the Pacific Community (SPC)
- Universal Postal Union (UPU)
Law and order in Guam
- Main article: Law of Guam
- Capital punishment in Guam
- Constitution of Guam
- Crime in Guam
- Human rights in Guam
- LGBT rights in Guam
- Freedom of religion in Guam
- Law enforcement in Guam
Military of Guam
- Main article: Military of Guam
- Command
- Commander-in-chief:
- Ministry of Defence of Guam
- Commander-in-chief:
- Forces
- Army of Guam
- Navy of Guam
- Air Force of Guam
- Special forces of Guam
- Military history of Guam
- Military ranks of Guam
Local government in Guam
Main article: Local government in GuamHistory of Guam
- Main article: History of Guam, Timeline of the history of Guam, and Current events of Guam
History of Guam, by period
- Indigenous peoples
- First European contact, 1521–1668
-
- On March 6, 1521, three Spanish ships under the command of Fernão de Magalhães (Ferdinand Magellan) land on the Island of Guam after a seemingly endless eleven week voyage across the Pacific Ocean. Magalhães names the archipelago Las Isles de las Velas Latinas (The Islands of the Latine Sails). When the Spaniards refuse to pay for supplies, natives take iron from the ships. Magalhães renames the archipelago Las Islas de los Ladrones (The Islands of the Thieves).
-
- Spanish East Indies, 1565-(1668–1898)-1899
- Diego Luis de San Vitores renames the Chamorro archipelago Islas Marianas in honor of his patroness, Queen Mariana of Austria, 1668
- Spanish-American War, April 23 – August 12, 1898
- Spanish Empire declares war on the United States, April 23, 1898
- United States capture of Guam, June 20–21, 1898
- Treaty of Paris, December 10, 1898
- United States Territory of Guam, since December 10, 1898
- World War I, June 28, 1914 – November 11, 1918
- United States enters Great War on April 6, 1917
- World War II, September 1, 1939 – September 2, 1945
- United States enters Second World War on December 8, 1941
- Battle of Guam of 1941
- Battle of Guam of 1944
- Cold War, March 5, 1946 – December 25, 1991
- Korean War, June 25, 1950 – July 27, 1953
- Guam Organic Act, August 1, 1950
- World War I, June 28, 1914 – November 11, 1918
Culture of Guam
- Main article: Culture of Guam
- Architecture of Guam
- Cuisine of Guam
- Ethnic minorities in Guam
- Festivals in Guam
- Humor in Guam
- Languages of Guam
- Media in Guam
- National symbols of Guam
- Coat of arms of Guam
- Flag of Guam
- National anthem of Guam
- People of Guam
- Prostitution in Guam
- Public holidays in Guam
- Records of Guam
- Religion in Guam
- Buddhism in Guam
- Christianity in Guam
- Hinduism in Guam
- Islam in Guam
- Judaism in Guam
- Sikhism in Guam
- World Heritage Sites in Guam: None
Art in Guam
- Art in Guam
- Cinema of Guam
- Literature of Guam
- Music of Guam
- Television in Guam
- Theatre in Guam
Sports in Guam
- Main article: Sports in Guam
- Football in Guam
- Guam at the Olympics
Economy and infrastructure of Guam
- Main article: Economy of Guam
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 150th (one hundred and fiftieth)
- Agriculture in Guam
- Banking in Guam
- National Bank of Guam
- Communications in Guam
- Internet in Guam
- Companies of Guam
- Currency of Guam: Dollar
- ISO 4217: USD
- Economic history of Guam
- Energy in Guam
- Energy policy of Guam
- Oil industry in Guam
- Mining in Guam
- Tourism in Guam
- Transport in Guam
- Guam Stock Exchange
Education in Guam
- Main article: Education in Guam
Infrastructure of Guam
- Health care in Guam
- Transportation in Guam
- Airports in Guam
- Rail transport in Guam
- Roads in Guam
- Water supply and sanitation in Guam
See also
Main article: Guam- Index of Guam-related articles
- List of Guam-related topics
- List of international rankings
- Outline of geography
- Outline of Oceania
- Outline of the United States
References
- ^ a b "Guam". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. July 2, 2009. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/gq.html. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ^ "USDOI Office of Insular Affairs" U.S. Territories, Retrieved November 4, 2007.
- ^ Rogers, Robert F. (1995). Destiny’s Landfall: A History of Guam. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 978-0824816780.
External links
- Government
- Official Portal for the Island of Guam
- Office of the Governor
- Congresswoman Madeleine Z. Bordallo, Delegate, U.S. Congress
- Guam Customs and Quarantine Agency
- Guam Election Commission
- Guam Code Annotated
- Guam Department of Revenue and Taxation
- Guam's Original Webpage
- Invasive species
- (Potentially) Invasive plant species on Guam (info from the Pacific Island Ecosystems at Risk project (PIER))
- Brown tree snake (Boiga irregularis) information from the Hawaiian Ecosystems at Risk project (HEAR)
- News
- Marianas Variety "Guam's only true independent news source"
- Pacific Daily News, A Gannett Newspaper
- KUAM, Guam's Primary News Channel
- "Pacific News Center - News You Can Trust
- Overviews
- allthingsguam A Guam History resource—virtual textbook, virtual workbook and more
- Guampedia, Guam's Online Encyclopedia
- Guam at the Open Directory Project
- U.S. Library of Congress - Portals to the World: Guam
- The World Factbook on Guam
- Guam Connection - Guam directory and internet portal.
- Military
- Commander, Naval Forces Marianas (COMNAVMAR) Guam
- Andersen Air Force Base (AAFB) Guam
- War in the Pacific - Liberation of Guam
- Congressional Testimony - Guam War Claims
- Tourism
- Others
- Guam Chamber of Commerce
- Maps - Perry-Castañeda Library Map Collection
- National Weather Service - Guam
Outlines General reference · Culture and the arts · Geography and places · Health and fitness · History and events · Mathematics and logic · Natural and physical sciences · People and self · Philosophy and thinking · Religion and belief systems · Society and social sciences · Technology and applied sciences Territory of Guam
Territory of GuamTopics Islands Villages Categories:- Outlines of countries
- Guam
- Guam-related lists
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


