- Attributes of God
-
Part of a series on Attributes of God in
Christian theologyAseity
Eternity
Graciousness
Holiness
Immanence
Immutability
Impassibility
Impeccability
Incorporeality
Jealousy
Love
Mission
Omnibenevolence
Omnipotence
Omnipresence
Omniscience
Oneness
Providence
Righteousness
Simplicity
Transcendence
Trinity
Veracity
Wrathv · God in Islam. The Attributes of God in Christian theology are those characteristics of God revealed in the Bible.
Classification
Many Reformed theologians distinguish between the communicable attributes (those that human beings can also have) and the incommunicable attributes (those that belong to God alone).[1] Donald Macleod, however, argues that "All the suggested classifications are artificial and misleading, not least that which has been most favoured by Reformed theologians - the division into communicable and incommunicable attributes."[2]
Many of these attributes only say what God is not - for example, saying he is immutable is saying that he does not change. The attributes of God may be classified under two main categories:
- His infinite powers.
- His personality attributes, like holiness and love.
Enumeration
The Westminster Shorter Catechism's definition of God is merely an enumeration of his attributes: "God is a Spirit, infinite, eternal, and unchangeable in his being, wisdom, power, holiness, justice, goodness, and truth."[3] The Westminster Larger Catechism adds certain attributes to this description, such as "all-sufficient," "incomprehensible," "every where present" and "knowing all things".[4] This answer has been criticised, however, as having "nothing specifically Christian about it."[5]
Aseity
The aseity of God means "God is so independent that he does not need us."[6] It is based on Acts 17:25, where it says that God "is not served by human hands, as if he needed anything" (NIV). This is often related to God's self-existence and his self-sufficiency.
Graciousness
The graciousness of God is a key tenet of Christianity.
Holiness
The holiness of God is that he is separate from sin and incorruptible. Noting the refrain of "Holy, holy, holy" in Isaiah 6:3 and Revelation 4:8, R. C. Sproul points out that "only once in sacred Scripture is an attribute of God elevated to the third degree... The Bible never says that God is love, love, love."[7]
Immanence
The immanence of God refers to him being in the world. It is thus contrasted with his transcendence.
Immutability
Immutability means God cannot change. James 1:17 refers to the "Father of the heavenly lights, who does not change like shifting shadows" (NIV).
Impassibility
The doctrine of the impassibility of God is a controversial one. It refers to the inability of God to suffer.
Impeccability
The impeccability of God is closely related to his holiness. It means that he cannot sin.
Incorporeality
The incorporeality or spirituality of God refers to him being a spirit. This is derived from Jesus' statement in John 4:24, "God is spirit." Robert Reymond suggests that it is the fact of his spiritual essence that underlies the second commandment, which prohibits every attempt to fashion an image of him."[8]
Incomprehensibility
The incomprehensibility of God means that he is not able to be fully known. Louis Berkhof states that "the consensus of opinion" through most of church history has been that God is the "Incomprehensible One". Berkhof, however, argues that "in so far as God reveals Himself in His attributes, we also have some knowledge of His Divine Being, though even so our knowledge is subject to human limitations."[9]
Infinity
The infinity of God includes both his eternity and his immensity. Isaiah 40:28 says that "Yahweh is the everlasting God," while Solomon acknowledges in 1 Kings 8:27 that "the heavens, even the highest heaven, cannot contain you". Infinity permeates all other attributes of God: His love is infinite, his powers are infinite...
Jealousy
Exodus 34:14 makes the surprising statement that "Yahweh, whose name is Jealousy, is a jealous God."
Love
1 John 4:16 says "God is Love." D. A. Carson speaks of the "difficult doctrine of the love of God," since "when informed Christians talk about the love of God they mean something very different from what is meant in the surrounding culture."[10] Carson distinguishes between the love the Father has for the Son, God's general love for his creation, God's "salvific stance towards his fallen world," his "particular, effectual, selecting love toward his elect," and love that is conditioned on obedience.
Mission
While the mission of God is not traditionally included in this list, David Bosch has argued that "mission is not primarily an activity of the church, but an attribute of God."[11]
Omnibenevolence
The omnibenevolence of God refers to him being "all good". God's goodness encompasses his grace, love, mercy and patience.
Omnipotence
The omnipotence of God refers to him being "all powerful". C. S. Lewis clarifies this concept: "His Omnipotence means power to do all that is intrinsically possible, not to do the intrinsically impossible. You may attribute miracles to him, but not nonsense. This is no limit to his power."[12]
Omnipresence
The omnipresence of God refers to him being present everywhere. Berkhof distinguishes between God's immensity and his omnipresence, saying that the former "points to the fact that God transcends all space and is not subject to its limitations," emphasising his transcendence, while the latter denotes that God "fills every part of space with His entire Being," emphasising his immanence.[13] In Psalm 139, David says, "If I go up to the heavens, you are there; if I make my bed in the depths, you are there" (Psalm 139:8, NIV).
Omniscience
The omniscience of God refers to him being "all knowing". Berkhof regards the wisdom of God as a "particular aspect of his knowledge."[14] Romans 16:27 speaks about the "only wise God".
Oneness
The oneness of God refers to his being one and only. See Monotheism and also Trinity.
Providence
While the providence of God usually refers to his activity in the world, it also implies his care for the universe, and is thus an attribute. A distinction is usually made between "general providence," which refers to God's continuous upholding the existence and natural order of the universe, and "special providence," which refers to God's extraordinary intervention in the life of people.[15]
Righteousness
The righteousness of God may refer to his holiness, to his justice, or to his saving activity.
Simplicity
The simplicity of God means he is not partly this and partly that, but that whatever he is, he is so entirely. It is thus related to the unity of God.
Sovereignty
The sovereignty of God is similar to his omnipotence and providence, yet it also encompasses his freedom.
Transcendence
Transcendence is that God is outside space and time, and therefore eternal and unable to be changed by forces within the universe.[16] It is thus closely related to God's immutability, and is contrasted with his immanence.
Trinity
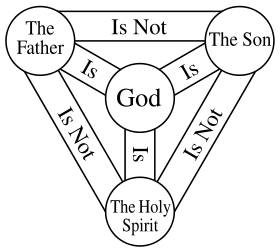
The Trinity of God refers to him being three in one. God is understood to be a unity of Father, Son, and the Holy Spirit.
Veracity
The veracity of God means his truth-telling. Titus 1:2 refers to "God, who does not lie."
Wrath
Moses praises the wrath of God in Exodus 15:7. Later in Deuteronomy 9, after the incident of The Golden Calf, Moses describes how: 'I feared the furious anger of the LORD, which turned him against you, would drive him to destroy you. But again he listened to me.' (9:19) In Psalm 69:24, the psalmist begs God to: 'consume' his enemies 'with your burning anger'.
In the New Testament, Jesus says in John 3:36, "Whoever believes in the Son has eternal life; whoever does not obey the Son shall not see life, but the wrath of God remains on him."
See also
References
- ^ Herman Bavinck, The Doctrine of God. Edinburgh: The Banner of Truth Trust, 1979.
- ^ Donald Macleod, Behold Your God (Christian Focus Publications, 1995), 20-21.
- ^ Westminster Shorter Catechism, Question and Answer 4.
- ^ Westminster Larger Catechism, Question and Answer 7.
- ^ James B. Jordan, "What is God?," Biblical Horizons Newsletter, No. 82.
- ^ D. A. Carson, The Gagging of God (Grand Rapids: Zondervan), 1996.
- ^ R. C. Sproul, The Holiness of God (Scripture Press Foundation, 1986), 38.
- ^ Robert L. Reymond, A New Systematic Theology of the Christian Faith (2nd ed., Nashville: Thomas Nelson, 1998), 167.
- ^ Louis Berkhof, Systematic Theology (London: Banner of Truth, 1949), 43.
- ^ D. A. Carson, The Difficult Doctrine of the Love of God (Leicester: Inter-Varsity Press, 2000), 10.
- ^ David J. Bosch, Transforming Mission (Maryknoll: Orbis Books, 1991), 390.
- ^ C. S. Lewis, The Problem of Pain (Fontana, 1966), 16.
- ^ Louis Berkhof, Systematic Theology (London: Banner of Truth, 1949), 61.
- ^ Louis Berkhof, Systematic Theology (London: Banner of Truth, 1949), 68.
- ^ Providence in The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions.
- ^ J. Gresham Machen, God Transcendent. Banner of Truth publishers, 1998. ISBN 0851513557
External links
- Attributes of God According to Thomas Aquinas at PhilosophersAnswer.com
- Articles on God at PhilosophersAnswer.Com
- Attributes of God, Enjoying God Ministries
v · d · eTheology Apologetics GeneralBahá'íChristianChristian apologetics · Christian apologists · List of Christian apologetic works · Ecumenical Apologetics · Presuppositional apologetics · Epistle to Diognetus · Trilemma · Urmonotheismus · More...MuslimMuslim apologistsConceptions of God Divine presenceGod as theGod inAbrahamic religions · Bahá'í Faith · Buddhism · Christianity · Hinduism · Islam · Jainism · Judaism · Sikhism · Zoroastrianism · More...Names of God inSingular GodBinitarianismTrinitarianismOtherAristotelian view of God · Attributes · Demiurge · Divine simplicity · Egotheism · Godhead (Christianity) · Godhead (Latter Day Saints) · Great Architect of the Universe · Great Spirit · Apophatic theology · Olelbis · Open theism · Personal god · Phenomenological definition of God · Philo's view of God · Sarav viāpak · Taryenyawagon · The All · Tian · Unmoved mover · More...Eschatology Afterlife · Apocalypticism · Buddhist · Christian · Concepts of Heaven · Doomsday films · Ghost Dance Movement · Ghosts · Hindu · Islamic · Jewish · Personifications of death · Taoist · Zoroastrian · MoreExistence of God arguments againstfromotherarguments forfromA proper basis · Beauty · Consciousness · Degree · Desire · Love · Miracles · Morality · Reason · Religious experienceotherChristological · Cosmological · Ontological · Pascal's wager · Teleological · Trademark · Transcendental · Witness · More...Opposition to religion Anti-Buddhism (Criticism · Persecution) · Catholicism · Christianity (Criticism · anti-Christian sentiment · Persecution) · Gnosticism · Hinduism (Criticism) · Islam (Criticism · Islamophobia · Persecution) · Jainism (Criticism) · Judaism (Criticism) · Protestantism · cult movement · Zoroastrianism · More...OtherTheism List of philosophical theories · Deity (Divinity · Numen · Male · Female · Gender of) · Deism · Dystheism · Henotheism · Hermeticism · Kathenotheism · Nontheism · Monolatrism · Monotheism · Mysticism · Panentheism · Pandeism · Pantheism · Polydeism · Polytheism · Spiritualism · Theopanism · More...Theologies History of · Outline · of the Bible · Terms · Christology · Cosmology · Ecclesiology · Ethics · Hamartiology · Law · Messianism · Movements · Nestorianism · New testament · Old testament · Philosophy · Practical · Sophiology · Soteriology · More...HinduJewishOtherEducation Anglican · Buddhist · Eastern Orthodox · Evangelical · Islamic · Jewish · Lutheran · Madrassas · Methodist · Reformed Church · Roman Catholic · More...Schools by religious affiliationBahá'í · Buddhist · Anglican · Assemblies of God · Baptist · Eastern Orthodox · Hindu · Islamic · Jewish · Latter Day Saints · Lutheran · Mennonite · Methodist · Nondenominational Christian · Presbyterian · Quaker · Roman Catholic · Seventh-Day AdventistResources List of theological journals · More...Practitioners Teachers · TheologiansCategories:- Christian theology
- Christian terms
- Attributes of God in Christian theology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
ATTRIBUTES OF GOD — those characteristics uniquely applicable to the divine BEING. Two classical ways of arriving at the attributes of God have been 1) the way of negation, via negativa rather than saying what God is, say what He is not; e.g. God is unlimited… … Concise dictionary of Religion
attributes of God — Атрибуты Бога … Вестминстерский словарь теологических терминов
Nature and Attributes of God — The Nature and Attributes of God † Catholic Encyclopedia ► The Nature and Attributes of God I. As Known Through Natural Reason A. Infinity of God B. Unity or Unicity of God C. Simplicity of God D. Divine Personality… … Catholic encyclopedia
attributes of God, absolute — Атрибуты Бога абсолютные … Вестминстерский словарь теологических терминов
attributes of God, communicable — Атрибуты Бога передающиеся … Вестминстерский словарь теологических терминов
attributes of God, émanant transitiv — Атрибуты Бога истекающие … Вестминстерский словарь теологических терминов
attributes of God, immanent intransitive — Атрибуты Бога имманентные … Вестминстерский словарь теологических терминов
attributes of God, incommunicable — Атрибуты Бога непередающиеся … Вестминстерский словарь теологических терминов
attributes of God, moral — Атрибуты Бога моральные … Вестминстерский словарь теологических терминов
attributes of God, natural — Атрибуты Бога природные … Вестминстерский словарь теологических терминов
18+© Academic, 2000-2024- Contact us: Technical Support, Advertising
Dictionaries export, created on PHP, Joomla, Drupal, WordPress, MODx.Share the article and excerpts
Attributes of God
- Attributes of God
-
Part of a series on Attributes of God in
Christian theologyAseity
Eternity
Graciousness
Holiness
Immanence
Immutability
Impassibility
Impeccability
Incorporeality
Jealousy
Love
Mission
Omnibenevolence
Omnipotence
Omnipresence
Omniscience
Oneness
Providence
Righteousness
Simplicity
Transcendence
Trinity
Veracity
Wrath