- Collagen, type XIII, alpha 1
-
Collagen, type XIII, alpha 1 Identifiers Symbols COL13A1; COLXIIIA1; FLJ42485 External IDs OMIM: 120350 MGI: 1277201 HomoloGene: 22421 GeneCards: COL13A1 Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • extracellular matrix structural constituent
• protein binding
• heparin bindingCellular component • collagen
• collagen type XIII
• plasma membrane
• cell-cell junction
• integral to membraneBiological process • morphogenesis of a branching structure
• endochondral ossification
• cell-matrix adhesion
• multicellular organismal development
• cell-cell adhesion
• cell differentiationSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 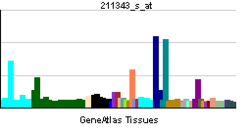
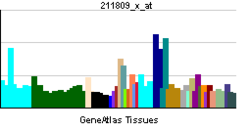
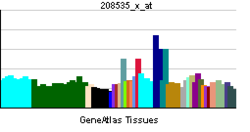
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 1305 12817 Ensembl ENSG00000197467 ENSMUSG00000058806 UniProt Q5TAT6 n/a RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001130103.1 NM_007731.2 RefSeq (protein) NP_001123575.1 NP_031757.1 Location (UCSC) Chr 10:
71.56 – 71.72 MbChr 10:
61.3 – 61.44 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Collagen alpha-1(XIII) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL13A1 gene.[1]
This gene encodes the alpha chain of one of the nonfibrillar collagens. The function of this gene product is not known, however, it has been detected at low levels in all connective tissue-producing cells so it may serve a general function in connective tissues. Unlike most of the collagens, which are secreted into the extracellular matrix, collagen XIII contains a transmembrane domain and the protein has been localized to the plasma membrane. The transcripts for this gene undergo complex and extensive splicing involving at least eight exons. Like other collagens, collagen XIII is a trimer; it is not known whether this trimer is composed of one or more than one alpha chain isomer. A number of alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, but the full length nature of some of them has not been determined.[1]
References
Further reading
- Juvonen M, Pihlajaniemi T (1992). "Characterization of the spectrum of alternative splicing of alpha 1 (XIII) collagen transcripts in HT-1080 cells and calvarial tissue resulted in identification of two previously unidentified alternatively spliced sequences, one previously unidentified exon, and nine new mRNA variants.". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (34): 24693–9. PMID 1447209.
- Juvonen M, Sandberg M, Pihlajaniemi T (1992). "Patterns of expression of the six alternatively spliced exons affecting the structures of the COL1 and NC2 domains of the alpha 1(XIII) collagen chain in human tissues and cell lines.". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (34): 24700–7. PMID 1447210.
- Pihlajaniemi T, Tamminen M (1990). "The alpha 1 chain of type XIII collagen consists of three collagenous and four noncollagenous domains, and its primary transcript undergoes complex alternative splicing.". J. Biol. Chem. 265 (28): 16922–8. PMID 1698771.
- Tikka L, Elomaa O, Pihlajaniemi T, Tryggvason K (1991). "Human alpha 1 (XIII) collagen gene. Multiple forms of the gene transcripts are generated through complex alternative splicing of several short exons.". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (26): 17713–9. PMID 1894651.
- Tikka L, Pihlajaniemi T, Henttu P, et al. (1988). "Gene structure for the alpha 1 chain of a human short-chain collagen (type XIII) with alternatively spliced transcripts and translation termination codon at the 5' end of the last exon.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85 (20): 7491–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.20.7491. PMID 2459707.
- Shows TB, Tikka L, Byers MG, et al. (1989). "Assignment of the human collagen alpha 1 (XIII) chain gene (COL13A1) to the q22 region of chromosome 10.". Genomics 5 (1): 128–33. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(89)90096-7. PMID 2767682.
- Pihlajaniemi T, Myllylä R, Seyer J, et al. (1987). "Partial characterization of a low molecular weight human collagen that undergoes alternative splicing.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (4): 940–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.4.940. PMID 3547403.
- Juvonen M, Pihlajaniemi T, Autio-Harmainen H (1994). "Location and alternative splicing of type XIII collagen RNA in the early human placenta.". Lab. Invest. 69 (5): 541–51. PMID 8246446.
- Hägg P, Rehn M, Huhtala P, et al. (1998). "Type XIII collagen is identified as a plasma membrane protein.". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (25): 15590–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.25.15590. PMID 9624150.
- Kvist AP, Latvanlehto A, Sund M, et al. (1999). "Complete exon-intron organization and chromosomal location of the gene for mouse type XIII collagen (col13a1) and comparison with its human homologue.". Matrix Biol. 18 (3): 261–74. doi:10.1016/S0945-053X(99)00018-9. PMID 10429945.
- Nykvist P, Tu H, Ivaska J, et al. (2000). "Distinct recognition of collagen subtypes by alpha(1)beta(1) and alpha(2)beta(1) integrins. Alpha(1)beta(1) mediates cell adhesion to type XIII collagen.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (11): 8255–61. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.11.8255. PMID 10713152.
- Sandberg-Lall M, Hägg PO, Wahlström I, Pihlajaniemi T (2000). "Type XIII collagen is widely expressed in the adult and developing human eye and accentuated in the ciliary muscle, the optic nerve and the neural retina.". Exp. Eye Res. 70 (4): 401–10. doi:10.1006/exer.1998.0826. PMID 10865988.
- Tu H, Sasaki T, Snellman A, et al. (2002). "The type XIII collagen ectodomain is a 150-nm rod and capable of binding to fibronectin, nidogen-2, perlecan, and heparin.". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (25): 23092–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107583200. PMID 11956183.
- Latvanlehto A, Snellman A, Tu H, Pihlajaniemi T (2003). "Type XIII collagen and some other transmembrane collagens contain two separate coiled-coil motifs, which may function as independent oligomerization domains.". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (39): 37590–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305974200. PMID 12832406.
Extracellular matrix Fibril formingOtherFACIT: type IX (COL9A1, COL9A2, COL9A3) · type XII (COL12A1) · COL14A1 · COL16A1 · COL19A1 · COL20A1 · COL21A1 · COL22A1
basement membrane: type IV (COL4A1, COL4A2, COL4A3, COL4A4, COL4A5, COL4A6)
multiplexin: COL15A1 · type XVIII (COL18A1, Endostatin)
transmembrane: COL13A1 · COL17A1 · COL23A1 · COL25A1
other: type VI (COL6A1, COL6A2, COL6A3) · type VII (COL7A1) · type VIII (COL8A1, COL8A2) · type X (COL10A1) · type XI (COL11A1, COL11A2) · COL27A1 · COL28A1 · COL29A1OtherALCAM · Elastin (Tropoelastin) · Vitronectin · FRAS1 · FREM2 · Decorin · FAM20C · ECM1 · Matrix gla protein · Tectorin (TECTA, TECTB)Other see also diseases
B proteins: BY STRUCTURE: membrane, globular (en, ca, an), fibrousCategories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 10 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
