- Organogenesis
-
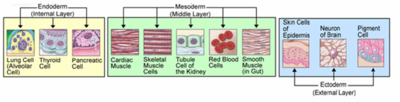 The endoderm produces tissue within the lungs, thyroid, and pancreas. The mesoderm aids in the production of cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, tissues within the kidneys, and red blood cells. The ectoderm produces tissues within the epidermis and aids in the formation of neurons within the brain, and melanocytes.
The endoderm produces tissue within the lungs, thyroid, and pancreas. The mesoderm aids in the production of cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, tissues within the kidneys, and red blood cells. The ectoderm produces tissues within the epidermis and aids in the formation of neurons within the brain, and melanocytes.
In animal development, organogenesis (organo-genesis, compound of the Greek words όργανον "that with which one works",[1] and γένεσις "origin, creation, generation"[2]) is the process by which the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm develop into the internal organs of the organism. Internal organs initiate development in humans within the 3rd to 8th weeks in utero. The germ layers in organogenesis differ by three processes: folds, splits, and condensation. Developing early during this stage in chordate animals are the neural tube and notochord. Vertebrate animals all differentiate from the gastrula the same way. Vertebrates develop a neural crest that differentiates into many structures, including some bones, muscles, and components of the peripheral nervous system. The coelom of the body forms from a split of the mesoderm along the somite axis.[citation needed]
In plants, organogenesis can occur from totipotent callus cells.
See also
- Ectoderm
- Embryogenesis
- Endoderm
- Eye development
- Germ layer
- Germ line development
- Heart development
- Histogenesis
- Limb development
- Mesoderm
- Morphogenesis
References
Developmental biology > Human embryogenesis (development of embryo) and development of fetus (TE E2.0) First three
weeksWeek 1Fertilization · Oocyte activation · Zygote · Cleavage · Morula · Blastula (Blastomere) · Blastocyst · Inner cell massWeek 2
(Bilaminar)Week 3
(Trilaminar)Archenteron/Primitive streak (Primitive pit, Primitive knot/Blastopore, Primitive groove) · Gastrula/Gastrulation · Regional specification · Embryonic discSplanchnopleuric mesenchymeChorda- · Paraxial (Somite/Somitomere) · Intermediate · Lateral plate (Intraembryonic coelom, Splanchnopleuric mesenchyme/Somatopleuric mesenchyme)Human cell types / list derived primarily from mesoderm Paraxial muscle: Myoblast → Myocyte · Myosatellite cell · Tendon cell · Cardiac muscle cell
adipose: Lipoblast → AdipocyteDigestive systemIntermediate Urinary system (RSC)Angioblast → Endothelial cell · Mesangial cell (Intraglomerular, Extraglomerular) · Juxtaglomerular cell · Macula densa cell
Stromal cell → Interstitial cell → Telocytes
Simple epithelial cell → Podocyte · Kidney proximal tubule brush border cellLateral plate/
hemangioblastsee lymphocytessee myeloid cellsCategories:- Developmental biology
- Embryology
- Greek loanwords
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
