- Sertoli cell
Infobox Anatomy
Name = PAGENAME
Latin =
GraySubject = 258
GrayPage = 1243
Caption = "Germinal epithelium of thetesticle ."
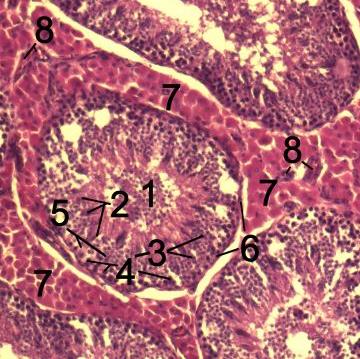
1:basal lamina
2:spermatogonia
3:spermatocyte 1st order
4: spermatocyte 2nd order
5:spermatid
6: mature spermatid
7:Sertoli cell
8:tight junction (blood testis barrier )
Caption2 = "Histological section through testicular parenchyma of aboar ."
1 Lumen ofTubulus seminiferus contortus
2spermatids
3spermatocytes
4 spermatogonia
5Sertoli cell
6Myofibroblasts
7Leydig cell s
8capillaries
System =
MeshName = Sertoli+Cells
MeshNumber = A05.360.444.849.789
A Sertoli cell (a kind ofsustentacular cell ) is a 'nurse' cell of the testes which is part of aseminiferous tubule .It is activated by
follicle-stimulating hormone , and hasFSH-receptor on its membranes.Functions
Its main function is to nurture the developing sperm cells through the stages of
spermatogenesis . Because of this, it has also been called the "mother cell".ecretory
Sertoli cells secrete the following substances:
* anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) - secreted during the early stages of fetal life.
*
inhibin andactivin s - secreted after puberty, and work together to regulate FSH secretion*
androgen binding protein - facilitate spermatogenesis and sperm maturation*
estradiol -aromatase from Sertoli cells converttestosterone to estrone to directspermatogenesis *
glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) - has been demonstrated to function in promoting undifferentiating spermatogonia, which ensures stem cell self-renewal during the perinatal period.* the Ets related molecule (
ERM transcription factor ) - needed for maintenance of the spermatogonial stem cell in the adult testis.*
transferrin [cite journal | author = Xiong X, Wang A, Liu G, Liu H, Wang C, Xia T, Chen X, Yang K | title = Effects of p,p'-dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene on the expressions of transferrin and androgen-binding protein in rat Sertoli cells | journal = Environ Res | volume = 101 | issue = 3 | pages = 334–9 | year = 2006 | pmid = 16380112 | doi = 10.1016/j.envres.2005.11.003]tructural
The tight junctions of Sertoli cells form the
blood-testis barrier , a structure that partitions the interstitialblood compartment of the testis from the adluminal compartment of the seminiferous tubules. Because of theapical progression of the spermatogonia, the tight junctions must be dynamically reformed and broken to allow the immunoidenticalspermatogonia to cross through the blood-testis barrier so they can become immunologically unique. Sertoli cells control the entry and exit ofnutrient s,hormone s and other chemicals into the tubules of the testis as well as make the adluminal compartment an immune-privileged site.The cell is also responsible for establishing and maintaining the spermatogonial
stem cell niche, which ensures the renewal of stem cells and the differentiation of spermatogonia into mature germ cells that progress stepwise through the long process of spermatogenesis, ending in the release of spermatozoa. Sertoli cells bind to spermatogonial cells via N-cadherins and galctosyltransferase (via carbohydrate residues).Other functions
During the Maturation phase of spermiogenesis, the Sertoli cells consume the unneeded portions of the spermatozoa.
Production of Sertoli cells
Once fully differentiated, the Sertoli cell is unable to proliferate. Therefore, once spermatogenesis has begun, no more Sertoli cells are created.
Recently however, some scientists have found a way to grow these cells outside of the body. This gives rise to the possibility of repairing some defects that cause male infertility.
Nomenclature
Sertoli cells are called so because of their
eponym Enrico Sertoli , an Italian physiologist who discovered them while studying medicine in the University of Pavia, Italy. [WhoNamedIt|synd|518]He published a description of this cell in 1865. The cell was discovered by Sertoli with a Belthle microscope purchased in 1862, which he used while studying medicine.
In the 1865 publication, his first description used the terms "tree-like cell" or "stringy cell" and most importantly he referred to these "mother cells." It was other scientists who used Enrico's family name, Sertoli, to label these cell in publications, starting in 1888. As of 2006, two textbooks that are devoted specifically to the Sertoli cell have been published.
Histology
On slides, using standard staining, it can be easy to confuse the Sertoli cells with the other cells of the germinal epithelium. The most distinctive of the Sertoli cells is the dark
nucleolus . [ [http://www.cvm.okstate.edu/instruction/mm_curr/histology/MR/HiMRP4.htm OSU Center for Veterinary Health Sciences - OSU-CVHS Home ] ]Pathology
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour are part of thesex cord-stromal tumour group of ovarian neoplasms.
=AdditionalReferences
ee also
*
Sertoli cell only syndrome External links
* [http://www.ufp.pt/~pedros/qfisio/reproduction.htm Reproductive Physiology at ufp.pt]
*
*
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

