- Coffea arabica
-
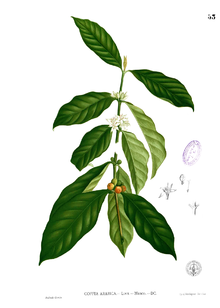
Coffea arabica Coffee flowers 
Coffee fruits Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae (unranked): Angiosperms (unranked): Eudicots (unranked): Asterids Order: Gentianales Family: Rubiaceae Subfamily: Ixoroideae Tribe: Coffeeae Genus: Coffea Species: C. arabica Binomial name Coffea arabica
L.Coffea arabica (
 /əˈræbɪkə/) is a species of Coffea originally indigenous to the mountains of Yemen in the Arabian Peninsula, hence its name, and also from the southwestern highlands of Ethiopia and southeastern Sudan. It is also known as the "coffee shrub of Arabia", "mountain coffee" or "arabica coffee". Coffea arabica is believed to be the first species of coffee to be cultivated, being grown in southwest Arabia for well over 1,000 years. It is said to produce better coffee than the other major commercially grown coffee species, Coffea canephora (robusta), but tastes vary. C. arabica contains less caffeine than any other commercially cultivated species of coffee. Wild plants grow to between 9 and 12 m tall, and have an open branching system; the leaves are opposite, simple elliptic-ovate to oblong, 6–12 cm long and 4–8 cm broad, glossy dark green. The flowers are white, 10–15 mm in diameter and grow in axillary clusters. The fruit is a drupe (though commonly called a "berry") 10–15 mm in diameter, maturing bright red to purple and typically contains two seeds (the coffee 'bean').
/əˈræbɪkə/) is a species of Coffea originally indigenous to the mountains of Yemen in the Arabian Peninsula, hence its name, and also from the southwestern highlands of Ethiopia and southeastern Sudan. It is also known as the "coffee shrub of Arabia", "mountain coffee" or "arabica coffee". Coffea arabica is believed to be the first species of coffee to be cultivated, being grown in southwest Arabia for well over 1,000 years. It is said to produce better coffee than the other major commercially grown coffee species, Coffea canephora (robusta), but tastes vary. C. arabica contains less caffeine than any other commercially cultivated species of coffee. Wild plants grow to between 9 and 12 m tall, and have an open branching system; the leaves are opposite, simple elliptic-ovate to oblong, 6–12 cm long and 4–8 cm broad, glossy dark green. The flowers are white, 10–15 mm in diameter and grow in axillary clusters. The fruit is a drupe (though commonly called a "berry") 10–15 mm in diameter, maturing bright red to purple and typically contains two seeds (the coffee 'bean').Contents
Distribution and Habitat
Originally found in the southwestern highlands of Ethiopia, Coffea arabica is now rare there in its native state, and many populations appear to be mixed native and planted trees. It is common there as an understorey shrub. It has also been recovered from the Boma Plateau in southeastern Sudan. C. arabica is also found on Mount Marsabit in northern Kenya, but it is unclear whether this is a truly native or naturalised occurrence.[1]
Cultivation and Use
C. arabica takes about seven years to mature fully, and does best with 1.0–1.5 meters (about 40–59 inches) of rain, evenly distributed throughout the year.[citation needed] It is usually cultivated between 1,300 and 1,500 m altitude, but there are plantations as low as sea level and as high as 2,800 m.[citation needed] The plant can tolerate low temperatures, but not frost, and it does best when the temperature hovers around 20 °C (68 °F).[citation needed] Commercial cultivars mostly only grow to about 5 m, and are frequently trimmed as low as 2 m to facilitate harvesting. Unlike Coffea canephora, C. arabica prefers to be grown in light shade.[citation needed]
Two to four years after planting, C. arabica produces small, white and highly fragrant flowers. The sweet fragrance resembles the sweet smell of jasmine flowers. When flowers open on sunny days, this results in the greatest numbers of berries. This can be a curse, however, as coffee plants tend to produce too many berries; this can lead to an inferior harvest and even damage yield in the following years, as the plant will favour the ripening of berries to the detriment of its own health. On well kept plantations, this is prevented by pruning the tree. The flowers themselves only last a few days, leaving behind only the thick dark green leaves. The berries then begin to appear. These are as dark green as the foliage, until they begin to ripen, at first to yellow and then light red and finally darkening to a glossy deep red. At this point they are called 'cherries' and are ready for picking. The berries are oblong and about 1 cm long. Inferior coffee results from picking them too early or too late, so many are picked by hand to be able to better select them, as they do not all ripen at the same time. They are sometimes shaken off the tree onto mats, which means that ripe and unripe berries are collected together.
The trees are difficult to cultivate and each tree can produce anywhere from 0.5–5.0 kg of dried beans, depending on the tree's individual character and the climate that season. The real prize of this cash crop are the beans inside. Each berry holds two locules containing the beans. The coffee beans are actually two seeds within the fruit, there is sometimes a third seed or one seed, a peaberry in the fruits at tips of the branches. These seeds are covered in two membranes, the outer one is called the "parchment coat" and the inner one is called the "silver skin."
On Java Island, trees are planted at all times of the year and are harvested year round. In parts of Brazil, however, the trees have a season and are harvested only in winter. The plants are vulnerable to damage in poor growing conditions (cold, low pH soil) and are also more vulnerable to pests than the C. robusta plant.[2] Gourmet coffees are almost exclusively high-quality mild varieties of arabica coffee, such as Colombian coffee.
Arabica coffee production in Indonesia began in 1699. Indonesian coffees, such as Sumatran and Java, are known for heavy body and low acidity. This makes them ideal for blending with the higher acidity coffees from Central America and East Africa.
In Hawaii, coffee was formerly more widely grown than at present, and it persists after cultivation in many areas. In some valleys, it is a highly invasive weed.[3]
History and Legend
According to legend, human cultivation of coffee began after goats in Ethiopia were seen mounting each other after eating the leaves and fruits of the coffee tree. However, in Ethiopia there are still some locales where people drink a tisane made from the leaves of the coffee tree.
The first written record of coffee made from roasted coffee beans comes from Arabian scholars who wrote that it was useful in prolonging their working hours. The Arab innovation in Yemen of making a brew from roasted beans, spread first among the Egyptians and Turks, and later on found its way around the world.
Taxonomy
Coffea arabica was first described by Antoine de Jussieu, who named it Jasminum arabicum after studying a specimen from the Botanic Gardens of Amsterdam. Linnaeus placed it in its own genus Coffea in 1737.[4]
Research
There is an Ethiopian Coffea arabica that naturally contains very little caffeine. Maria Bernadete Silvarolla, a researcher of Instituto Agronomico de Campinas (IAC), published findings in the journal Nature about these strains of C. arabica plants. While beans of normal C. arabica plants contain 12 milligrams of caffeine per gram of dry mass, these newly found mutants contain only 0.76 milligrams of caffeine per gram, but with all the taste of normal coffee.[citation needed]
References
- ^ Charrier A, Berthaud, p. 20
- ^ "Coffee: The World in Your Cup. Seattle, WA: Burke Museum at the University of Washington
- ^ "Coffea arabica (PIER species info)". http://www.hear.org/pier/species/coffea_arabica.htm. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- ^ Charrier A, Berthaud J (1985). "Botanical Classification of Coffee". In Clifford MH, Wilson KC. Coffee: Botany, Biochemistry and Production of Beans and Beverage. Westport, Connecticut: AVI Publishing. p. 14. ISBN 0-7099-0787-7.
Further reading
 Media related to Coffea arabica at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Coffea arabica at Wikimedia Commons- Silvarolla, Maria B.; Mazzafera, Paulo; Fazuoli, Luiz C. (2004). "A naturally decaffeinated arabica coffee". Nature 429 (6994): 826. doi:10.1038/429826a. PMID 15215853.
- Weinberg, Bennet Alan; Bealer, Bonnie K. (2001). The World of Caffeine: The Science and Culture of the World's Most Popular Drug. New York: Routledge. ISBN 0415927226.
External links
Coffee Topics - Economics
- Fair trade
- Health effects
- History
Production by
countrySpecies and
varieties- List of varieties
- Arabica
- Robusta
- Charrieriana
- Liberica
Major
componentsProcessing Preparation Popular
beverages- Affogato
- Americano
- Bicerin
- Cà phê sữa đá
- Café au lait
- Café con leche
- Café Cubano
- Cafe mocha
- Caffè corretto
- Caffè macchiato
- Cappuccino
- Carajillo
- Coffee milk
- Cortado
- Espresso
- Flat white
- Frappuccino
- Galão
- Greek frappé coffee
- Iced coffee
- Indian filter coffee
- Ipoh white coffee
- Irish coffee
- Kopi Luwak
- Latte
- Latte macchiato
- Liqueur coffee
- Long black
- Red eye
- Ristretto
- Turkish coffee
Substitutes Lifestyle Categories:- Coffea
- Flora of Ethiopia
- Flora of Yemen
- Crops originating from Ethiopia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.