- Ritonavir
-
Ritonavir 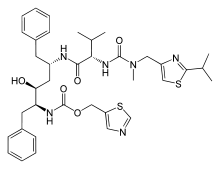
Systematic (IUPAC) name 1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethyl N-[(2S,3S,5S)-3-hydroxy-5-[(2S)-3-methyl-2-{[methyl({[2-(propan-2-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methyl})carbamoyl]amino}butanamido]-1,6-diphenylhexan-2-yl]carbamate Clinical data Trade names Norvir AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a696029 Pregnancy cat. B (U.S.) Legal status ℞-only (U.S.) Routes oral Pharmacokinetic data Protein binding 98-99% Half-life 3-5 hours Excretion mostly fecal Identifiers CAS number 155213-67-5 
ATC code J05AE03 PubChem CID 392622 DrugBank APRD00312 ChemSpider 347980 
UNII O3J8G9O825 
KEGG D00427 
ChEMBL CHEMBL163 
Chemical data Formula C37H48N6O5S2 Mol. mass 720.946 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem - InChI=1S/C37H48N6O5S2/c1-24(2)33(42-36(46)43(5)20-29-22-49-35(40-29)25(3)4)34(45)39-28(16-26-12-8-6-9-13-26)18-32(44)31(17-27-14-10-7-11-15-27)41-37(47)48-21-30-19-38-23-50-30/h6-15,19,22-25,28,31-33,44H,16-18,20-21H2,1-5H3,(H,39,45)(H,41,47)(H,42,46)/t28-,31-,32-,33-/m0/s1

Key:NCDNCNXCDXHOMX-XGKFQTDJSA-N
 (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Ritonavir, with trade name Norvir (Abbott Laboratories), is an antiretroviral drug from the protease inhibitor class used to treat HIV infection and AIDS.
Ritonavir is frequently prescribed with HAART, not for its antiviral action, but as it inhibits the same host enzyme that metabolizes other protease inhibitors. This inhibition leads to higher plasma concentrations of these latter drugs, allowing the clinician to lower their dose and frequency and improving their clinical efficacy.
Contents
History
Ritonavir is manufactured as Norvir by Abbott Laboratories. Research that led to the drug's development was financed by a $3,500,000 federal grant through the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and over $200,000,000 by Abbott Labs. Most of the $200,000,000 figure cited by Abbott paid for clinical trials-despite NIH offering to pay for them-because Abbott was concerned about "public interest" responses to the high prices they projected Norvir would command.[1] The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved ritonavir on March 1, 1996, making it the seventh approved antiretroviral drug in the United States. In 2003, Abbott raised the price of a Norvir course from USD $1.71 per day to $8.57 per day, leading to claims of price gouging by patients' groups and some members of Congress. Consumer group Essential Inventions petitioned the NIH to override the Norvir patent, but the NIH announced on August 4, 2004 that it lacked the legal right to allow generic production of Norvir.[2]
Method of action
Ritonavir was originally developed as an inhibitor of HIV protease. It is one of the most complex inhibitors. It is now rarely used for its own antiviral activity, but remains widely used as a booster of other protease inhibitors. More specifically, ritonavir is used to inhibit a particular liver enzyme that normally metabolizes protease inhibitors, cytochrome P450-3A4 (CYP3A4).[3] The drug's molecular structure inhibits CYP3A4, so a low dose can be used to enhance other protease inhibitors. This discovery, which has drastically reduced the adverse effects and improved the efficacy of PI's and HAART, was first communicated in an article published in the AIDS Journal in 1997 by the University of Liverpool. This effect does come with a price: it also affects the efficacy of numerous other medications, making it difficult to know how to administer them concurrently. In addition it can cause a large number of side-effects on its own.
Drug interactions
Concomitant therapy of ritonavir with a variety of medications may result in serious and sometimes fatal drug interactions.[4] These interactions can occur with strong inhibitors, strong or moderate inducers or substrates of hepatic cytochrome P450 CYP3A4 isoform.
The list of clinically significant interactions of ritonavir includes but is not limited to following drugs:
- amiodarone - decreased metabolism, possible toxicity
- midazolam and triazolam - contraindicated
- carbamazepine - decreased metabolism, possible toxicity
- cisapride - decreased metabolism, possible prolongation of Q-T interval and life-threatening arrythmias
- disulfiram (with ritonavir oral preparation) - decreased metabolism of ritonavir
- eplerenone
- etravirine
- flecainide - decreased metabolism, possible toxicity
- MDMA
- meperidine - build-up of toxic concentrations of a metabolite possible
- nilotinib
- nisoldipine
- pimozide
- quinidine
- ranolazine
- salmeterol
- St John's wort
- statins - decreased metabolism, without dosage modification increased risk of rhabomyolisis
- thioridazine
- topotecan
- voriconazole - ritonavir increases metabolism of voriconazole
Side effects
The most common side effects of ritonavir therapy are[5]:
- asthenia, malaise
- diarrhea
- nausea and vomiting
- abdominal pain
- dizziness
- insomnia
- sweating
- taste abonormality
- metabolic
- hypercholesterolemia
- hypertriglyceridemia
- elevated transaminases
- elevated CPK
One of ritonavir's side effects is hyperglycemia. It appears that ritonavir directly inhibits the GLUT4 insulin-regulated transporter, keeping glucose from entering fat and muscle cells[citation needed]. This can lead to insulin resistance and cause problems for Type Ⅱ diabetics.
Conformational polymorphism
Norvir was originally dispensed as an ordinary capsule, which did not require refrigeration. The API of the original capsule exhibited strong conformational polymorphism. This threatened existing supplies of ritonavir as the lower energy polymorph caused the therapeutically effective polymorph to convert to the lower energy polymorph on contact. This lower energy polymorph, which was not therapeutically effective, entered production lines and effectively halted production processes.[6] After this discovery in the late 1990s, Abbot withdrew the original capsules from the market, and recommended patients switch to Norvir suspension while researchers worked to solve the problem. The capsules have been replaced with refrigerated gelcaps, to solve the crystallization problem of the original capsules. More recently Norvir has been reformulated into a white oblong solid tablet that no longer required refrigeration.
References
- ^ James Love (2004-06-03). "How much has the public invested in ritonavir, and how much has Abbott?". Essential Inventions. http://www.essentialinventions.org/drug/ei06032004.html. Retrieved 2008-05-06..
- ^ Ceci Connolly (2004-08-05). "NIH Declines to Enter AIDS Drug Price Battle". Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/articles/A40430-2004Aug4.html. Retrieved 2006-01-16.
- ^ Zeldin RK, Petruschke RA (2004). "Pharmacological and therapeutic properties of ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor therapy in HIV-infected patients". Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 53 (1): 4–9. doi:10.1093/jac/dkh029. PMID 14657084. http://jac.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/53/1/4.
- ^ http://www.merck.com/mmpe/lexicomp/ritonavir.html
- ^ http://www.rxlist.com/cgi/generic/ritonavirsol_ad.htm
- ^ Bauer J, et al. (2004). "Ritonavir: An Extraordinary Example of Conformational Polymorphism". Pharmaceutical Research 18 (6): 859–866. doi:10.1023/A:1011052932607. PMID 11474792. http://www.springerlink.com/content/k655264600tjh122/.
Further reading
- Chemburkar, Sanjay R.; Bauer, John; Deming, Kris; Spiwek, Harry; Patel, Ketan; Morris, John; Henry, Rodger; Spanton, Stephen et al. (2000). "Dealing with the Impact of Ritonavir Polymorphs on the Late Stages of Bulk Drug Process Development". Organic Process Research & Development 4 (5): 413. doi:10.1021/op000023y.
External links
- PubPK - Ritonavir pharmacokinetics
- Norvir (manufacturer's website)
- Ritonavir (patient information)
Categories:- Protease inhibitors
- Thiazoles
- World Health Organization essential medicines
- Ureas
- Carbamates
- Abbott Laboratories
- InChI=1S/C37H48N6O5S2/c1-24(2)33(42-36(46)43(5)20-29-22-49-35(40-29)25(3)4)34(45)39-28(16-26-12-8-6-9-13-26)18-32(44)31(17-27-14-10-7-11-15-27)41-37(47)48-21-30-19-38-23-50-30/h6-15,19,22-25,28,31-33,44H,16-18,20-21H2,1-5H3,(H,39,45)(H,41,47)(H,42,46)/t28-,31-,32-,33-/m0/s1
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

