- New York State Route 8
-
This article is about the current alignment of NY 8. For the former alignment of NY 8 in Orange County, see New York State Route 8 (1924–1930).
NYS Route 8 
Map of eastern New York with NY 8 highlighted in redRoute information Maintained by NYSDOT Length: 208.17 mi[2] (335.02 km) Existed: 1930[1] – present Major junctions South end: 
 NY 10 / NY 17 in Deposit
NY 10 / NY 17 in Deposit I-88 in Sidney
I-88 in Sidney
 NY 80 in New Berlin
NY 80 in New Berlin
 US 20 in Bridgewater
US 20 in Bridgewater


 I-790 / NY 5 / NY 12 in Utica
I-790 / NY 5 / NY 12 in Utica
 NY 30 in Speculator
NY 30 in Speculator
 I-87 in Chestertown
I-87 in ChestertownNorth end:  NY 9N in Hague
NY 9N in HagueLocation Counties: Delaware, Otsego, Chenango, Madison, Oneida, Herkimer, Hamilton, Warren Highway system Numbered highways in New York
Interstate • U.S. • N.Y. (former) • Reference • County←  NY 7
NY 7US 9  →
→New York State Route 8 (NY 8) is a state highway in the central part of New York in the United States. It runs in a southwest-to-northeast direction from the Southern Tier to the northern part of Lake George. The southern terminus of the route is at an interchange with NY 17 in the town of Deposit, where it begins concurrent with NY 10. Its northern terminus is at a junction with NY 9N in the town of Hague. Roughly midway between the two endpoints, NY 8 passes through Utica, where it overlaps NY 5, NY 12, and Interstate 790 (I-790) along one segment of the North–South Arterial.
NY 8 was assigned as part of the 1930 renumbering of state highways in New York and originally extended north to a ferry across Lake Champlain at Putnam Station, where it connected to Vermont Route F-10 (VT F-10). The route was realigned slightly on its northern end by 1933 to connect to another ferry leading to VT F-9 east of Ticonderoga. By the following year, it was altered again to use the new Champlain Bridge at Crown Point to connect to VT 17. This was made possible by way of a long concurrency with NY 9N and NY 22. NY 8 was truncated to its current northern terminus ca. 1968. In the 1960s and 1970s, NY 8 was moved onto new freeways around and through the city of Utica.
Contents
Route description
Southern Tier
NY 8 begins at an interchange with NY 17 in Deposit that also serves as the southern terminus of NY 10. NY 8 and NY 10 form a brief concurrency north along the West Branch of the Delaware River before separating at the southeastern edge of the Cannonsville Reservoir northeast of Deposit. While NY 10 follows the southern edge of the reservoir to the east, NY 8 continues north, passing to the east of Oquaga Creek State Park (and connecting to the park via a pair of local roads) before meeting NY 206 in Masonville. From Masonville, NY 8 heads north to Sidney, where it meets I-88 at an interchange, crosses the Susquehanna River, and intersects NY 7 before leaving the village adjacent to the Unadilla River, a tributary of the Susquehanna.
NY 8 parallels the Unadilla River northward through Mount Upton to New Berlin, where it meets NY 80. The routes overlap for a short distance to the north before NY 80 separates to the northwest toward Sherburne. NY 8, however, continues along the Unadilla River through several small communities before separating from the river just south of the Madison-Oneida County line.[3]
Utica area
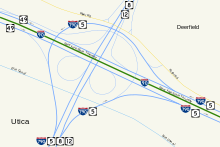
Shortly after crossing into Oneida County, NY 8 intersects U.S. Route 20 (US 20) in Bridgewater. The route continues northward, passing through Cassville and Clayville before becoming a limited-access highway just north of Clayville. Near Sauquoit, NY 8 has exits for Pinnacle Road and Elm Street prior to entering the Utica suburbs. In New Hartford, the route has an exit with Genesee Street prior to meeting NY 5 and NY 12 at a cloverleaf interchange southwest of downtown Utica. While the right-of-way of NY 8 continues to the northeast through the cloverleaf as NY 840, NY 8 joins NY 5 and NY 12 as the three routes enter downtown on the North–South Arterial.
Near the northern edge of downtown, NY 5, NY 8, and NY 12 interchange with NY 5A and NY 5S on the southern bank of the Mohawk River. At the exit, the three states are joined on the arterial by I-790, which follows NY 5, NY 8, and NY 12 across the Mohawk River and the neighboring Erie Canal to a large interchange north of the canal. Here, I-790 and NY 5 separate from the concurrency while NY 8 and NY 12 remain concurrent into Deerfield as a limited-access highway. After an interchange with a former routing of NY 12, NY 8 separates from the highway and returns to an at-grade roadway as it heads northeast to Poland. Near the Oneida-Herkimer County line (here delimited by West Canada Creek), NY 8 merges with NY 28 and follows the route across the county line (as well as the creek) into Poland. In the center of the village, NY 8 splits from NY 28 and heads northeast into Adirondack Park.[3]
Adirondack Park
Within Adirondack Park, NY 8 follows a northeast–southwest routing as it crosses the lower half of the park. Near Ohio, NY 8 intersects NY 365 due north of where it enters the park. Past NY 365, NY 8 becomes signed as an east–west highway as it heads east to Higgins Bay, where it intersects the northern terminus of NY 10. The route continues northeast to Speculator, where it meets NY 30. NY 30 turns east onto NY 8, forming an overlap southeast to Wells, where NY 8 separates from NY 30 and heads to the northeast into Warren County.
In Wevertown, NY 8 intersects NY 28 for the final time prior to meeting US 9 at Loon Lake. The two routes merge, forming an overlap east to Chestertown, where US 9 splits from NY 8 and continues south. NY 8, however, heads east, meeting I-87 shortly after departing US 9. Past I-87, NY 8 follows the southern edge of Brant Lake to the northeast before turning to the east toward Hague, where it terminates at NY 9N.[3]
History
Origins and terminus changes
In the 1930 renumbering of state highways in New York, NY 8 was assigned to most of its current alignment from Deposit to Hague.[1][4] The route also extended eastward to Wright (southeast of Ticonderoga) on modern NY 9N, NY 22, and County Route 2 (CR 2), where it connected to VT F-10 by way of a ferry across Lake Champlain.[4] From Clayville to Utica, NY 8 was originally routed along Oneida Street before overlapping with NY 5 and NY 12 along Genesee Street in downtown Utica.[5] After crossing the Mohawk River and the Erie Canal, the three routes separated at the intersection of Herkimer Road, Trenton Road, and Coventry Avenue northeast of downtown. NY 8 then followed Coventry Avenue and Walker Road northeast to Deerfield, where NY 8 joined its modern alignment.[6]
Prior to 1930, what became NY 8 in the renumbering carried multiple designations along its routing. In 1924, the segment of Genesee Street in Utica that became NY 8 was designated as part of NY 5 and NY 12. Additionally, the portion of NY 8 from Wevertown to Chestertown became part of NY 10. The segment from the modern intersection of US 9 and NY 8 to Chestertown was also designated as part of NY 6.[7] By 1926, what became NY 8 from Sidney to New Berlin and from Bridgewater to downtown Utica was designated as NY 44. Between New Berlin and Bridgewater, NY 44 followed what is now NY 80 through Edmeston to West Burlington and NY 51 from West Burlington to US 20. NY 44 overlapped US 20 west to Bridgewater. From Utica to Wells, the 1930 routing of NY 8 was part of NY 54. Between Chestertown and Ticonderoga, NY 8 was designated NY 47.[8] Until the renumbering, what became NY 8 was unbuilt from Deposit to Masonville and unnumbered from Masonville to Sidney.[4] Additionally, the segments from New Berlin to Bridgewater and from Wells to Wevertown were unnumbered.[8]
NY 8 was rerouted by 1933 to exit Ticonderoga to the east, using what is now NY 74 to reach Lake Champlain instead. At the lake, NY 8 connected to VT F-9 via the Fort Ticonderoga – Larrabees Point Ferry.[9] The route was realigned again ca. 1934 to follow NY 9N and NY 22 north from Ticonderoga to south of Port Henry, where NY 8 turned northeast to follow what is now NY 185 to the Champlain Bridge. The route became VT 17 on the opposite lakeshore.[9][10] NY 8 was truncated to Hague ca. 1968, eliminating its overlaps with NY 9N and NY 22.[11][12]
Relocation onto expressways
In the early 1950s, construction began on a new arterial highway—known as the North–South Arterial—through downtown Utica.[13][14] The first portion of the highway to open was the segment between River Road and Trenton Road, which was completed by 1956.[15] It was extended southward to Oriskany Street (NY 5A) by 1961[16] and completed entirely by 1964; however, NY 8 was not initially realigned to follow the highway.[17] In the mid-1960s, plans were made to construct a new limited-access highway along the NY 8 corridor from Clayville north to New Hartford, where it would connect with the North–South Arterial.[12]
The freeway was constructed and completed in the early 1970s. NY 8 was realigned to follow the highway to New Hartford, from where it continued through Utica on the Arterial and I-790. It rejoined its previous alignment at I-790's interchange with Genesee Street. During this same period, the section of NY 12 between Deerfield and South Trenton was moved onto a new freeway built adjacent to NY 12's original alignment. A connector between NY 12 and NY 8 by way of the Miller Road corridor was built at this time.[18][19] NY 8 was rerouted in the mid-1970s to follow NY 12 north to its exit with the connector.[20][21] Here, NY 8 left NY 12 and continued east on the connector to rejoin its original alignment at Walker Road. Ownership and maintenance of NY 8's former routing north of the Utica city limits was transferred to Oneida County, which designated the highway as CR 92.[22]
Major intersections
County Location Mile[2] Destinations Notes Delaware Village of Deposit 0.00 
 NY 10 / NY 17
NY 10 / NY 17Exit 84 (NY 17); southern terminus of NY 8 / NY 10 overlap; southern terminus of NY 10 2.14  NY 10 north
NY 10 northNorthern terminus of NY 8 / NY 10 overlap Masonville 15.29  NY 206
NY 206Village of Sidney 19.84  I-88
I-88Exit 9 (I-88) Otsego Town of Unadilla 21.69  NY 7
NY 7Chenango Guilford 29.96  NY 51
NY 51Southern terminus of NY 51 Town of New Berlin 37.94  NY 23
NY 23Village of New Berlin 45.68  NY 80 east
NY 80 eastSouthern terminus of NY 8 / NY 80 overlap Town of New Berlin 46.95  NY 80 west
NY 80 westNorthern terminus of NY 8 / NY 80 overlap Oneida Village of Bridgewater 64.60  US 20
US 20Utica 79.89 

 NY 5 west / NY 12 south / NY 840
NY 5 west / NY 12 south / NY 840Cloverleaf interchange; southern terminus of NY 5 / NY 8 and NY 8 / NY 12 overlaps; eastern terminus of NY 840 83.18 

 I-790 / NY 5A / NY 5S
I-790 / NY 5A / NY 5SEastern terminus of NY 5A; western terminus of NY 5S; southern terminus of I-790 / NY 8 overlap; southern terminus of I-790 84.05 

 I-790 north / NY 5 east to NY 49
I-790 north / NY 5 east to NY 49Northern terminus of I-790 / NY 8 and NY 5 / NY 8 overlaps; eastern terminus of NY 49; to I-90 / Thruway (via I-790 / NY 5) Deerfield 89.17  NY 12 north
NY 12 northNorthern terminus of NY 8 / NY 12 overlap 95.92  NY 28 north
NY 28 northSouthern terminus of NY 8 / NY 28 overlap Herkimer Poland 97.42  NY 28 south
NY 28 southNorthern terminus of NY 8 / NY 28 overlap Ohio 111.11  NY 365
NY 365Eastern terminus of NY 365 Hamilton Arietta 133.51  NY 10
NY 10Northern terminus of NY 10 Speculator 145.76  NY 30 north
NY 30 northSouthern terminus of NY 8 / NY 30 overlap Wells 155.46  NY 30 south
NY 30 southNorthern terminus of NY 8 / NY 30 overlap Warren Johnsburg 178.87  NY 28
NY 28Chester 184.56  US 9 north
US 9 northSouthern terminus of US 9 / NY 8 overlap 188.38  US 9 south
US 9 southNorthern terminus of US 9 / NY 8 overlap 189.86  I-87
I-87Exit 25 (I-87) Hague 208.17  NY 9N
NY 9N1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi References
- ^ a b Dickinson, Leon A. (January 12, 1930). "New Signs for State Highways". The New York Times: p. 136.
- ^ a b "2008 Traffic Data Report for New York State" (PDF). New York State Department of Transportation. June 16, 2009. pp. 99–101. https://www.nysdot.gov/divisions/engineering/technical-services/hds-respository/NYSDOT_Traffic_Data_Report_2008.pdf. Retrieved December 8, 2009.
- ^ a b c Rand McNally (2008). The Road Atlas (Map). p. 71, section NI14-NM14.
- ^ a b c Automobile Legal Association (ALA) Automobile Green Book, 1930/31 and 1931/32 editions, (Scarborough Motor Guide Co., Boston, 1930 and 1931). The 1930/31 edition shows New York state routes prior to the 1930 renumbering
- ^ Automobile Legal Association (ALA) Automobile Green Book (1931–32 ed.). Boston: Scarborough Motor Guide Co. 1931.
- ^ Standard Oil Company of New York (1930). Road Map of New York (Map). Cartography by General Drafting.
- ^ "New York's Main Highways Designated by Numbers". The New York Times: p. XX9. December 21, 1924.
- ^ a b Rand McNally and Company (1926). Rand McNally Auto Road Atlas (eastern New York) (Map). http://www.broermapsonline.org/members/NorthAmerica/UnitedStates/Midatlantic/NewYork/unitedstates1926ra_009.html. Retrieved December 26, 2009.
- ^ a b Texas Oil Company (1932). Texaco Road Map – New England (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company.
- ^ Texas Oil Company (1934). Road Map of New York (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company.
- ^ United States Geological Survey (1967). Glens Falls, NY Quadrangle (Map). 1:250,000. Eastern United States 1:250,000. http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/topo/250k/txu-pclmaps-topo-us-glens_falls-1967.jpg. Retrieved December 7, 2007.
- ^ a b Esso (1968). New York (Map). Cartography by General Drafting (1969–70 ed.).
- ^ Sunoco (1952). New York (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company.
- ^ Esso (1954). New York with Special Maps of Putnam–Rockland–Westchester Counties and Finger Lakes Region (Map). Cartography by General Drafting (1955–56 ed.).
- ^ Esso (1956). New York with Special Maps of Putnam–Rockland–Westchester Counties and Finger Lakes Region (Map). Cartography by General Drafting (1957 ed.).
- ^ Sunoco (1961). New York and Metropolitan New York (Map). Cartography by H.M. Gousha Company (1961–62 ed.).
- ^ Sinclair (1964). New York and Metropolitan New York (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company.
- ^ New York State Thruway Authority (1971). New York Thruway (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company.
- ^ Shell Oil Company (1973). New York (Map). Cartography by H.M. Gousha Company (1973 ed.).
- ^ Gulf (1974). New York and New Jersey Tourgide Map (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company.
- ^ Exxon (1977). New York (Map). Cartography by General Drafting (1977–78 ed.).
- ^ New York State Department of Transportation (1978). South Trenton Digital Raster Quadrangle (Map). 1:24,000. http://www.nysgis.state.ny.us/gisdata/quads/drg24/dotpreview/index.cfm?code=o37. Retrieved December 26, 2009.
External links
- Alps' Roads – New York State Route 8
- New York Routes – New York State Route 8
- New York State Highway Termini – New York State Route 8
- NY Route 8: Southern Adirondack Trail
 Highways in Essex County, New York
Highways in Essex County, New YorkInterstate 87 • New York State Route 185 • New York State Route 192 • New York State Route 373 • New York State Route 431 • New York State Route 910K • New York State Route 910M • New York State Route 912T • New York State Route 913Q • New York State Route 915F • New York State Route 915K
 Highways in Hamilton County, New York
Highways in Hamilton County, New YorkNew York State Route 8 • New York State Route 10 • New York State Route 28 • New York State Route 28N • New York State Route 30
Categories:- State highways in New York
- Transportation in Chenango County, New York
- Transportation in Delaware County, New York
- Transportation in Hamilton County, New York
- Transportation in Herkimer County, New York
- Transportation in Madison County, New York
- Transportation in Oneida County, New York
- Transportation in Otsego County, New York
- Transportation in Warren County, New York
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.