- Telmisartan
-
Telmisartan 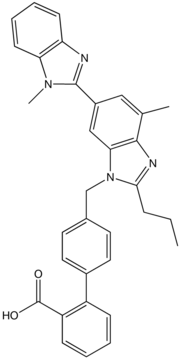
Systematic (IUPAC) name 2-(4-{[4-methyl-6-(1-methyl-1H-1,3-benzodiazol-2-yl)-2-propyl-1H-1,3-benzodiazol-1-yl]methyl}phenyl)benzoic acid Clinical data Trade names Micardis AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a601249 Pregnancy cat. D (Au), D (U.S.) Legal status S4 (Au), POM (UK), ℞-only (U.S.) Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 42–100% Protein binding ≥99.5% Metabolism Minimal hepatic Half-life 24 hours Excretion Faecal 97% Identifiers CAS number 144701-48-4 
ATC code C09CA07 PubChem CID 65999 IUPHAR ligand 592 DrugBank APRD01247 ChemSpider 59391 
UNII U5SYW473RQ 
KEGG D00627 
ChEBI CHEBI:9434 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1017 
Chemical data Formula C33H30N4O2 Mol. mass 514.617 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Telmisartan (INN) (
 /tɛlmɪˈsɑrtən/) is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist (angiotensin receptor blocker, ARB) used in the management of hypertension. It is marketed under the trade name Micardis (by Boehringer Ingelheim), among others.
/tɛlmɪˈsɑrtən/) is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist (angiotensin receptor blocker, ARB) used in the management of hypertension. It is marketed under the trade name Micardis (by Boehringer Ingelheim), among others.Contents
Indication
Telmisartan is indicated in the treatment of essential hypertension.[1]
Administration
The usually effective dose telmisartan is (20–)40–80 mg once daily. Some patients may already benefit at a daily dose of 20 mg. In cases where the target blood pressure is not achieved, telmisartan dose can be increased to a maximum of 80 mg once daily.[1]
Contraindications
Telmisartan is contraindicated during pregnancy. Like other drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), telmisartan can cause birth defects, stillbirths, and neonatal deaths. It should not be taken by breastfeeding women since it is not known whether the drug passes into the breast milk.[2]
Side effects
Side effects are similar to other angiotensin II receptor antagonists and include tachycardia and bradycardia (fast or slow heartbeat), hypotension (low blood pressure), edema (swelling of arms, legs, lips, tongue, or throat, the latter leading to breathing problems), and allergic reactions.[2]
Mode of action
Telmisartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker that shows high affinity for the angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1), with a binding affinity 3000 times greater for AT1 than AT2. It has the longest half-life of any ARB (24 hours)[1][3] and the largest volume of distribution.[citation needed]
In addition to blocking the RAs, telmisartan acts as a selective modulator of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), a central regulator of insulin and glucose metabolism. It is believed that telmisartan’s dual mode of action may provide protective benefits against the vascular and renal damage caused by diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD).[3]
Clinical trials
ONTARGET
The ONTARGET Trial Programme (The Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial) was one of the largest ARB clinical study programmes ever undertaken.[4] 25,620 patients from 733 centres in 41 countries were randomised for 5.5 years of treatment of either telmisartan, the ACE inhibitor ramipril or a combination of the two. The study aimed to investigate the role of telmisartan in cardiovascular (CV) protection through the primary composite outcome of death from CV causes, myocardial infarction, stroke or hospilization for heart failure, in high CV risk patients.
The study showed that telmisartan was as effective as ramipril but with lower rates of cough and angioedema which led to fewer discontinuations. The combination group experienced similar efficacy but with increased risk of hypotensive symptoms. Moreover, in a patient population selected to tolerate ACE inhibitors, telmisartan was shown to be better tolerated and associated with higher treatment compliance than ramipril.[5]
TRANSCEND
As part of the ONTARGET study, patients who could not tolerate ACE inhibitors were randomly assigned to receive either telmisartan or placebo as part of the TRANSCEND (Telmisartan Randomized Assessment Study in ACE Intolerant Subjects with Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)) study. An accompanying editorial comments: "Overall, data supporting use of angiotensin-receptor blockers to prevent vascular events in various cardiovascular groups, other than heart failure, are incomplete. TRANSCEND's results challenge the non-inferiority shown in ONTARGET and suggest no more than a modest effect, if any at all."[6]
PRoFESS
PRoFESS (Prevention Regimen For Effectively Avoiding Second Strokes) investigated therapy with telmisartan initiated soon after an ischemic stroke and continued for 2.5 years. This treatment did not significantly lower the rate of recurrent stroke, major cardiovascular events, or diabetes.[7]
Trade names
Apart from the original name Micardis, telmisartan is marketed as Telpres (Abbott Healthcare Pvt Ltd-India), Targit (Pfizer India), Axeten (Organon India), Temax (Wockhardt), Telma (Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd.) and Telmore (Morepen), and others.
See also
References
- ^ a b c Pritor prescribing information
- ^ a b Drugs.com: Micardis
- ^ a b Benson, S. C.; Pershadsingh, H.; Ho, C.; Chittiboyina, A.; Desai, P.; Pravenec, M.; Qi, N.; Wang, J. et al. (2004). "Identification of Telmisartan as a Unique Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist with Selective PPAR -Modulating Activity". Hypertension 43 (5): 993. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000123072.34629.57. PMID 15007034.
- ^ Ontarget, I.; Yusuf, S.; Teo, K.; Pogue, J.; Dyal, L.; Copland, I.; Schumacher, H.; Dagenais, G. et al. (2008). "Telmisartan, Ramipril, or Both in Patients at High Risk for Vascular Events". New England Journal of Medicine 358 (15): 1547. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0801317. PMID 18378520.
- ^ Bayer Healthcare: Telmisartan approved by the European Commission to reduce the risk of cardiovascular (CV) morbidity in a broad spectrum of at risk patients
- ^ Ripley, T. L.; Harrison, D. (2008). "The power to TRANSCEND". The Lancet 372 (9644): 1128. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61243-X. PMID 18757086.
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00153062 PRoFESS - Prevention Regimen For Effectively Avoiding Second Strokes
Antihypertensives: agents acting on the renin-angiotensin system (C09) ACE inhibitors
("-pril")Sulfhydryl-containing: Captopril • Zofenopril
Dicarboxylate-containing: Enalapril# • Ramipril • Quinapril • Perindopril • Lisinopril (+HCT) • Benazepril
Phosphonate-containing: Fosinopril
Other/ungrouped: Alacepril • Cilazapril • Delapril • Imidapril • Moexipril • Rentiapril • Spirapril • Temocapril • TrandolaprilAIIRAs/
("-sartan")Azilsartan • Candesartan • Eprosartan • Irbesartan • Losartan • Olmesartan • Tasosartan§ • Telmisartan (+HCT) • Valsartan (+HCT)Renin inhibitors/
("-kiren")#WHO-EM. ‡Withdrawn from market. Clinical trials: †Phase III. §Never to phase III Categories:- Angiotensin II receptor antagonists
- Benzimidazoles
- Benzoic acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
