- Mud volcano
-
 A series of mud volcanoes in Gobustan, Azerbaijan
A series of mud volcanoes in Gobustan, Azerbaijan
 Mud volcano in the Gulf of Mexico sea bottom
Mud volcano in the Gulf of Mexico sea bottom
- The geothermal phenomena known as "mud volcanoes" are often not true mud volcanoes (pelovolcano). See mudpot for further information.
The term mud volcano or mud dome are used to refer to formations created by geo-excreted liquids and gases, although there are several different processes which may cause such activity. Hot water mixes with mud and surface deposits. Mud volcanoes are associated with subduction zones and about 700 have been identified. Temperatures are much cooler in these processes than found at igneous volcanoes. The largest mud volcano structures are 10 kilometres (6 mi) in diameter and reach 700 metres (2,300 ft) in height.[citation needed][where?]
About 86% of the gas released from these structures is methane, with much less carbon dioxide and nitrogen emitted. Ejected materials are often a slurry of fine solids suspended in liquids which may include water, which is frequently acidic or salty, and hydrocarbon fluids.
Possible mud volcanoes have been identified on Mars.[1]
Contents
Details
A mud volcano may be the result of a piercement structure created by a pressurized mud diapir which breaches the Earth's surface or ocean bottom. Their temperatures may be as low as the freezing point of the ejected materials, particularly when venting is associated with the creation of hydrocarbon clathrate hydrate deposits. Mud volcanoes are often associated with petroleum deposits and tectonic subduction zones and orogenic belts; hydrocarbon gases are often erupted. They are also often associated with lava volcanoes; in the case of such close proximity, mud volcanoes emit incombustible gases including helium, whereas lone mud volcanoes are more likely to emit methane.
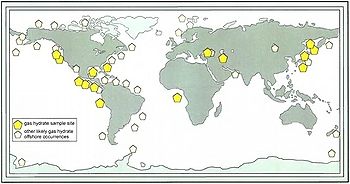
Approximately 1,100 mud volcanoes have been identified on land and in shallow water. It has been estimated that well over 10,000 may exist on continental slopes and abyssal plains.
Features
- Gryphon: steep-sided cone shorter than 3 meters that extrudes mud
- Mud cone: high cone shorter than 10 meters that extrudes mud and rock fragments
- Scoria cone: cone formed by heating of mud deposits during fires
- Salse: water-dominated pools with gas seeps
- Spring: water-dominated outlets smaller than 0.5 meters
- Mud shield
Emissions
Most liquid and solid material is released during eruptions, but various seeps occur during dormant periods.
First order estimates of mud volcano emissions have recently been made (1 Tg = 1 million metric tonnes).
- 2002: L.I. Dimitrov estimated that 10.2–12.6 Tg/yr of methane is released from onshore and shallow offshore mud volcanoes.
- 2002: Etiope and Klusman estimated at least 1–2 and as much as 10–20 Tg/yr of methane may be emitted from onshore mud volcanoes.
- 2003: Etiope, in an estimate based on 120 mud volcanoes: "The emission results to be conservatively between 5 and 9 Tg/yr, that is 3–6% of the natural methane sources officially considered in the atmospheric methane budget. The total geologic source, including MVs (this work), seepage from seafloor (Kvenvolden et al., 2001), microseepage in hydrocarbon-prone areas and geothermal sources (Etiope and Klusman, 2002), would amount to 35–45 Tg/yr."[2]
- 2003: analysis by Milkov et al. suggests that the global gas flux may be as high as 33 Tg/yr (15.9 Tg/yr during quiescent periods plus 17.1 Tg/yr during eruptions). Six teragrams per year of greenhouse gases are from onshore and shallow offshore mud volcanoes. Deep-water sources may emit 27 Tg/yr. Total may be 9% of fossil CH4 missing in the modern atmospheric CH4 budget, and 12% in the preindustrial budget.[3]
- 2003: Alexei Milkov estimated approximately 30.5 Tg/yr of gases (mainly methane and CO2) may escape from mud volcanoes to the atmosphere and the ocean.[4]
- 2003: Achim J. Kopf estimated 1.97×1011 to 1.23×1014 m³ of methane is released by all mud volcanoes per year, of which 4.66×107 to 3.28×1011 m³ is from surface volcanoes.[5] That converts to 141–88,000 Tg/yr from all mud volcanoes, of which 0.033–235 Tg is from surface volcanoes.
Locations
Europe
There are generally few mud volcanoes in Europe, but dozens can be found on the Taman Peninsula of Russia and the Kerch Peninsula of southeastern Ukraine. In Italy, they are common in the northern front of the Apennines and in Sicily. Another relatively accessible place where mud volcanoes can be found in Europe are the Berca Mud Volcanoes near Berca in Buzău County, Romania, close to the Carpathian Mountains.
Asia
Lusi (Indonesia)
Drilling[6][7][8] or an earthquake[9][10] may have resulted in the Sidoarjo mud flow on May 29, 2006, in the Porong subdistrict of East Java province, Indonesia. The mud covered about 440 hectares, 1,087 acres (4.40 km2) (2.73mi^2), and inundated four villages, homes, roads, rice fields, and factories, displacing about 24,000 people and killing 14. The gas exploration company involved was operated by PT Lapindo Brantas and the earthquake that may have triggered the Mud Volcano was the Yogyakarta earthquake of May 27, 2006. In 2008, it was termed the world's largest mud volcano and is beginning to show signs of catastrophic collapse, according to geologists who have been monitoring it and the surrounding area. A catastrophic collapse could sag the vent and surrounding area by up to 150 metres (490 ft) in the next decade. In March 2008, the scientists observed drops of up to 3 metres (9.8 ft) in one night. Most of the subsidence in the area around the volcano is more gradual, at around 0.1 centimetres (0.039 in) per day. A study by a group of Indonesian geo-scientists led by Bambang Istadi predicted the area affected by the mudflow over a ten year period.[11] More recent studies carried out in 2011 predict that the mud will flow for another 20 years, or even longer. [12] Now named Lusi – a contraction of Lumpur Sidoarjo, where lumpur is the Indonesian word for "mud" – the mud volcano appears to be a hydrocarbon/hydrothermal hybrid.
Central Asia
Many mud volcanoes exist on the shores of the Black Sea and Caspian Sea. Tectonic forces and large sedimentary deposits around the latter have created several fields of mud volcanoes, many of them emitting methane and other hydrocarbons. Features over 200 metres (656 ft) high exist in Azerbaijan, with large eruptions sometimes producing flames of similar scale (see below). Iran and Pakistan also possess mud volcanoes in the Makran range of mountains in the south of the two countries. In fact, the world's largest and highest volcano is located in Balochistan, Pakistan.[13]
Azerbaijan
Main article: Gobustan State ReserveAzerbaijan and its Caspian coastline are home to nearly 400 mud volcanoes, more than half the total throughout the continents. In 2001, one mud volcano 15 kilometres (9 mi) from Baku made world headlines when it suddenly started ejecting flames 15 metres (49 ft) high.[14]
In Azerbaijan, eruptions are driven from a deep mud reservoir which is connected to the surface even during dormant periods, when seeping water still shows a deep origin. Seeps have temperatures up to 2 °C (3.6 °F) - 3 °C (5.4 °F) above the ambient temperature.[15]
Iran
There are many mud volcanoes in Iran: in Hormozgan province, Sistan and Baluchestan Province and Golestan Province.
India
The island of Baratang, part of the Great Andaman archipelago in the Andaman Islands, Indian Ocean, has several sites of mud volcanic activity. There was a significant eruption event in 2003.
Pakistan
In Pakistan there are more than 80 active mud volcanoes in Balochistan province; there are about 10 locations having clusters of mud volcanoes. In the west, in Gwadar District, the mud volcanoes are very small and mostly sit in the south of Jabal-e-Mehdi toward Sur Bandar. Many more exist in the north-east of Ormara. The remainder are in Lasbela District and are scattered between south of Gorangatti on Koh Hinglaj to Koh Kuk in the North of Miani Hor in the Hangol Valley. In this region, the heights of mud volcanoes range between 800 to 1,550 feet (243.8 to 472.4 m).[citation needed] The most famous is Chandaragup. The biggest crater found at 25°33'13.63"N. 65°44'09.66"E is about 450 feet (137.16 m) in diameter. Most mud volcanoes in this region are situated in out-of-reach areas having very difficult terrain. Dormant mud volcanoes stand like columns of mud in many other areas.[citation needed]
Philippines
In the Turtle Islands, in the province of Tawi-Tawi, the southwestern edge of the Philippines bordering Malaysia, presence of mud volcanoes are evident on three of the islands - Lihiman, Great Bakkungan and Boan Islands. The northeastern part of Lihiman Island is distinguished for having more violent kind of mud extrusions mixed with large pieces of rocks, creating a 20-m (66-ft) wide crater on that hilly part of the island.[16] Such extrusions are reported to be accompanied by mild earthquakes and evidence of extruded materials can be found high up the surrounding trees. Submarine mud extrusions off the island, have also been observed by local residents.[17]
Other Asian locations
- China has a number of mud volcanoes in Xinjiang province.
- There are also mud volcanoes at the Arakan Coast in Myanmar (Burma).
- There are two active mud volcanoes in South Taiwan, and several inactive ones. The Wushan Mud Volcanoes (烏山頂泥火山 in Chinese) are located in the Yanchao District of Kaohsiung City.
- There are mud volcanoes on the island of Pulau Tiga, off the western coast of the Malaysian state of Sabah on Borneo.
- A drilling accident offshore of Brunei on Borneo in 1979 caused a mud volcano which took 20 relief wells and nearly 30 years to halt the eruption.
North America
Mud volcanoes of the North American continent include:
- A field of small (<2 metres (6.6 ft) high) fault controlled cold mud volcanoes is located on California's Mendocino Coast, near Glenblair and Fort Bragg, California. The fine grained clay is occasionally harvested by local potters.[18]
- Shrub and Klawasi mud volcanoes in the Copper River basin by the Wrangell Mountains, Alaska. Emissions are mostly CO2 and nitrogen; the volcanoes are associated with magmatic processes.
- An unnamed mud volcano 30 metres (98 ft) high and with a top about 100 metres (328 ft) wide, 24 kilometres (15 mi) off Redondo Beach, California, and 800 metres (2,620 ft) under the surface of the Pacific Ocean.
- A field of small (<3 metres (9.8 ft)) mud volcanoes in the Salton Sea geothermal area near the town of Niland, California. Emissions are mostly CO2.
- Smooth Ridge mud volcano in 1,000 metres (3,280 ft) of water near Monterey Canyon, California.
- Kaglulik mud volcano, 43 metres (141 ft) under the surface of the Beaufort Sea, near the northern boundary of Alaska and Canada. Petroleum deposits are believed to exist in the area.
- Maquinna mud volcano, located 16–18 kilometres (9.9–11 mi) west of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada.
- There are many mud volcanoes in Trinidad and Tobago in the Caribbean, near oil reserves in southern parts of the island of Trinidad. As of August 15, 2007, the mud volcano titled the Moruga Bouffle was said to being spitting up methane gas which shows signs that it is definitely active. There are also several other mud volcanoes in the tropical island which include:
- the Devils Woodyard mud volcano near Hindustan
- the Moruga Bouffe mud volcano near Moruga
- the Piparo mud volcano
- the Chatham mud volcano located underwater in the Columbus Channel; this mud volcano periodically produces a short-lived island.
 Yellowstone's "Mud Volcano" feature[19]
Yellowstone's "Mud Volcano" feature[19]
Yellowstone's "Mud Volcano"
The name of Yellowstone National Park's "Mud Volcano" feature and the surrounding area is misleading; it consists of hot springs, mud pots and fumaroles, rather than a true mud volcano. Depending upon the precise definition of the term mud volcano, the Yellowstone formation could be considered a hydrothermal mud volcano cluster. The feature is much less active than in its first recorded description, although the area is quite dynamic. Yellowstone is an active geothermal area with a magma chamber near the surface, and active gases are chiefly steam, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide.However, there are some Mud Volcanoes and Mud Geysers elsewhere in Yellowstone. One, the "Vertically Gifted Cyclic Mud Pot" sometimes acts as a geyser, throwing mud up to 30 feet high. [20]
The mud volcano in Yellowstone was previously a mound, until suddenly, it tore itself apart into the formation seen today.[21]
South America
Venezuela
The eastern part of Venezuela contains several mud volcanoes, all of them, as in Trinidad, having an origin related to oil deposits. The image shows the Volcán de lodo de Yagrumito, about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) from Maturín, Venezuela. Its mud contains, water, biogenic gas, a certain amount of hydrocarbons and an important quantity of salt. Cows from the savanna often gather around to lick the dried mud for its salt content, which is an integral part of their diet needed to produce milk.
Colombia
Volcan El Totumo,[22] which marks the division between Bolívar and Atlantico in Colombia. This volcano is approximately 50 feet (15 m) high and can accommodate 10 to 15 people on its crater; many tourists and locals visit this volcano due to the medicinal benefits of the mud; the volcano is located next to a cienaga, or lake. This volcano is currently under legal dispute between the Bolivar and Atlantico Departamentos because of its tourist value.
External Link
See also
- Abiogenic petroleum origin
- Asphalt volcano
- Black smoker
- Cold seep
- Hydrothermal vent
- Lahar - mud flow
- Methane hydrate
- Nikolai Kudryavtsev
- Sand volcano
- Seamount
- Volcano - igneous volcano
Notes
- ^ "Mars domes may be 'mud volcanoes'". BBC. March 26, 2009. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/7966437.stm. Retrieved 2009-03-27.
- ^ Etiope, Giuseppe (2003). "A NEW ESTIMATE OF GLOBAL METHANE FLUX TO THE ATMOSPHERE FROM ONSHORE AND SHALLOW SUBMARINE MUD VOLCANOES". Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs. pp. 115. "A NEW ESTIMATE OF GLOBAL METHANE FLUX TO THE ATMOSPHERE FROM ONSHORE AND SHALLOW SUBMARINE MUD VOLCANOES". XVI INQUA Congress. http://gsa.confex.com/gsa/inqu/finalprogram/abstract_53365.htm. Retrieved April 20, 2005.
- ^ Milkov, A. V., R. Sassen, T. V. Apanasovich, and F. G. Dadashev (2003). "Global gas flux from mud volcanoes: A significant source of fossil methane in the atmosphere and the ocean". Geophys. Res. Lett. 30 (2): 1037. doi:10.1029/2002GL016358.
- ^ "Global Distribution and Significance of Mud Volcanoes". AAPG Annual Meeting 2003: Energy - Our Monumental Task. Archived from the original on November 18, 2005. http://web.archive.org/web/20051118210840/http://aapg.confex.com/aapg/sl2003/techprogram/paper_77807.htm. Retrieved April 20, 2005.
- ^ Achim J. Kopf (2003). "Global methane emission through mud volcanoes and its past and present impact on the Earth's climate". International Journal of Earth Sciences 92 (5): 806–816. doi:10.1007/s00531-003-0341-z. ISSN 1437-3254 (Paper) ISSN 1437-3262 (Online)
- ^ Davies, R.J., Brumm, M., Manga, M., Rubiandini, R., Swarbrick, R., Tingay, M. (2008). "The East Java mud volcano (2006 to present): an earthquake or drilling trigger?". Earth and Planetary Science Letters 272 (3-4): 627–638.
- ^ Sawolo, N., Sutriono, E., Istadi, B., Darmoyo, A.B. (2009). "The LUSI mud volcano triggering controversy: was it caused by drilling?". Marine & Petroleum Geology 26 (9): 1766–1784. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.04.002.
- ^ Sawolo, N., Sutriono, E., Istadi, B., Darmoyo, A.B. (2010). "Was LUSI caused by drilling? – Authors reply to discussion". Marine & Petroleum Geology 27 (7): 1658–1675. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.01.018.
- ^ Mazzini, A., Svensen, H., Akhmanov, G.G., Aloisi, G., Planke, S., Malthe-Sorenssen, A., Istadi, B. (2007). "Triggering and dynamic evolution of the LUSI mud volcano, Indonesia". Earth and Planetary Science Letters 261 (3-4): 375–388.
- ^ Mazzini, A., Nermoen, A., Krotkiewski, M., Podladchikov, Y., Planke, S., Svensen, H. (2009). "Strike-slip faulting as a trigger mechanism for overpressure release through piercement structures. Implications for the LUSI mud volcano, Indonesia". Marine and Petroleum Geology 26(8): 1751–1765.
- ^ Istadi, B., Pramono, G.H., Sumintadireja, P., Alam, S. (2009). "Simulation on growth and potential Geohazard of East Java Mud Volcano, Indonesia". Marine & Petroleum Geology, Mud volcano special issue 26: 1724–1739.
- ^ Dennis Normile (24 February 2011). "Indonesia's Infamous Mud Volcano Could Outlive All of Us". Science (AAAS). http://news.sciencemag.org/sciencenow/2011/02/indonesias-infamous-mud-volcano-.html?ref=hp. Retrieved 15 April 2011.
- ^ http://pakistaniat.com/2007/03/02/mud-volcanoes-volcano-balochistan-baluchistan-hingol-offroad-makran-pasni-hinglaj/
- ^ "Azeri mud volcano flares". BBC News. October 29, 2001. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/1626310.stm. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
- ^ S. Planke, H. Svensen, M. Hovland, D. A. Banks, B. Jamtveit (December 2003). "Mud and fluid migration in active mud volcanoes in Azerbaijan". Geo-Marine Letters 23 (3–4): 258–268. doi:10.1007/s00367-003-0152-z.
- ^ "Geo-physical Features of Philippine Turtle Island". Ocean Ambassadors Track a Turtle. Retrieved on 2010-10-05.
- ^ "Lihiman Island". Ocean Ambassadors Track a Turtle. Retrieved on 2010-10-05.
- ^ "Discover northern california". Independent Travel Tours. http://www.gfxedge.com/itt/discover_northern_california.shtml. Retrieved 25 February 2010.
- ^ NPS, Peaco, 1998
- ^ "Mud volcano". USGS Photo glossary of volcano terms. Archived from the original on April 4, 2005. http://web.archive.org/web/20050404035116/http://volcanoes.usgs.gov/Products/Pglossary/MudVolcano.html. Retrieved April 20, 2005.
- ^ Whittlesey, Lee (1995) [1995]. Death in Yellowstone: Accidents and Foolhardiness in the First National Park. Lanham, Maryland: Roberts Rinehart Publishers. ISBN 1-5709802-1-7.
- ^ http://www.isic.org/sisp/index.htm?fx=event&event_id=29975
External links
- Origin of mud volcanoes
- Cold water mud volcanoes created by artesian pressure in Minnesota's Nemadji River basin
- Bulletin Of Mud Volcanology Azerbaijan Academy Of Sciences (in English)
- Gaia's Breath—Methane and the Future of Natural Gas - USGS, June 2003
- Azeri mud volcano flares - October 29, 2001, BBC report
- Redondo Beach mud volcano with methane hydrate deposits
- Hydrocarbons Associated with Fluid Venting Process in Monterey Bay, California
- Hydrothermal Activity and Carbon-Dioxide Discharge at Shrub and Upper Klawasi Mud Volcanoes, Wrangell Mountains, Alaska - U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 00-4207
- Mud Volcano Eruption at Baratang, Middle Andamans
- Article on mud volcanoes from Azerbaijan International
- Mud volcano floods Java, August 2006
- Mud volcano work suspended, 25 Feb 2007, Al Jazeera English
- Possible mud volcano on Mars (BBC News)
- Of Mud Pots and the End of the San Andreas Fault (Seismo Blog)
Categories:- Mud volcanoes
- Volcanology
- Subduction volcanoes
- Petrology
- Hydrothermal vents
- Volcanic landforms
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.