- Kauai
-
Kauaʻi The Garden Isle 
August 1995 satellite photo.
Location in the state of Hawaii.Geography Location 22°05′N 159°30′W / 22.083°N 159.5°W Area 562.3 sq mi (1,456 km2) Rank 4th largest Hawaiian Island Highest point Kawaikini Max elevation 5,243 ft (1,598 m) Demographics Population 65,689 (as of 2008[1]) Density 106/sq mi (41/km²) Official Insignia Flower Mokihana (Melicope anisata)[2] Color Poni (purple) Kauaʻi or Kauai[3] (
 /ˈkaʊ.aɪ/; Hawaiian: [kɔuˈwɐʔi]), known as Tauaʻi in the ancient Kaua'i dialect, is geologically the oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands. With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth largest of the main islands in the Hawaiian archipelago, and the 21st largest island in the United States.[4] Known also as the "Garden Isle", Kauaʻi lies 105 miles (169 km) across the Kauaʻi Channel, northwest of Oʻahu. This island is the site of Waimea Canyon State Park.
/ˈkaʊ.aɪ/; Hawaiian: [kɔuˈwɐʔi]), known as Tauaʻi in the ancient Kaua'i dialect, is geologically the oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands. With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth largest of the main islands in the Hawaiian archipelago, and the 21st largest island in the United States.[4] Known also as the "Garden Isle", Kauaʻi lies 105 miles (169 km) across the Kauaʻi Channel, northwest of Oʻahu. This island is the site of Waimea Canyon State Park.The United States Census Bureau defines Kauaʻi as Census Tracts 401 through 409 of Kauaʻi County, Hawaiʻi, which is all of the county except for the islands of Kaʻula, Lehua, and Niʻihau. The 2000 census population of Kauaʻi (the island) was 58,303.[5]
Contents
Etymology and language
Native Hawaiian tradition indicates the name's origin in the legend of Hawaiʻiloa — the Polynesian navigator attributed with discovery of the Hawaiian Islands. The story relates how he named the island of Kauaʻi after a favorite son; therefore a possible translation of Kauaʻi is "place around the neck", meaning how a father would carry a favorite child. Another possible translation is "food season."[6]
Kauaʻi was known for its distinct dialect of the Hawaiian language before it went extinct there. Whereas the standard language today is based on the dialect of Hawaiʻi island, which has the sound [k] at the beginning of words, the Kauaʻi dialect was known for pronouncing this as [t]. In effect, Kauaʻi dialect retained the old pan-Polynesian /t/, while 'standard' Hawaiʻi dialect has innovated and changed it to the [k]. Therefore, the native name for Kauaʻi was Tauaʻi, and the major settlement of Kapaʻa would have been called Tapaʻa.
Geography
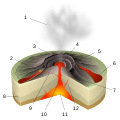
Kauaʻi's origins are volcanic, the island having been formed by the passage of the Pacific plate over the Hawaii hotspot. At approximately six million years old, it is the oldest of the main islands. The highest peak on this mountainous island is Kawaikini at 5,243 feet (1,598 m).[7] The second highest peak is Mount Waiʻaleʻale near the center of the island, 5,148 feet (1,569 m) above sea level. One of the wettest spots on earth, with an annual average rainfall of 460 inches (1,200 cm), is located on the east side of Mount Waiʻaleʻale. The high annual rainfall has eroded deep valleys in the central mountains, carving out canyons with many scenic waterfalls. On the west side of the island, Waimea town is located at the mouth of the Waimea River, whose flow formed Waimea Canyon, one of the world's most scenic canyons, and which is part of Waimea Canyon State Park. At 3,000 feet (914 m) deep, Waimea Canyon is often referred to as "The Grand Canyon of the Pacific". The Na Pali Coast is a center for recreation in a wild setting, including kayaking past the beaches, or hiking on the trail along the coastal cliffs. [8]
History
In 1778, captain James Cook arrived at Waimea Bay, the first European known to have reached the Hawaiian islands, which he named after his patron the Earl of Sandwich.
During the reign of King Kamehameha, the islands of Kauaʻi and Niʻihau were the last Hawaiian Islands to join his Kingdom of Hawaiʻi. Their ruler, Kaumualiʻi, resisted Kamehameha for years. King Kamehameha twice prepared a huge armada of ships and canoes to take the islands by force, and twice failed; once due to a storm, and once due to an epidemic. In the face of the threat of a further invasion, however, Kaumualiʻi decided to join the kingdom without bloodshed, and became Kamehameha's vassal in 1810, ceding the island to the Kingdom of Hawaiʻi upon his death in 1824.
In 1815-17, Kaumualiʻi led secret negotiations with representatives of the Russian-American Company in an attempt to gain Russia's military support against Kamehameha; however, the negotiations folded and the Russians were forced to abandon all of their presence in Kauaʻi, including Fort Elizabeth, after it was revealed that they did not have the support of Tsar Alexander I.
In 1835 Old Koloa Town opened a sugar mill. Missionaries also came in the 19th century.
Economy
Tourism is Kauaʻi's largest industry. In 2007, 1,271,000 visitors came to Kauaʻi. The two largest groups were from the United States (84% of all visitors) and Japan (3%).[9] As of 2003, there were a total of approximately 27,000 jobs on Kauaʻi, of which the largest sector was accommodation/food services (26%, 6,800 jobs) followed by government (15%) and retail (14.5%), with agriculture accounting for just 2.9% (780 jobs) and educational services providing just 0.7% (183 jobs).[10] In terms of income, the various sectors that constitute the visitors industry accounted for one third of Kauai's income.[10] On the other hand, employment is dominated by small businesses, with 87% of all nonfarm businesses having fewer than 20 employees.[10] As of 2003, Kauaʻi's unemployment rate was 3.9%, compared to 3.0% for the entire state and 5.7% for the United States as a whole; and, Kauaʻi's poverty rate was 10.5%, compared to the State's 10.7%.[10]
As of mid-2004, the median price of a single-family home was $528,000, a 40% increase over 2003. As of 2003, Kauaʻi's percentage of home ownership, 48%, was significantly lower than the State's 64%, and vacation homes were a far larger part of the housing stock than the State-wide percentage (Kauaʻi 15%, State 5%).[10]
Agriculture
In the past, sugar plantations were Kauaʻi's most important industry. In 1835 the first sugar plantation was founded on Kauaʻi and for the next century the industry would dominate the economy of Hawaii.[11] The minimum wage law (Federal Labor Standards Act) and protected the rights of workers to unionize led to the closure of most of the sugar plantation.[citation needed] Now most of that land is now used for ranching.[9] Kauaʻi's sole remaining sugar operation, the 118-year-old Gay & Robinson Plantation plans to transform itself into a manufacturer of sugar-cane ethanol.[9]
Land in Kauaʻi is very fertile and is home to many varieties of fruits and crops. Guava, coffee, sugarcane, mango, banana, papaya, avocado, star fruit, kava and pineapple are all cultivated.
Island facts
Hawaii Standard Time is observed on Kaua'i year-round. During DST, for example, the time on Kaua'i is three hours behind the West Coast of the United States and six hours behind the East Coast.[12]
The city of Līhuʻe, on the island's southeast coast, is the seat of Kauaʻi County and the second largest city on the island. Kapaʻa, on the "Coconut Coast" (site of an old coconut plantation) about 6 miles (9.7 km) north of Līhuʻe, has a population of nearly 10,000, or about 50% greater than Līhuʻe. Waimea, once the capital of Kauaʻi on the island's southwest side, was the first place in Hawaii visited by British explorer Captain James Cook in 1778. Kauaʻi is home to thousands of wild chickens, who have few natural predators. Kauaʻi's chickens originated from the original Polynesian settlers, who brought them as a food source. The feral chicken population exploded after hurricane Inki in 1992 when chicken and egg farms were damaged and chickens escaped captivity.
Kauaʻi is home to the U.S. Navy's "Barking Sands" Pacific Missile Range Facility, on the sunny and dry western shore.
HF ("shortwave") radio station WWVH, sister station to WWV and WWVB in Ft. Collins, Colorado, is located on the west coast of Kauai about 5 km south of Barking Sands. WWVH, WWV and WWVB are operated by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology, broadcasting standard time and frequency information to the public.
The Kauaʻi Heritage Center of Hawaiian Culture and the Arts was founded in 1998. Their mission is to nurture a greater sense of appreciation and respect for the Hawaiian culture. They offer classes in Hawaiian language, hula, lei and cordage making, the lunar calendar and chanting. Plus trips to cultural sites.
 A view of the Hanalei Valley in Northern Kauaʻi. The Hanalei River runs through the valley and 60% of Hawaii's taro is grown in its fields.
A view of the Hanalei Valley in Northern Kauaʻi. The Hanalei River runs through the valley and 60% of Hawaii's taro is grown in its fields.
 A view of the Nā Pali coastline from the ocean. It is part of the Nā Pali Coast State Park which encompasses 6,175 acres (20 km2) of land and is located on the northwest side of Kauaʻi.
A view of the Nā Pali coastline from the ocean. It is part of the Nā Pali Coast State Park which encompasses 6,175 acres (20 km2) of land and is located on the northwest side of Kauaʻi.
Important towns and cities
Cities and towns on Kauaʻi range in population from the roughly 9,500 people in Kapaʻa to tiny hamlets. The list below lists the larger or more notable of those from the northernmost end of Hawaii Route 560 to the western terminus of Hawaii Route 50.
- Hāʻena
- Wainiha
- Hanalei
- Princeville
- Kalihiwai
- Kilauea
- Anahola
- Kapaʻa
- Wailua
- Hanamāʻulu
- Līhuʻe
- Poʻipū
- Kōloa
- Lāwaʻi
- Kalāheo
- ʻEleʻele
- Hanapēpe
- Kaumakani
- Waimea
- Kekaha
Transportation
Air
Located on the eastern end of the island, Lihue Airport is the aviation gateway to Kauaʻi. Lihuʻe Airport has direct routes to Honolulu, Kahului/Maui, the United States mainland and Vancouver, Canada.
Highways
Several state highways serve Kauaʻi County:
- Hawaii Route 50, also known as Kaumualiʻi Highway, is a thirty-three mile road that stretches from Hawaii Route 56 at the junction of Rice Street in Lihuʻe to a point approximately 1/5 mile north of the northernmost entrance of the Pacific Missile Range Facility on the far western shore.
- Hawaii Route 58 stretches two miles (3 km) from Route 50 in Lihuʻe to the junction of Wapaa Road with Hawaii 51 near Nawiliwili Harbor on Kauaʻi.
- Hawaii Route 56, also known as Kuhio Highway, runs twenty-eight miles from Hawaii Route 50 at the junction of Rice Street in Lihuʻe to the junction of Hawaii Route 560 in Princeville.
- Hawaii Route 560 passes ten miles (16 km) from the junction of Route 56 in Princeville and dead ends at Keʻe Beach in Haena State Park.
Other major highways that link other parts of the Island to the main highways of Kauaʻi are:
- Hawaii Route 55 covers 7.6 miles (12.2 km) from the junction of Route 50 in Kekaha to meet with Hawaii Route 550 south of Kokeʻe State Park in the Waimea Canyon.
- Hawaii Route 550 spans 15 miles (24 km) from Route 50 in Waimea to Kōkeʻe State Park.
- Hawaii Route 540 goes four miles (6 km) from Route 50 in Kalaheo to Route 50 in Eleʻele. The road is mainly an access to residential areas and Kauaʻi Coffee.
- Hawaii Route 530, also called Kōloa Road, stretches 3.4 miles (5.5 km) from Route 50 between Kalaheo and Lawai to Route 520 in Koloa. The road is mainly an alternative to Route 520 for travel from the west side to Poʻipū.
- Hawaii Route 520 runs five miles (8 km) from the "Tunnel of Trees" at Route 50 to Poʻipū on the south shore.
- Hawaii Route 570 covers one mile (1.6 km) from Route 56 in Lihuʻe to Lihuʻe Airport.
- Hawaii Route 580 spans five miles (8 km) from Route 56 in Wailua to where the road is no longer serviced just south of the Wailua Reservoir.
- Hawaii Route 581 passes five miles (8 km) from Route 580 in the Wailua Homesteads to a roundabout just west of Kapaʻa Town.
- Hawaii Route 583, also known as Maalo Road, stretches 3.9 miles (6.3 km) from Route 56 just north of Lihuʻe to dead-end at Wailua Falls Overlook in the interior.
Mass transit
The Kauaʻi Bus is the public transportation service of the County of Kauaʻi. It is operated by Roberts Hawaii.
Places of interest
- Alakai Wilderness Area
- Allerton Garden
- Bell stone
- Camp Naue YMCA
- Fern Grotto
- Hanalei Bay
- Honopo arch
- Iraivan temple
- Keʻe Beach
- Kokeʻe State Park
- Limahuli Garden and Preserve
- Makauwahi Cave Reserve
- Makeleha Mountains
- McBryde Garden
- Moir Gardens
- Moloaa Bay
- Na 'Aina Kai Botanical Gardens
- Nā Pali Coast State Park
- Na'Pali-Kona Forest Reserve
- Poi'pu Beach State Park
- Polihale State Park
- Princeville North Shore
- 'Opaeka'a Falls
- Sleeping Giant (Nounou Mountain)
- Spouting Horn
- Wailua River
- Waimea Canyon
In films
The island of Kauaʻi has been featured in more than seventy Hollywood movies and television shows, including the musical South Pacific and Disney's 2002 animated feature film and television series Lilo & Stitch, Lilo & Stitch 2: Stitch Has a Glitch, Stitch! The Movie, and Lilo & Stitch: The Series. Scenes from South Pacific were filmed in the vicinity of Hanalei. Waimea Canyon was used in the filming of the 1993 film Jurassic Park. Parts of the island were also used for the opening scenes of Indiana Jones' Raiders of the Lost Ark. Other movies filmed here include Six Days Seven Nights, the 2005 remake of King Kong and John Ford's 1963 film Donovan's Reef. Recent films include Tropic Thunder and a biopic of Bethany Hamilton entitled Soul Surfer. A scene in the opening credits of popular TV show M*A*S*H was filmed in Kauai (helicopter flying over mountain top). Some scenes from Just Go with It and Pirates of the Caribbean: On Stranger Tides were also filmed in Kauai.
Parts of the 2002 film Dragonfly were filmed there (although the people and the land were presented as South American) and the producers hired extras (at least three with speaking parts) from the ancient Hawaiʻian native population, which seeks to preserve its cultural heritage,[13] including the pre-USA name of these two islands, Atooi or Tauaʻi.[14][15]
Major parts of the 1966 Elvis Presley film Paradise, Hawaiian Style were filmed at various locations on Kauai. One of the most famous was the Coco Palms resort. During Hurricane Iniki, the Coco Palms was decimated and never rebuilt, but the film showcases the resort at its peak.
See also
- Hurricane Iniki
- Kauai cave wolf spider
- List of beaches in Kauai
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Hawaii#Kauai
- Tourism on Kauaʻi
Notes
- ^ Kauai County QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau
- ^ "Mokihana". Native Hawaiian Plants. Kapiʻolani Community College. http://old.kcc.hawaii.edu/campus/tour/plants/pmokihana.htm. Retrieved 2009-03-07.
- ^ The spelling with the ʻokina accent (as "Kauaʻi") indicates syllable "i" with respelled pronunciation as "cow-Eye" or "cow-a-ee". Sometimes, an apostrophe or grave is used, as: Kaua'i or Kaua`i.
- ^ "Table 5.08 - Land Area of Islands: 2000". 2004 State of Hawaii Data Book. State of Hawaii. 2004. http://www.hawaii.gov/dbedt/info/economic/databook/db2004/section05.pdf. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ Census Tracts 401 through 409, Kauaʻi County United States Census Bureau
- ^ Pukui, Mary Kawena. Place Names of Hawaii. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 0-8248-0524-0.
- ^ "Table 5.11 - Elevations of Major Summits". 2004 State of Hawaii Data Book. State of Hawaii. 2004. http://www.hawaii.gov/dbedt/info/economic/databook/db2004/section05.pdf. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ Kalalau Trail General Information
- ^ a b c "Kauai Economic Outlook Summary: Tourism Woes Mean No Growth Through 2009". University of Hawaii Economic Research Organization]. 2008. http://www.kauai.gov/Government/Departments/EconomicDevelopment/EconomicStatisticsandForecasting/tabid/256/Default.aspx. Retrieved 2008-11-05.
- ^ a b c d e "Kauai Economic Development Plan 2005-20015". County of Kauai Office of Economic Development,Kauai Economic Development Board. 2004. http://www.kauai.gov/portals/0/oed/KEDP_2005-2015.pdf. Retrieved 2008-11-05.
- ^ Kauai Plantation Railway - Kauai Sugar Plantations
- ^ Discover Kauai
- ^ Background of loss of language and culture: the takeover of Hawaiʻi by the USA in 1893.
- ^ Current interest in the language and culture.
- ^ Original name and language discussion.
References
- Edward Joesting. Kauaʻi, the Separate Kingdom. University of Hawaiʻi Press and Kauaʻi Museum Association. Honolulu. 1984. ISBN 0-8248-1162-3
- Cook, Chris (October 1996). The Kaua’i Movie Book. Landscape photography by David Boynton. Honolulu: Mutual Publishing. ISBN 1-56647-141-9.
External links
- Kauai Tourism links at the Open Directory Project
- Kauai Business and Economy links at the Open Directory Project
- Kauaʻi Chamber of Commerce
 State of Hawaii
State of HawaiiTopics - Geography
- Government
- Delegations
- History
- Islands
- Music
- Language
- People
- Visitor Attractions
Society Main Islands Northwestern
IslandsCommunities Counties Hawaiian volcanism topics (List) Windward
IslesLeeward
IslesEmperor
SeamountsTopics Hawaiian – Emperor seamount chain · Evolution of Hawaiian volcanoes · Hawaiian eruption · ʻAʻā (lava) · Pāhoehoe (lava) · Pele's hair · Limu o Pele · Pele's tears · Lava fountain · Hawaiian Volcano Observatory · Hawaii Volcanoes National Park · Haleakala National Park · 1955 Hawaiian submarine eruptionCategories:- Volcanoes of Hawaii
- Pliocene volcanism
- Extinct volcanoes
- Kauai
- Islands of Hawaii
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.