- Bundelkhand
-
Historical region of North India
BundelkhandLocation Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh State established: 914 AD Language Bundeli Dynasties Chandel Rajputs (till 15th c.)
Bundela Rajputs (1501-1950)Historical capitals Khajuraho, Mahoba, Orchha Separated states Orchha (1501), Datia, Panna (1732), Ajaigarh (1765), Bijawar (1765), Beri[disambiguation needed  ], Charkhari, Samthar, Sarila, other
], Charkhari, Samthar, Sarila, otherBundelkhand anciently known as Chedi Kingdom (Bundeli, Hindi: बुन्देलखण्ड, Urdu: بندیل کھنڈ; got its name from Bundela Rajputs until the 16th century, during the rule of Chandel Rajputs later on by Bundela Rajputs, known as Jaijak bhukti or Jejaka bhukti) is a geographic region of central India. The region is now divided between the states of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, with the larger portion lying in the latter.
The major towns are Jhansi, Datia, Tikamgarh, Rath , Lalitpur, Sagar, Damoh, Orai, Panna , Hamirpur , Mahoba , Banda Narsinghpur and Chhatarpur. However, the cities of Gwalior, Jabalpur and even Bhopal are under close cultural influence of Bundelkhand, especially linguistically. Bundelkhand's most well known place, however, is Khajuraho which has a number of 10th century temples devoted to fine-living and eroticism. The mines of Panna have been famous for magnificent diamonds; and a very large one dug from the last was kept in the fort of Kalinjar.
Contents
Geography
Bundelkhand lies between the Indo-Gangetic Plain to the north and the Vindhya Range to the south. It is a gently sloping upland, distinguished by barren hilly terrain with sparse vegetation, although it was historically forested. The plains of Bundelkhand are intersected by three mountain ranges, the Vindhya, Fauna and Bander chains, the highest elevation not exceeding 600 meters above sea-level. Beyond these ranges the country is further diversified by isolated hills rising abruptly from a common level, and presenting from their steep and nearly inaccessible scarps eligible sites for forts and strongholds of local kings. The general slope of the country is towards the northeast, as indicated by the course of the rivers which traverse or bound the territory, and finally discharge themselves into the Yamuna River.
The principal rivers are the Sindh, Betwa, Shahzad River, Ken, Bagahin, Tons, Pahuj, Dhasan and Chambal. The Kali Sindh, rising in Malwa, marks the western frontier of Bundelkhand. Parallel to this river, but further east, is the course of the Betwa. Still farther to the east flows the Ken, followed in succession by the Bagahin and Tons. The Yamuna and the Ken are the only two navigable rivers. Notwithstanding the large number of streams, the depression of their channels and height of their banks render them for the most part unsuitable for the purposes of irrigation, which is conducted by means of ponds and tanks. These artificial lakes are usually formed by throwing embankments across the lower extremities of valleys, and thus arresting and impounding the waters flowing through them.
Ecology
History
Medieval Period
The Chandela Rajput clan ruled Bundelkhand from the 10th to the 16th centuries. In the early 10th century they were feudatories of the Pratiharas of Kannauj, and ruled from the fortress-city of Kalinjar. A dynastic struggle among the Pratiharas from 912 to 914 allowed the Chandelas and other feudatories to assert their independence. The Chandelas captured the strategic fortress of Gwalior c. 950. Dhanga (c. 950-1008) left many inscriptions, and endowed a large number of Jain and Hindu temples. Dhanga's grandson Vidyadhara (1017–29) expanded the Chandela kingdom to its greatest extent, extending the Chandela dominions to the Chambal river in the northwest and south to the Narmada River. The Afghan king Mahmud of Ghazni attacked the Chandela dominions during Vidydhara's reign, but did not retain any Chandela territory. the Chandelas built the famous temple-city of Khajuraho between the mid-10th and mid-11th centuries. During the Chandela period, Bundelkhand was home to a flourishing Jain community and numerous Jain temples were built in that period.
See also: Dauwa ahirsAccording to India by Fannie Roper Feudge, copyright 1895, In the fourteenth century, Hurdeo Singh, a Rajput prince was expelled from the Kshatriya caste for marrying a Bourdi slave-girl, and left the Rajputs to go and reside at the court of one of the smaller sovereigns of Central India, where a young family grew up around him. In process of time the king's son became enamoured of Hurdeo's beautiful daughter, and asked her in marriage of her father. Hurdeo gace his consent, on condition that the king and his whole court would be present at a banquet to be prepared by Hurdeo's own hand, thus forfeiting, as he himself had done, the right to the rank Kshatriya. From affection for his son the aged king consented to set aside his scruples, and on the nuptial day all the court were seated around Hurdeo's princely board. There in magnificent goblets of silver and gold, drinks containing opium were served to the guests who, being thus deprived of the power of resistance, fell an easy prey to Hurdeo's hired assassins, who stood concealed, each man armed with his weapon, behind the tapestry at the upper end of the hall. Hurdeo having thus gained possession of this throne, soon made himself master of all the surrounding country; and, with his sons and the numerous adherents he had enlisted in his cause, he formed a new clan known as the Bourdillas, or 'Sons of the Slave;' thus giving the country its present name of Boundilacund or Bundelcund. Since then Warriors from the region have often gone into battle shouting Bund lelo.
In the 12th century, the Rajput Chauhan rulers of Ajmer challenged the Chandelas. The Muslim conquests of the early 13th century reduced the Chandela domains, although they survived until the 16th century as minor chieftains. Bundela Rajputs grew to prominence starting in the 16th century. Orchha was founded in the sixteenth century by the Bundeli chief Rudra Pratap, who became the first Raja of Orchha. In 1545 Sher Shah Suri, the only Indian king to defeat Mughals and sit on Delhi throne, was killed while attempting to capture Kalinjar from the local Bundeli kings.
The region came under nominal Mughal rule during the 16th-18th centuries, although the hilly, forested terrain of the sparsely populated region made it difficult to control. Akbar's governors at Kalpi maintained a nominal authority over the surrounding district, and the Bundela chiefs were in a state of chronic revolt, which culminated in the war of independence under Chhatrasal. On the outbreak of his rebellion in 1671 he occupied a large province to the south of the Yamuna. Setting out from this base, and assisted by the Marathas, he conquered the whole of Bundelkhand. On his death in 1732 he bequathed one-third of his dominions, including Jalaun and Jhansi, to his Maratha allies, who before long succeeded in controlling the whole of Bundelkhand, with the local rulers as tributaries to the Marathas. Under Maratha rule the country was a prey to constant anarchy and strife. By the end of the 18th century, the Bundelas had freed themselves to some extent from Maratha power. A grandson of the Maratha Peshwa, sought to restore Maratha control of Bundelkhand from his base at Banda. Ali Bahadur warred with the Bundelas from 1790 until 1802, when he died while attempting to capture Kalinjar.
British rule, 1802-1947
Main article: Bundelkhand AgencyThe Marathas ceded parts of Bundelkhand, which were later called later British Bundelkhand, to the British in the 1802 Treaty of Bassein. After 1802, many of the local rulers were granted sanads (leases) by the British, which entitled them to the lands they controlled at the death of Ali Bahadur, in return for the rulers signing a written bond of allegiance (ikrarnama) to the British. A political officer attached to the British forces in Bundelkhand supervised British relations with the sanad states. In 1806 British protection was promised to the Maratha ruler of Jhansi, and in 1817 the British recognized his hereditary rights to Jhansi state. In 1818 the Peshwa in Pune ceded all his rights over Bundelkhand to the British at the conclusion of the Third Anglo-Maratha War.
The sanad states were organized into the Bundelkhand Agency in 1811, when a political agent to the Governor-General of India was appointed and headquartered at Banda. In 1818 the headquarters were moved to Kalpi, in 1824 to Hamirpur, and in 1832 back to Banda. The political agent was placed under the authority of the Lieutenant-Governor of the North-Western Provinces, headquartered in Agra, in 1835. In 1849 authority over the Bundelkhand Agency was placed briefly under the Commissioner for the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories, who appointed a political assistant based at Jhansi. Shortly thereafter, authority over Bundelkhand was placed under the Resident at Gwalior, and the headquarters of the political assistant was moved to Nowgong[disambiguation needed
 ], which remained until 1947. In 1853 the Raja of Jhansi died childless, and his territory was annexed to British Bundelkhand. The Jhansi state and the Jalaun and Chanderi districts were then formed into a superintendency. In 1854 Bundelkhand Agency was placed under the authority of the newly created Central India Agency, headquartered at Indore.
], which remained until 1947. In 1853 the Raja of Jhansi died childless, and his territory was annexed to British Bundelkhand. The Jhansi state and the Jalaun and Chanderi districts were then formed into a superintendency. In 1854 Bundelkhand Agency was placed under the authority of the newly created Central India Agency, headquartered at Indore.The widow of the Raja of Jhansi, Rani Lakshmi Bai, protested the annexation because she was not allowed to adopt an heir, and because the slaughter of cattle was permitted in the Jhansi territory. The Revolt of 1857 found Jhansi ripe for rebellion. In June a few men of the 12th native infantry seized the fort containing the treasure and magazine, and massacred the European officers of the garrison. The Rani put herself at the head of the rebels, and they captured several of the neighboring British districts and princely states allied to the British. She died bravely in battle in Gwalior in 1858. It was not till November 1858 that Jhansi was brought under British control.
After the revolt, Jhansi was given to the Maharaja of Gwalior, but came under British rule in 1886 when it was swapped for Gwalior fort. In 1865 the political assistant was replaced with a political agent. The eastern portion of the Agency was detached to form Bagelkhand agency in 1871. The state of Khaniadhana was transferred to the authority of the Gwalior Resident in 1888, and in 1896 Baraunda, Jaso, and the Chaube jagirs were transferred to Bagelkhand. In 1901 there were 9 states, 13 estates, and the pargana of Alampur belonging to Indore state, with a total area of 9,851 sq mi (25,510 km2). and a total population of 1,308,326 in 1901. The most important of the states were Orchha, Panna, Samthar, Charkhari, Chhatarpur, Datia, Bijawar and Ajaigarh. Deforestation accelerated during British rule. The population of the agency decreased 13% between 1891 and 1901 due to the effects of famine. In 1931 Bagelkhand Agency, with the exception of the state of Rewa, was merged into Bundelkhand.
Independent India, 1947-present
After Indian independence in 1947, the princely states of Bundelkhand Agency were combined with those of the former Bagelkhand Agency to form the province of Vindhya Pradesh, which became an Indian state in 1950. On November 1, 1956, Vindhya Pradesh was merged into Madhya Pradesh. Notorious dacoits like Pooran Sing alias Puja babba and Moorath Singh besides other robber gangs once ruled the area. Currently the area is economically and industrially one of the most backward areas in India. Lack of resources, poor communications, and infertile land are some of the reasons for under-development in the region.
Proposed Bundelkhand state
Since last 50 years there is a movement for separation of bundelkhand state. Bundelkhand is geographically the central part of India covering some part of MP and some of UP.The population of this region is apprx. 5 crores.In spite of being rich in minerals, the people of Bundelkhand are very poor and backward because of no representation in the state and central politics. For their development they are demanding it's separate statehood so that it can be developed.The local parties and local leaders are running several movements having different names. Few movements are for its development, few are for its formation as a state." Bundelkhand Akikrit Party.", and "Bundelkhand Mukti Morcha" are two political organisations for this cause. These parties demand formation of state with Lalitpur as the capital of new state.
In november 2011 Uttar Pradesh CM proposed to split UP in four parts , with one part being bundelkhand. The proposed state includes the following districts:
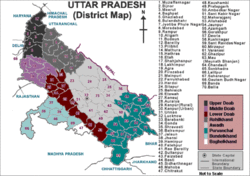 Regions of Uttar Pradesh
Regions of Uttar Pradesh
From Uttar Pradesh
From Madhya Pradesh
In addition to the above districts, sometimes the following districts of Madhya Pradesh are sometimes considered as the part of Bundelkhand: Madhya Bharat/Gird region
Culture
The Bundeli language is the most common of the Hindi dialects spoken in the area. It in turn consists of several subdialects. The accent varies in various regions even though unmistakably of a single origin.
The region is predominantly Hindu. However, Jainism is historically significant in Bundelkhand, and several Tirthas are located in this region. Many prominent Jain scholars of the 20th century have been from this region.
Folk dances
Bundelkhand has following folk dances. Badhai , Rai, Saira, Jawara, Akhada, Shaitan, Dhimrai.
Fiction
In the novel The Mysterious Island (1874) by Jules Verne, the fictional character Captain Nemo's real identity is revealed as that of Prince Dakkar of Bundelkund, aka Bundelkhand. The Prince had supposedly been involved in the Sepoy Revolt of 1857.
In the novel Around the World in Eighty Days, the protagonist, Phileas Fogg, rescues a woman (Aouda) about to be burned at the pyre in a Sati ceremony while traveling through the Bundelkhand region.
Prominent Bundelkhandis
- Goswami Tulsidas, the author of 'RAMCHARITMANAS' born in RajapurBanda.
- Dhyan Chand the world famous Hockey player.
- Ayodhya Prasad Gupta 'Kumud'
- Chandrashekhar Sitaram Tiwari, better known as Chandrasekhar Azad, is one of the most important Indian revolutionaries, and is considered the mentor of Bhagat Singh.
- Rani Lakshmibai, (1828–1858) Queen of princely state of Jhansi, one of the key figures in first Indian war of independence 1857.
- Maithili Sharan Gupt, National Hindi Poet
- Tarana Swami, (1448-) (founder of Taran Panth)
- Pandit Nathuram Premi (1881–1960), Prominent publisher of Hindi, Sanskrit and Urdu literature as well as Jain literature. Independent scholar, Jain historian and editor of several Jain works. Founder of Hindi Granth Ratnakar Karyalay, (24 September 1912), Manikacandra Digambara Jain Granthamala and Jain Hitaishi.
- Dr Hiralal Jain, Sanskritist and Jain Scholar best remembered for his work on the Satkhandāgama
- Pandit Phulacandra Shastri, Traditional Jain Scholar, best remembered for his work on the Satkhandāgama and the Kasāyapāhuda
- Pandit Hiralal Shastri (Sadumal), Traditional Jain Scholar, Prakritist and Nyaya specialist, remembered for his Hindi translation of the Kasāyapāhuda mula patha along with the Curni by Yativrsabha.
- Osho Rajneesh (1931–1990)
- Pandit Jaganmohanlal Shastri, Traditional Jain Scholar
- Pandit Ramakant Malviya, Sanskrit scholar and authority on Ramcharitmanas from Lalitpur.
- Dr. Hari Singh Gaur, Member of Constitution draft committee & founder of University of Saugar.
- Vrindavan Lal Verma, Hindi novelist (Mrig Nayani, Jhansi Ki Rani)
- Indeevar, one of the leading Hindi film lyricists in 1960s and 70s
- Rani Durgavati, Queen of Gondwana (born to Chandelas of Mahoba / Kalinjar) immortalized owing to her bravery in defending her kingdom against invasion by Mughal emperor Akbar
- Alha and Udal, warriors in the court of the Chandela dynasty King Parmal in Mahoba
- Maharishi Mahesh Yogi, of Transcendental Meditation
- Harishankar Parsai
- Dr Som Prakash Srivastava, scientist
- Dewan Shatrughan Singh
- Rani Rajendra Kumari (Rani Saheb of Maudaha)
- pandit Suresh chandra Mishra, famous editor of Dainik Karmayug Prakash
- Dr. Acharya Prabhakar Mishra, President, Bramhin International
- Phoolan Devi (1963–2001), Indian Bandit Queen and Politician
- Thakur kishor singh Lodhi (1857 ki kranti) Hindoriya Damoh
- Pandit Parmeshthidas Jain (1909-1977) Freedom Fighter/Jain Scholar(Nayay Teerth), Lalitpur,UP
- Hari Nath Singh Bundhelkandh (1947--till date) Jam Bazaar Jaggu Bhai,Chennai TN
See also
- Chandela
- Dauwa ahirs
References
- Hunter, William Wilson, Sir, et al. (1908). Imperial Gazetteer of India, Volume 12. 1908-1931; Clarendon Press, Oxford.
- "Bundelkhand Agency". The Imperial Gazetteer of India, Vol. 9. Oxford at Clarendon Press. 1909. p. 74-77. http://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gazetteer/pager.html?objectid=DS405.1.I34_V09_080.gif.
- "British Bundelkhand". The Imperial Gazetteer of India, Vol. 9. Oxford at Clarendon Press. 1909. p. 68-74. http://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gazetteer/pager.html?objectid=DS405.1.I34_V09_074.gif.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.Historical regions of North India Ajmer · Awadh · Bagelkhand · Braj · Bundelkhand · Delhi · Doab · Doaba · Dhundhar · Garhwal · Gird · Godwar · Hadoti · Jaisalmer · Jangladesh · Kumaun · Magadha · Mahakoshal · Majha · Malwa · Malwa (Punjab) · Marwar · Mewar · Mewat · Mithila · Nimar · Purvanchal · Rohilkhand · Shekhawati · Vagad
Aspirant states of India Bodoland (Assam) · Bundelkhand (Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh) · Delhi · Gondwana (northern Deccan Plateau) · Gorkhaland (West Bengal) · Harit Pradesh (Uttar Pradesh) · Kamtapur / Greater Cooch Behar (West Bengal) · Karbi Anglong (Assam) · Kodagu (Karnataka) · Kongu Nadu (Tamil Nadu) · Kosal/Koshal (Orissa) · Ladakh (Jammu and Kashmir) · Mahakoshal (Madhya Pradesh) · Mithila (Bihar) · Panun Kashmir (Jammu and Kashmir) · Purvanchal (Uttar Pradesh) · Rayalaseema (Andhra Pradesh) · Telangana (Andhra Pradesh) · Tulu Nadu (Karnataka and Kerala) · Vidarbha (Maharashtra) · Maru Pradesh (Rajasthan) · Vindhya Pradesh (Madhya Pradesh)Jhansi division topics General Bundelkhand • Jhansi Fort • Mahavir Swami SanctuaryMythology, history Districts Rivers, dams, lakes Languages, people Transport Industries Parichha Thermal Power StationLok Sabha constituencies See also Cities and towns in Jalaun district • Cities and towns in Jhansi district • Cities and towns in Lalitpur district • Villages in Jalaun district • Villages in Lalitpur district • People from Jalaun • People from Jhansi • People from LalitpurOther Divisions Agra • Aligarh • Allahabad • Azamgarh • Bareilly • Basti • Chitrakoot • Devipatan • Faizabad • Gorakhpur • Kanpur • Lucknow • Meerut • Mirzapur • Moradabad • Saharanpur • VaranasiExternal links
Categories:- Bundelkhand
- Jhansi
- Proposed states and union territories in India
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.