- Zutphen
-
Zutphen — Municipality — St Walburga's Church 
Flag
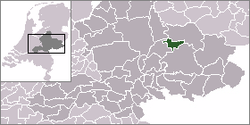
Coat of armsLocation of Zutphen in Gelderland, Netherlands Coordinates: 52°8′N 6°12′E / 52.133°N 6.2°E Country Netherlands Province Gelderland Area(2006) – Total 42.84 km2 (16.5 sq mi) – Land 41.00 km2 (15.8 sq mi) – Water 1.84 km2 (0.7 sq mi) Population (1 January 2007) – Total 46,709 – Density 1,139/km2 (2,950/sq mi) Source: CBS, Statline. Time zone CET (UTC+1) – Summer (DST) CEST (UTC+2) Zutphen (Dutch pronunciation: [ˈzʏtfə(n)] (
 listen)) is a city in the province of Gelderland in the Netherlands. It lies some 30 km north-east of Arnhem, on the Eastern bank of the river IJssel at the point where it is joined by the Berkel. The name Zutphen (first mentioned in the eleventh century) appears to mean 'zuid-veen', or in English, south-fen.
listen)) is a city in the province of Gelderland in the Netherlands. It lies some 30 km north-east of Arnhem, on the Eastern bank of the river IJssel at the point where it is joined by the Berkel. The name Zutphen (first mentioned in the eleventh century) appears to mean 'zuid-veen', or in English, south-fen.In 2005, the municipality of Zutphen was merged with the municipality of Warnsveld, retaining its name. The municipality has about 47,000 inhabitants.
Zutphen is also twinned with the English town Shrewsbury, in the Midlands county of Shropshire.
Contents
History
About 300 AD a Germanic settlement was the first permanent town on a complex of low river dunes. Whereas many such settlements were abandoned in the early Middle Ages, Zutphen on its strategic confluence of IJssel and Berkel stayed. After the incorporation of the IJssel lands in Charlemagne's Francia, Zutphen became a local centre of governance under a count. The Normans raided and ravaged it in 882. Afterwards a circular fortress was build to protect the budding town against Viking attacks.
In the eleventh century Zutphen was a royal residence for a number of years; a pfalz was built, together with a large chapter church, the predecessor of the present St. Walburgis. The counts of Zutphen acquired a lot of power, until the line of counts became extinct in the twelfth century. After the death of her father and her brother, Ermgard, the heiress of Zutphen married the count of Guelders; her son Henry I, Count of Guelders was the first to wear both titles.
The settlement received town rights between 1191 and 1196, making it one of the oldest towns in the country. This allowed it to self govern and have a judicial court. Only Utrecht, and Deventer preceded it in receiving town rights. Zutphen, in turn, became the mother town of several other towns in Guelders, such as Arnhem, Doetinchem, Doesburg, Lochem, Harderwijk, Venlo and Emmerich. It also became part of the Hanseatic League, a group of towns with great wealth; this league was the economic centre in that part of Europe.
The largest and oldest church of the city is the St. Walburgis (Saint Walpurga) church, which originally dates from the eleventh century. The present Gothic building contains monuments of the former counts of Zutphen, a fourteenth century candelabrum, an elaborate copper font (1527), and a monument to the Van Heeckeren family (1700). The chapter-house of library ("Librije") contains a pre-Reformation library which includes some valuable manuscripts and incunabula. It is considered one of only 5 remaining medieval libraries in Europe (the other 4 being in England and Italy). The old books are still chained to their ancient wooden desk, a habit of centuries ago, dating from the times when the library was a "public library" and the chains prevented the books from being stolen.
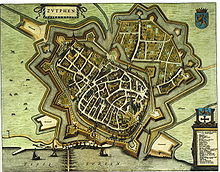
Having been fortified the town withstood several sieges, specially during the wars of freedom waged by the Dutch against Spain, the most celebrated fight under its walls being the Battle of Zutphen in September 1586 when Sir Philip Sidney was mortally wounded. Taken by the Spanish in 1587 by the treachery of the English commander Rowland York, Zutphen was recovered by Maurice, prince of Orange, in 1591, and except for two short periods, one in 1672 and the other during the French Revolutionary Wars, it has since then remained a part of the Netherlands. Its fortifications were dismantled in 1874. In World War II the town was bombed several times by the allied forces because the bridge over the IJssel was vital to support the German troops at Arnhem after the Operation Market Garden. After two weeks of battle the town was liberated on the 14th of April 1945. After the war a renovation program started. Nowadays Zutphen has one of the best preserved medieval town centres of North-Western Europe, including the remains of the medieval town wall and a few hundred buildings dating from the 13th - 15th century.
Modern city
The old center survived the Second World War almost in its entirety, though some parts of the city were lost, especially the area around the railway station, in the northern part of the city center, known as the Nieuwstad (English: New City). The city center includes many monumental buildings dating back to the 14th and 15th centuries, and some even date back to the 13th century such as a retirement home area. There are also remains of the old town walls in several places.
Today, Zutphen is a modern small city. The urban area, which includes the village of Warnsveld, has about 51,000 inhabitants. Stores are opened from 9:30 to 18:00 (6 p.m.) on weekdays, on Friday evening until 21:00 (9 p.m.) and on Saturday until 17:00 (5 p.m.). Some stores open earlier, and the larger supermarkets usually stay open until 22:00 (10 p.m.)
Regional center
Juridical centre
Zutphen, although a relatively small town, houses one of the Netherlands' 13 courts, the national training institution for judges and public prosecutors (SSR), the national police academy for senior police investigators, three prisons and a large number of lawyers. It is the early emergence of Zutphen in the Middle Ages as the main town of a county that explains its current position in the juridical system.
Besides a 'normal' prison, one may find in Zutphen the JPC de Sprengen penitentiary facility for boys. There are several buildings: new institutions replacing the old facilities, but the old prisons remained open after completion of the new facilities. Only the old prison called Lunette did not meet today's standards and has closed in 2008.[1]
Medical centre
Located in Zutphen is the "Spittaal", location of the Gelre Ziekenhuizen (Gelre Hospitals) group. This is a regular hospital offering all common specialities (no cardio-thoracic or neurosurgery) and a 24/7 emergency department. It is located in the southeastern part of the city, in the district of Leesten. A new hospital is due to be built soon to replace the old building, which dates from the 1970s. The new hospital will be built adjacent to the old one and is due to be completed in 2010.
A sizable number of practitioners of alternative medicine are located in Zutphen.Educational centre
Zutphen is home to several well-known schools for secondary education on all levels. These include the "Stedelijk Dalton College", "Baudartius College", "Vrije School Zutphen", (a "Vrije School" being a Waldorf School) and "Isendoorn College" (located in Warnsveld). Students from a wide area around Zutphen learn at these schools.
Transportation
Rail
- Zutphen railway station
Zutphen is an important regional railway centre. The main electrified lines, to Deventer and Zwolle in the north, and to Arnhem in the south, are run by the national railway company Nederlandse Spoorwegen (NS). The secondary lines to Winterswijk and Hengelo are operated by Syntus. The regional rail service to Apeldoorn is run by a special subsidiary of the NS. All secondary lines run diesel trains. Zutphen's old station building (1863), upgraded in 1875, was partly destroyed during World War II. In the early 1950s a modern new station was erected, a typical post-war building with concrete as its main material.[2] However, in October 2007 the station building was designated as a State Monument. In 2006 and 2007, the area surrounding the railway station was completely renovated: a new bus terminal and an underground bicycle parking lot were constructed, and the main road leading from the railway station to the city centre was turned into a road for pedestrians and cyclists only.
Road
Zutphen lies 10 kilometers south of the A1 motorway, which can be entered where it passes Deventer. From there the A1 leads East to Hengelo and West past Apeldoorn to Amsterdam. Main roads are the N348 (Arnhem - Zutphen - Deventer - Ommen), N314 (Zutphen - Doetinchem), N319 (Zutphen - Vorden - Winterswijk), N345 (Zutphen - Lochem - Hengelo), N826 (Zutphen - Almen - Laren).
Bus
Almost all buses in and around Zutphen are operated by Syntus. There are three internal city bus lines, and regional lines to Doetinchem, to Deventer and to Almen. The bus lines towards Vorden, Apeldoorn and Dieren were cancelled in the past; these towns and the destinations in between can now only be reached by car or by train.
Population centres
- Zutphen
- Warnsveld
- Warken
International relations
Main article: List of twin towns and sister cities in The NetherlandsTwin towns — Sister cities
Zutphen is twinned with:
 Satu Mare, Romania
Satu Mare, Romania Tartu, Estonia
Tartu, Estonia Shrewsbury, United Kingdom
Shrewsbury, United Kingdom Villa Sandino, Nicaragua
Villa Sandino, Nicaragua Horstmar, Germany
Horstmar, Germany
Delegations including the mayors of the cities visit each other, and developmental aid programs are in place with Satu Mare, Tartu and Villa Sandino.
People from Zutphen
- Gerard Zerbolt of Zutphen (1367–1398), mystical writer
- Jan Brandts Buys (1868–1933), composer
- Lambertus Doedes (1878–1955), sailor
- Jo Spier (1900–1978), illustrator
- Robert van Gulik (1910–1967), orientalist, diplomat, and writer
Photogallery
Reference(s)
- ^ Min. of Justice, Inspectie voor Sanctietoepassing (2007) (PDF). Inspectierapport Doorlichting PI Achterhoek, lokatie Lunette. http://www.inspectiesanctietoepassing.nl/images/Inspectierapport%20PI%20Achterhoek%20locatie%20Lunette_tcm56-75983.pdf. Retrieved 2008-05-05.
- ^ Bramer, Wichor (updated 2008-01-31). "Station Zutphen". Railwaystations in the Netherlands. Stationsweb. http://www.stationsweb.com/zutphen. Retrieved 2008-05-05..
External links
- Official Website
- Photo Album of Zutphen (in Dutch only)
- Hanseatic Cities in the Netherlands
- Zutphen on Wikitravel
Members of the Hanseatic League by Quarter Chief cities are highlighted; Free Imperial Cities of the Holy Roman Empire are shown in italics.Wendish Quarter Anklam · Demmin · Greifswald · Hamburg · Kolberg (Kołobrzeg) · Lüneburg · Rostock · Rügenwalde (Darłowo) · Stettin (Szczecin) · Stolp (Słupsk) · Stockholm · Stralsund · Visby · Wismar
Saxon Quarter Baltic Quarter Westphalian
QuarterPrincipal Kontore Subsidiary Kontore Other cities  Burgundian Circle (1512–1806) of the Holy Roman EmpireRemained
Burgundian Circle (1512–1806) of the Holy Roman EmpireRemained
County Imperial City Besançon3Dependent territories Aalten · Apeldoorn · Arnhem · Barneveld · Berkelland · Beuningen · Brummen · Bronckhorst · Buren · Culemborg · Doesburg · Doetinchem · Druten · Duiven · Ede · Elburg · Epe · Ermelo · Geldermalsen · Groesbeek · Harderwijk · Hattem · Heerde · Heumen · Lingewaal · Lingewaard · Lochem · Maasdriel · Millingen aan de Rijn · Montferland · Neder-Betuwe · Neerijnen · Nijkerk · Nijmegen · Nunspeet · Oldebroek · Oost Gelre · Oude IJsselstreek · Overbetuwe · Putten · Renkum · Rheden · Rijnwaarden · Rozendaal · Scherpenzeel · Tiel · Ubbergen · Voorst · Wageningen · West Maas en Waal · Westervoort · Wijchen · Winterswijk · Zaltbommel · Zevenaar · Zutphen
 Categories:
Categories:- Zutphen
- Cities in the Netherlands
- Populated places in Gelderland
- Burgundian Circle
- Hanseatic League
- Seventeen Provinces
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.